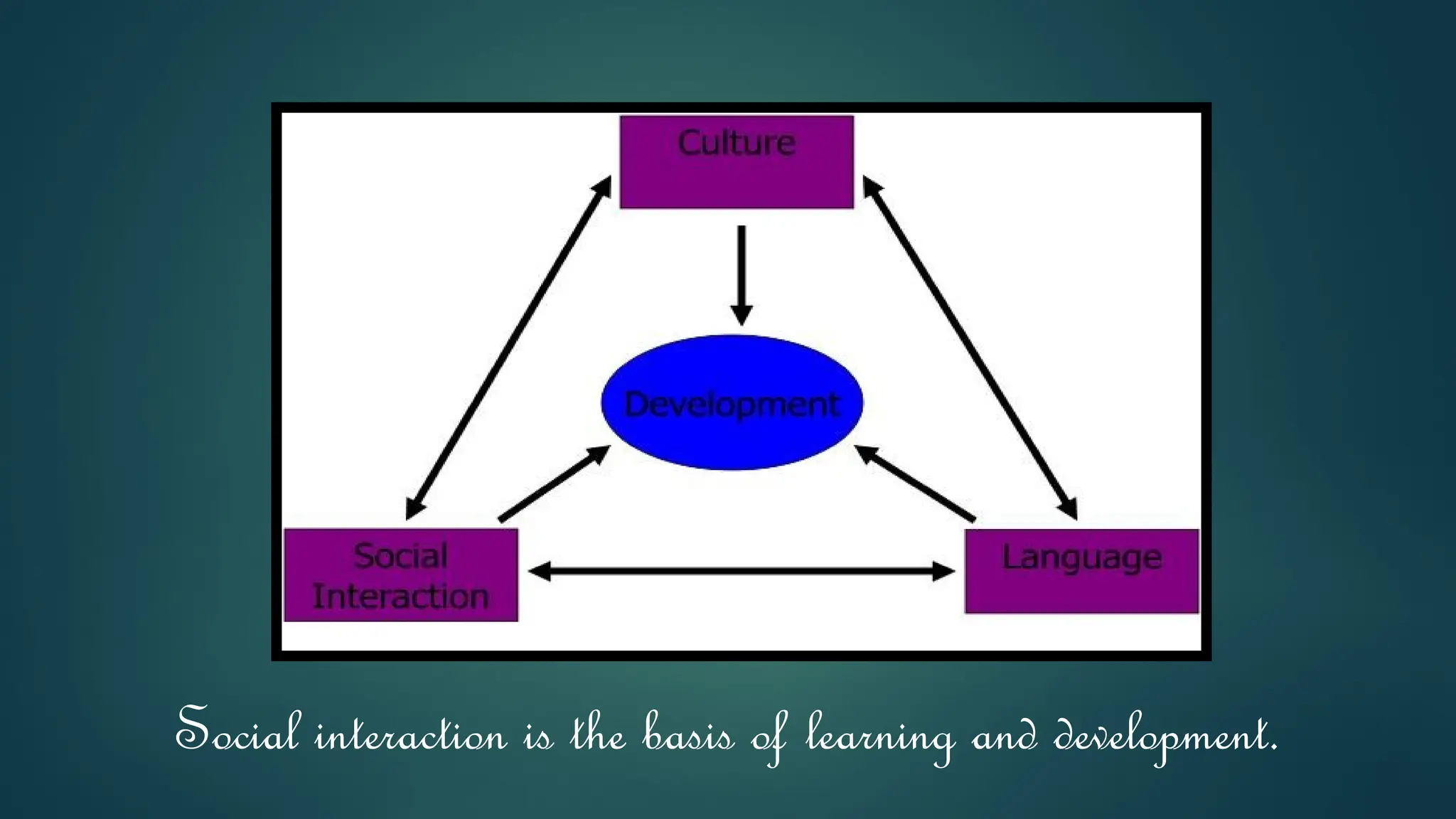
Lev Vygotsky's sociocultural theory posits that cognitive development is shaped by social interactions and cultural contexts, emphasizing the role of language and tools in learning. It introduces concepts such as the Zone of Proximal Development, mediated learning, and the evolution of elementary mental functions into higher mental functions through social engagement. Critiques of Vygotsky's theory highlight issues like the dichotomy between lower and higher psychological processes, the lack of clarity on developmental processes, and the overemphasis on language.