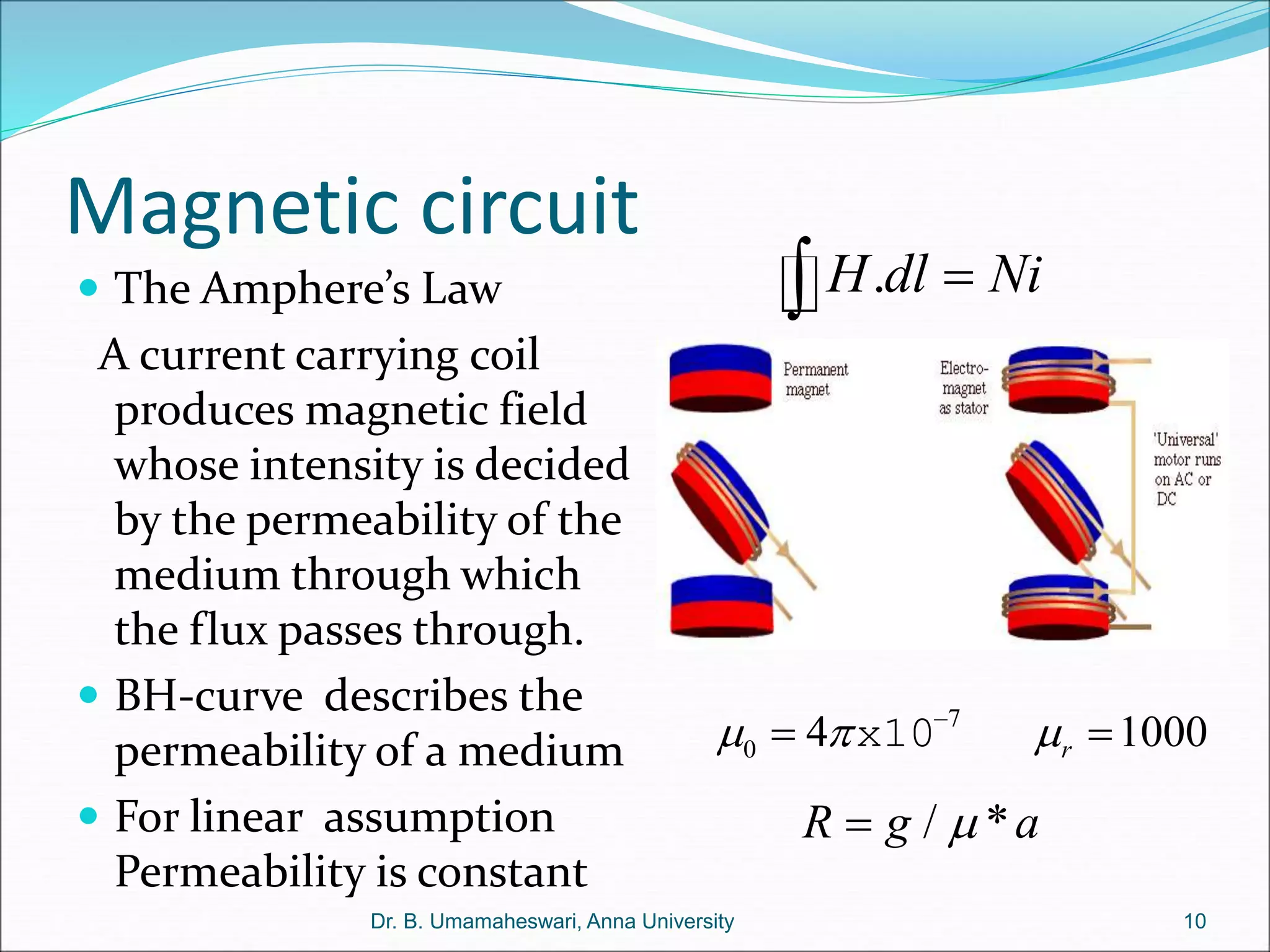
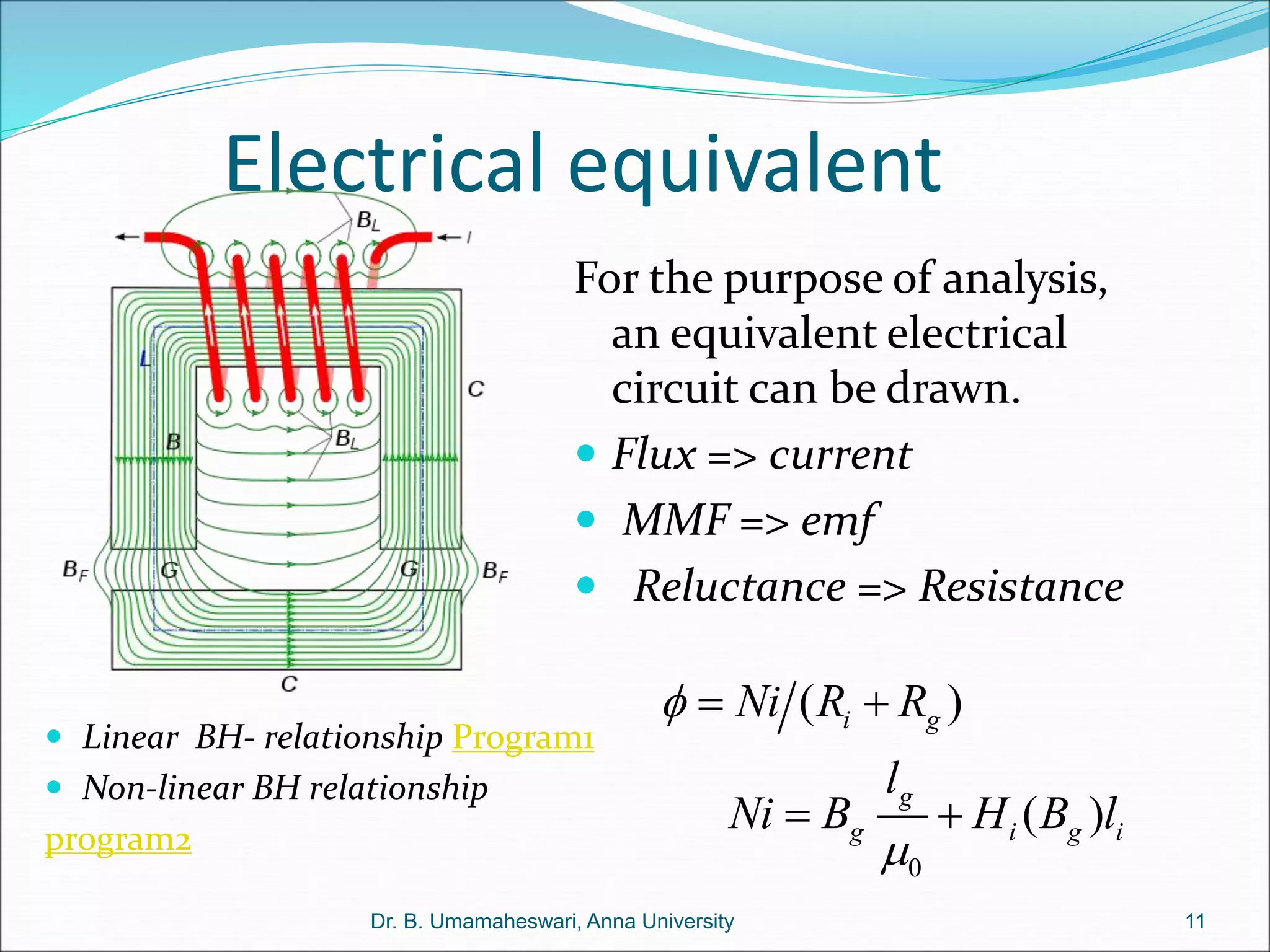
