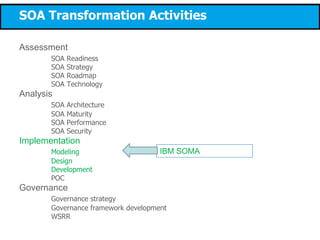
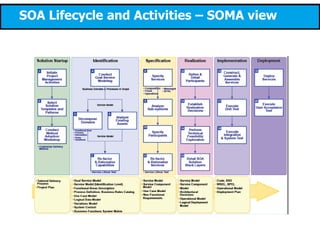
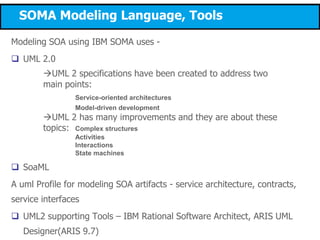
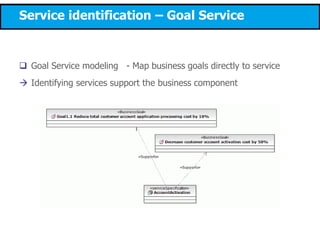
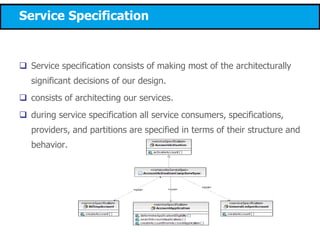
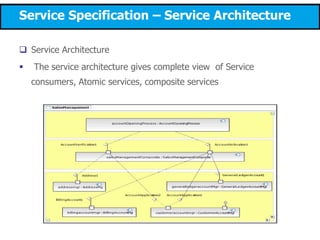
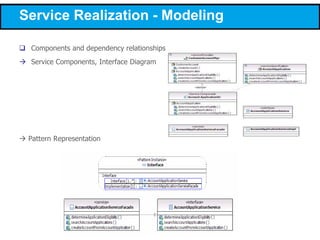
This document discusses modeling a service-oriented architecture (SOA) project using IBM's Service Oriented Modeling and Architecture (SOMA) methodology. It describes SOMA's stages of service identification, specification, realization, implementation and deployment. It recommends using UML 2.0, SoaML and tools like IBM Rational Software Architect and ARIS to model SOA artifacts at each stage. Finally, it proposes an incremental adoption plan and reference architecture for the SOA transformation.