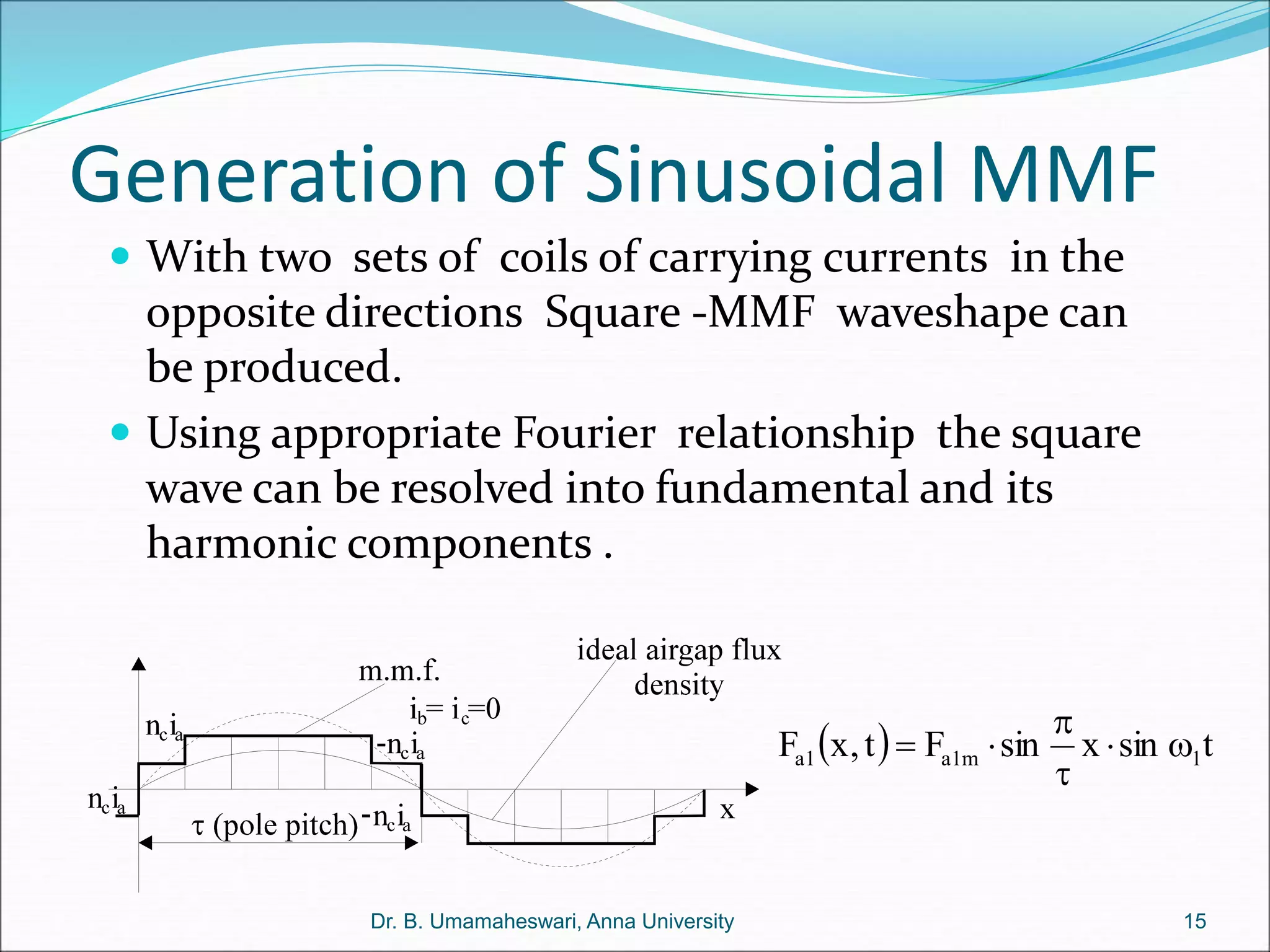
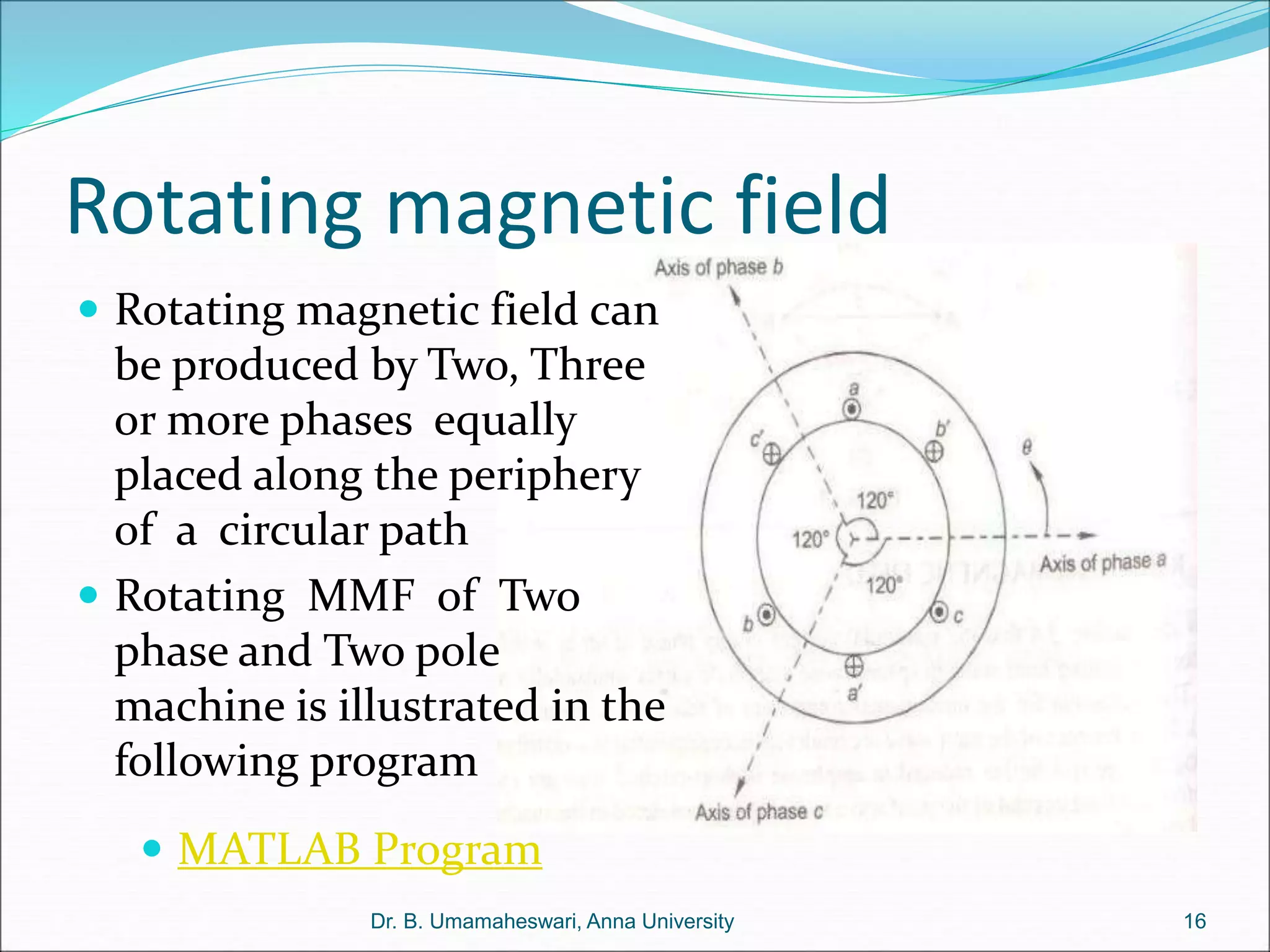
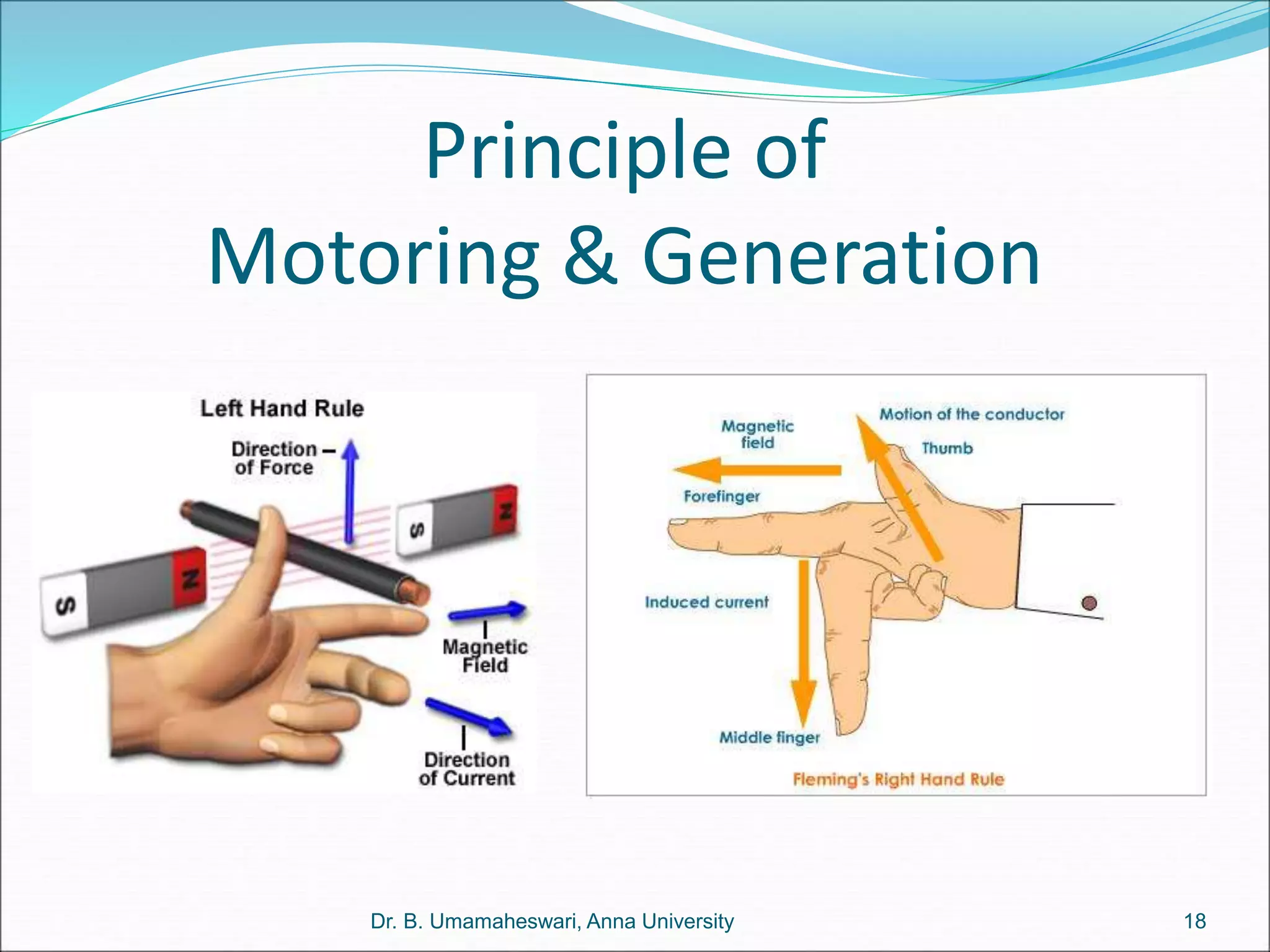
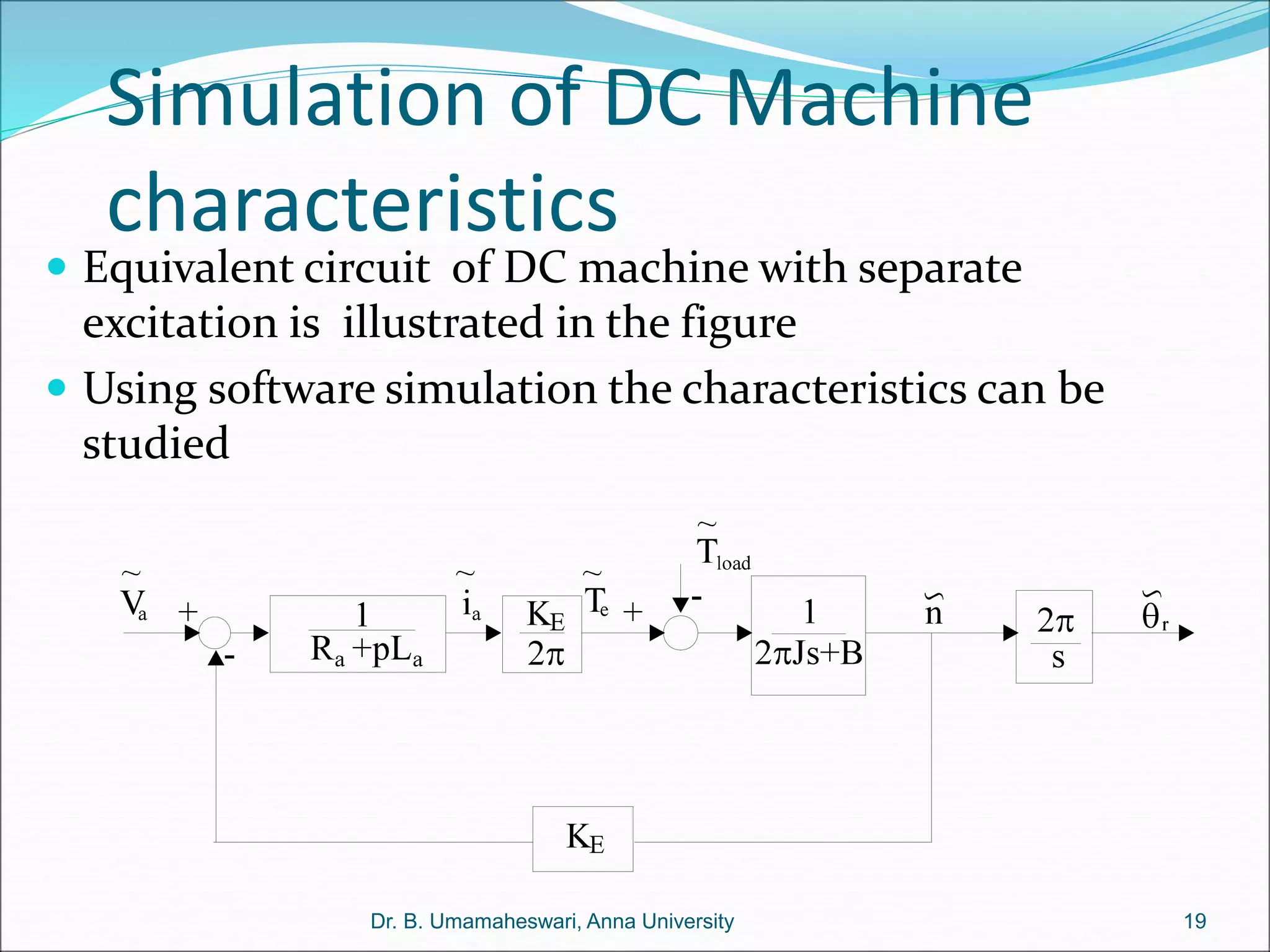
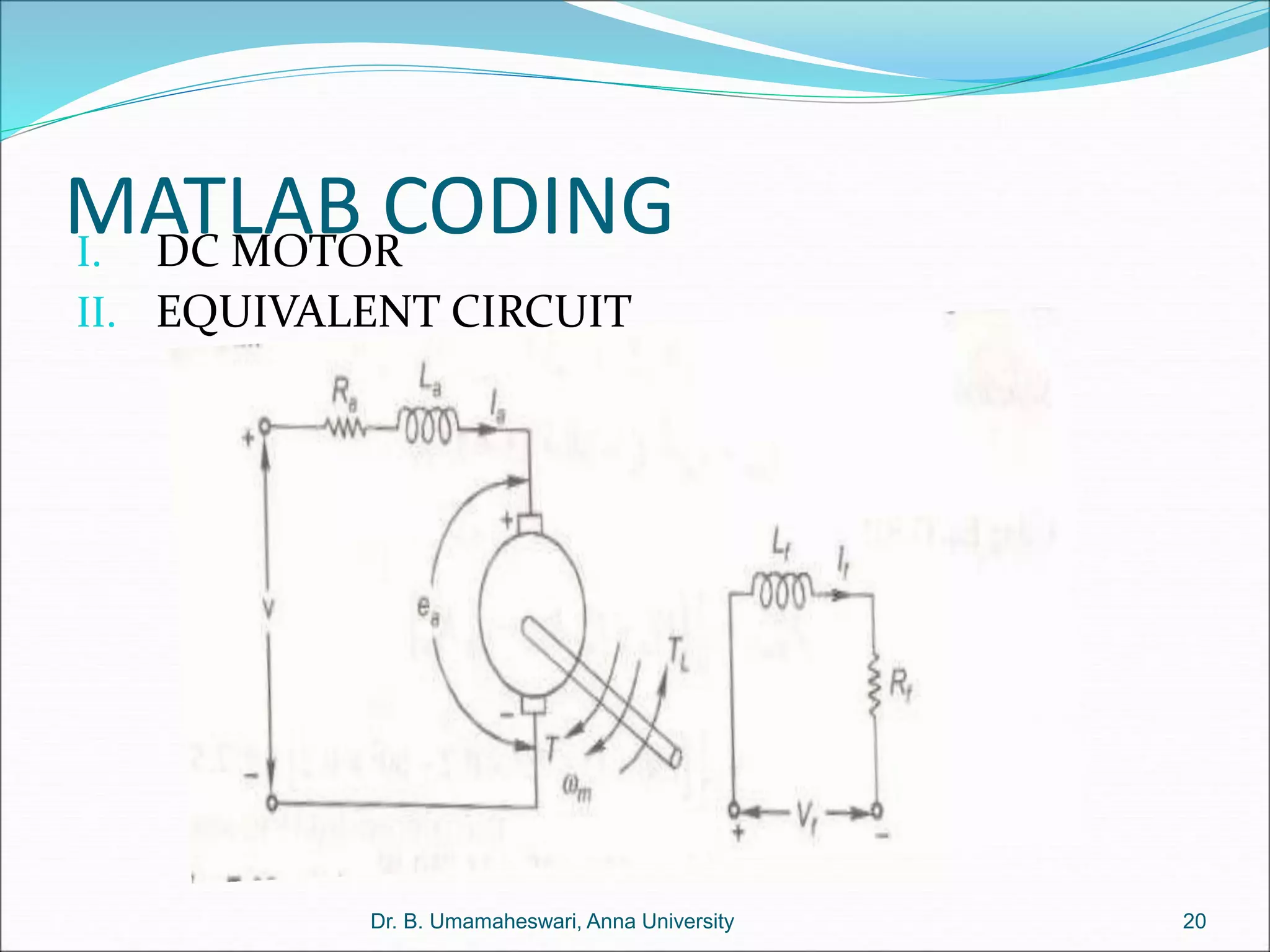
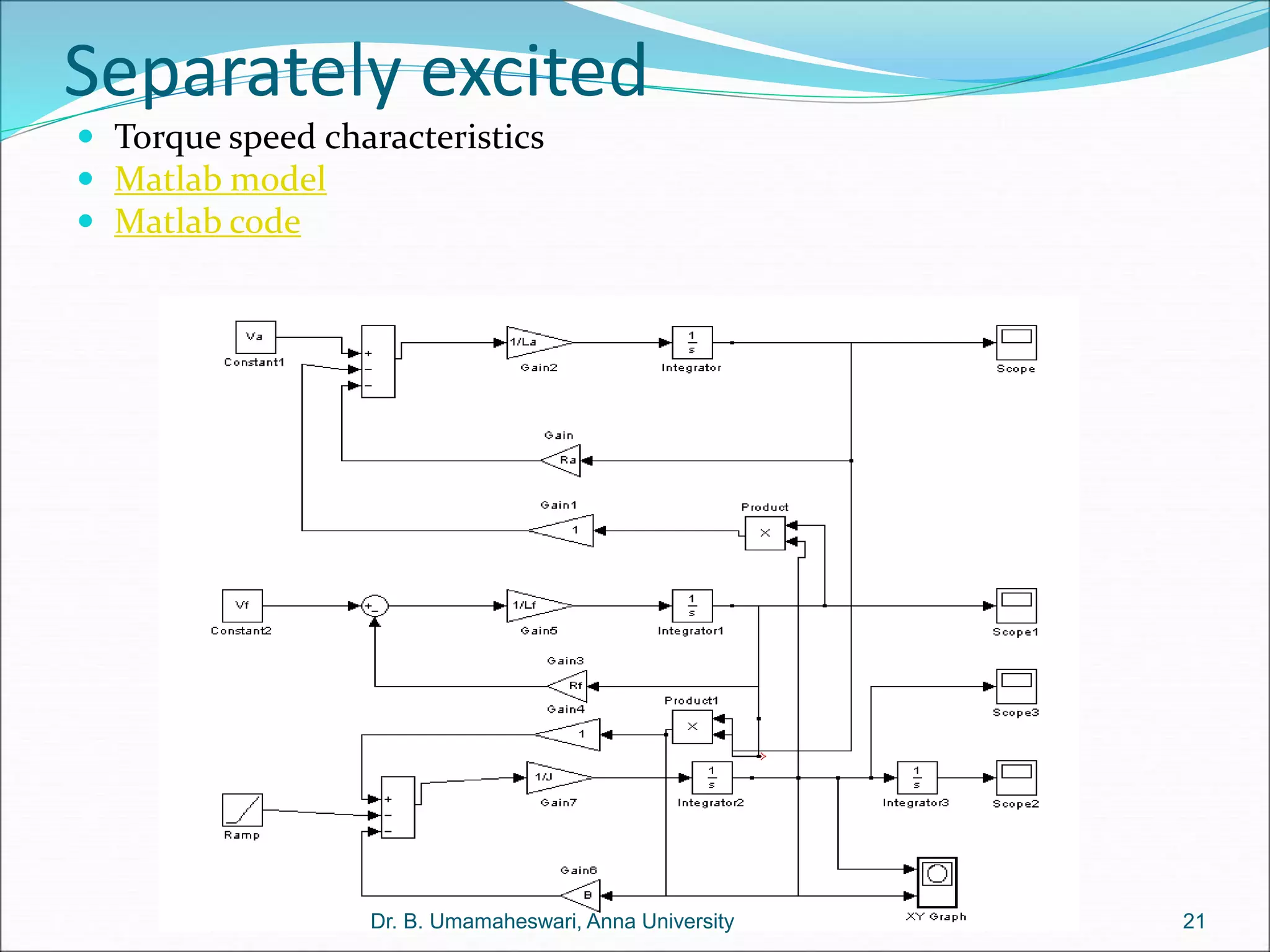
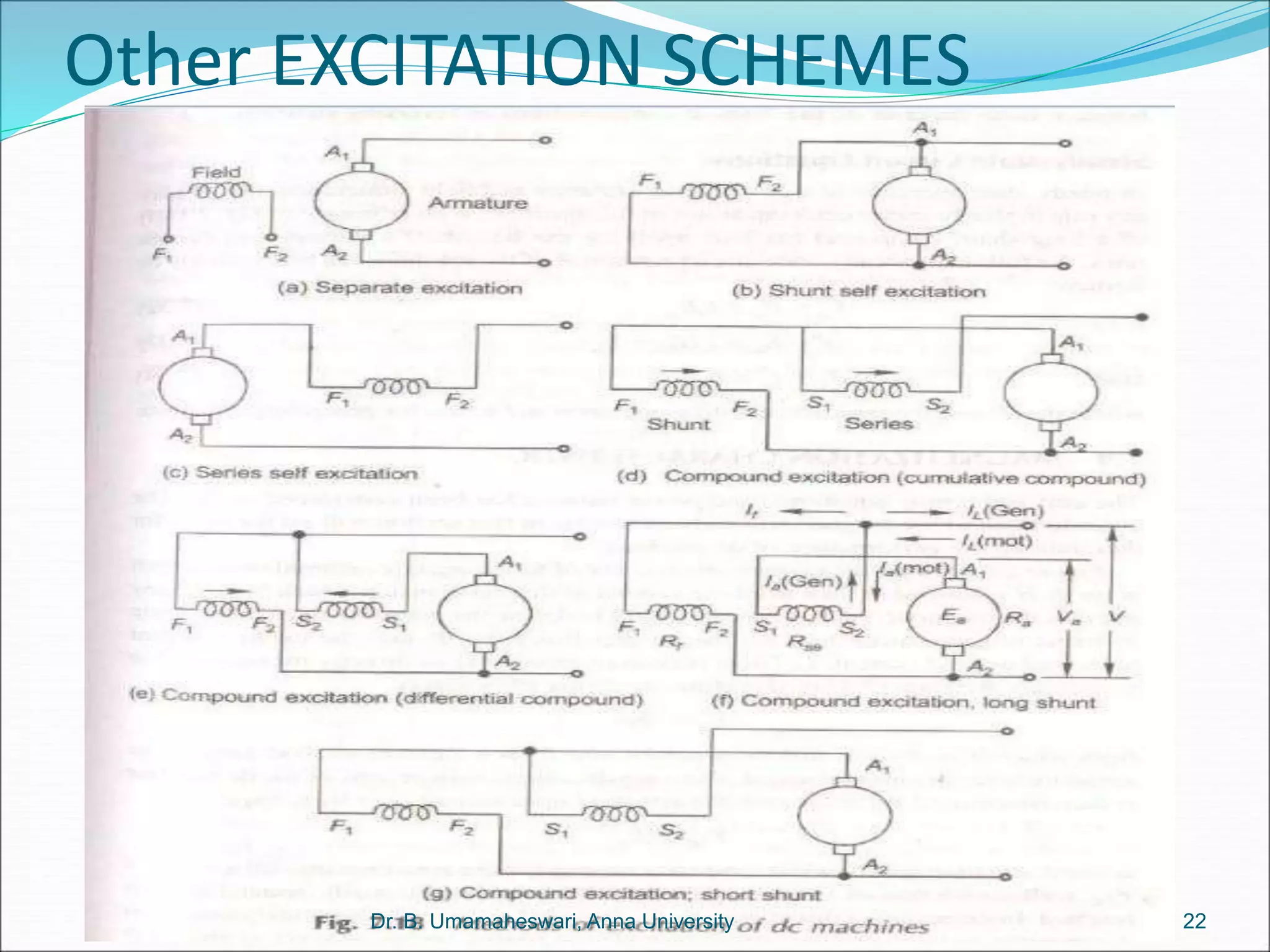
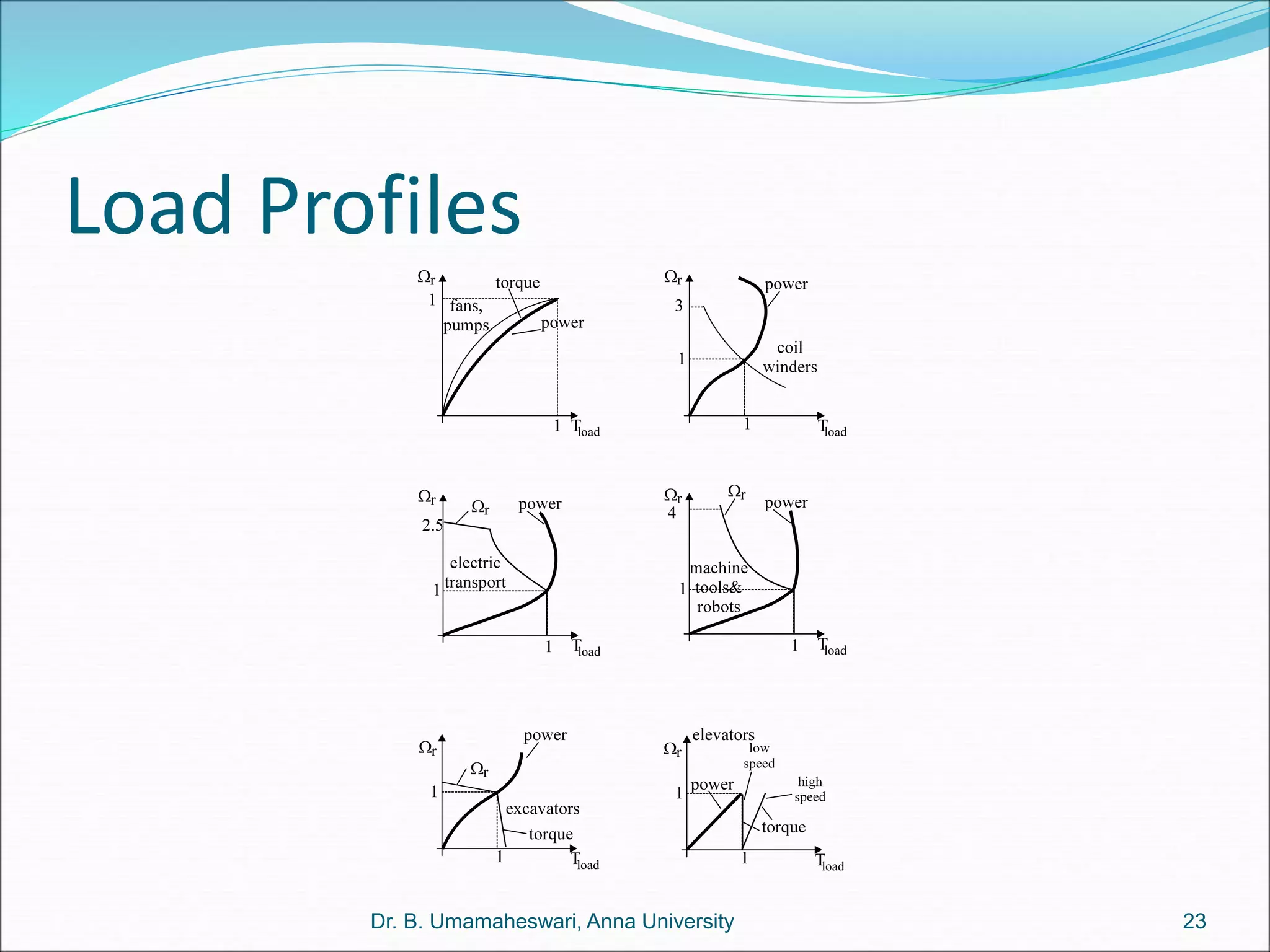
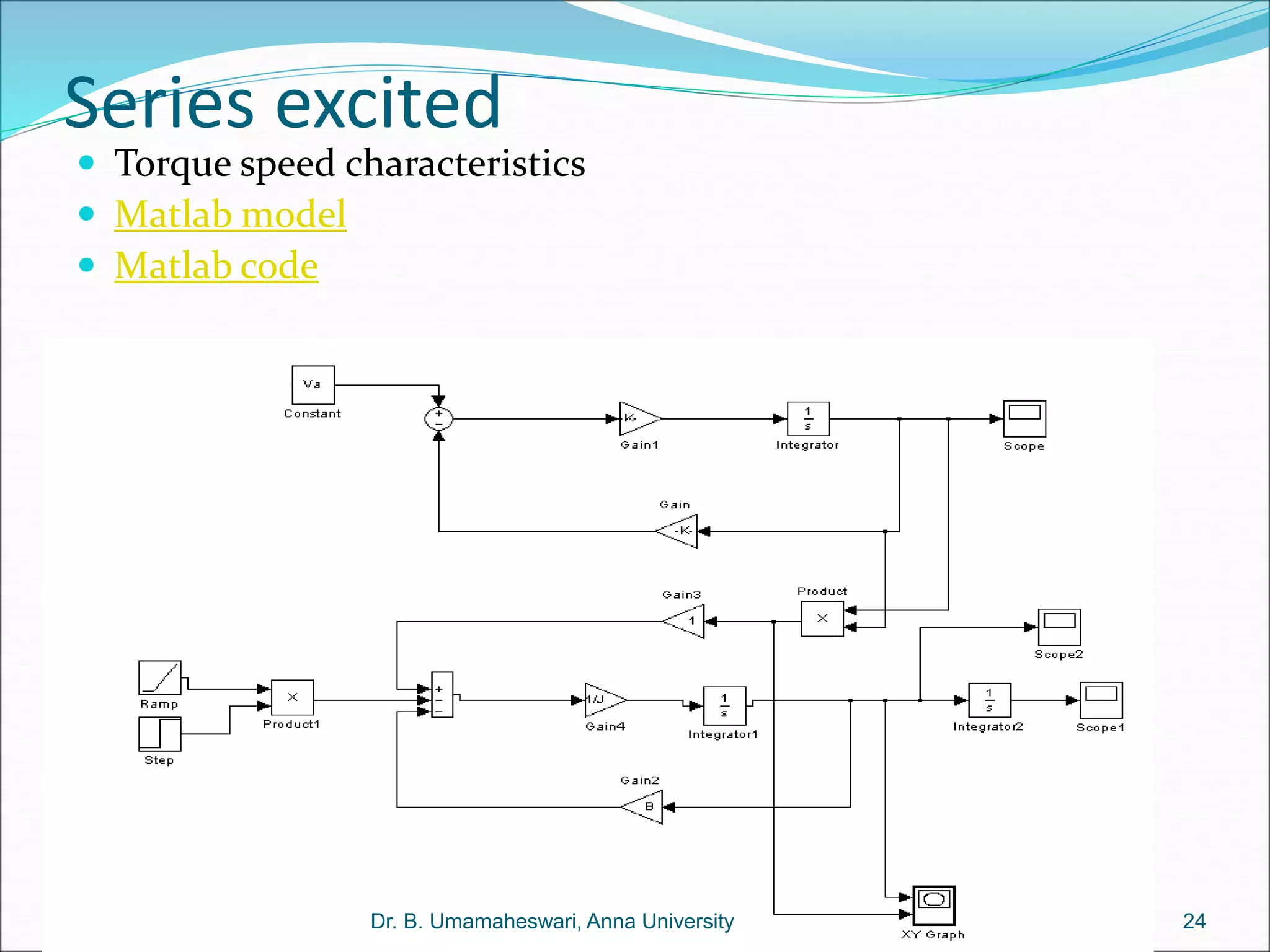
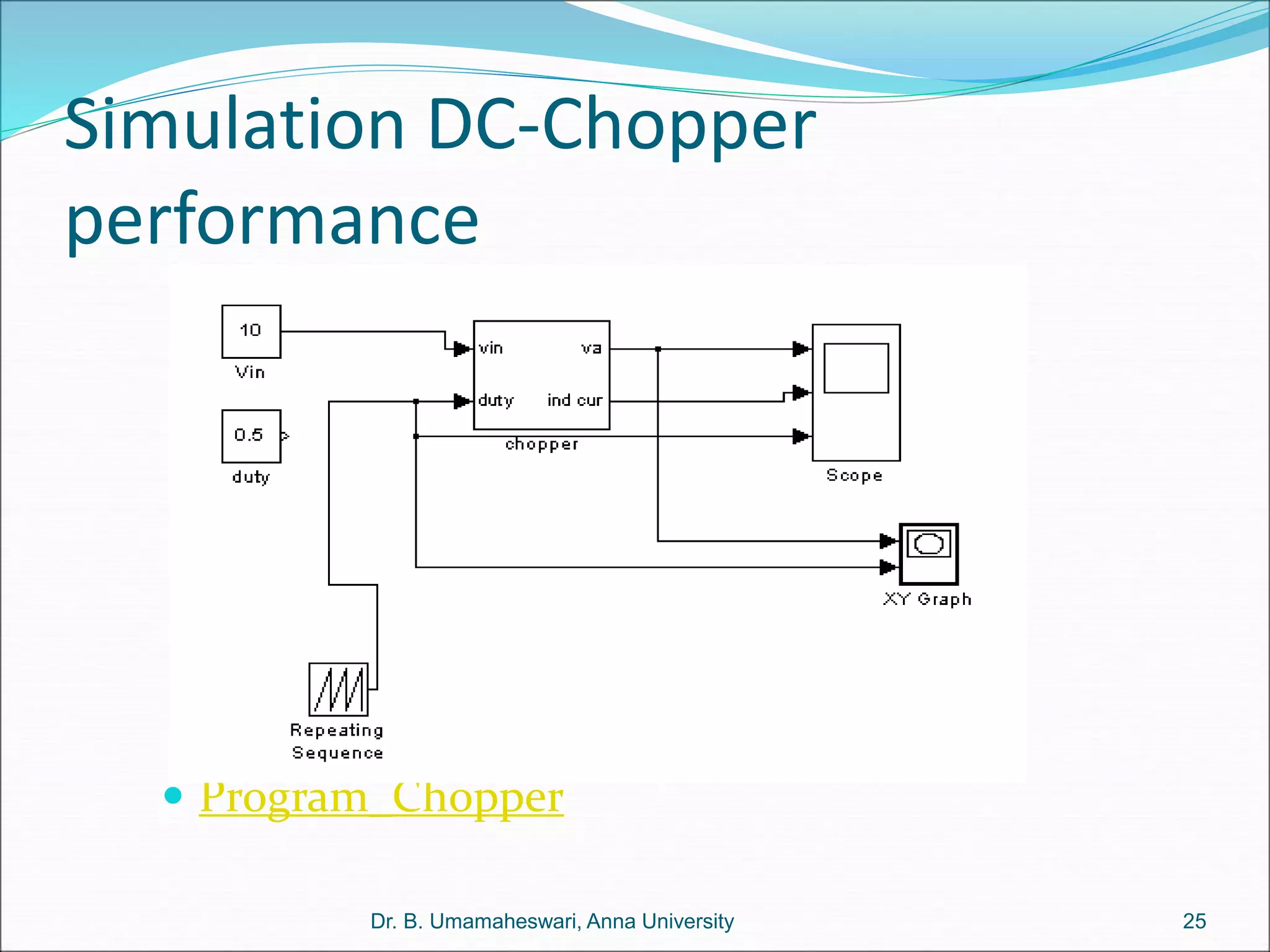
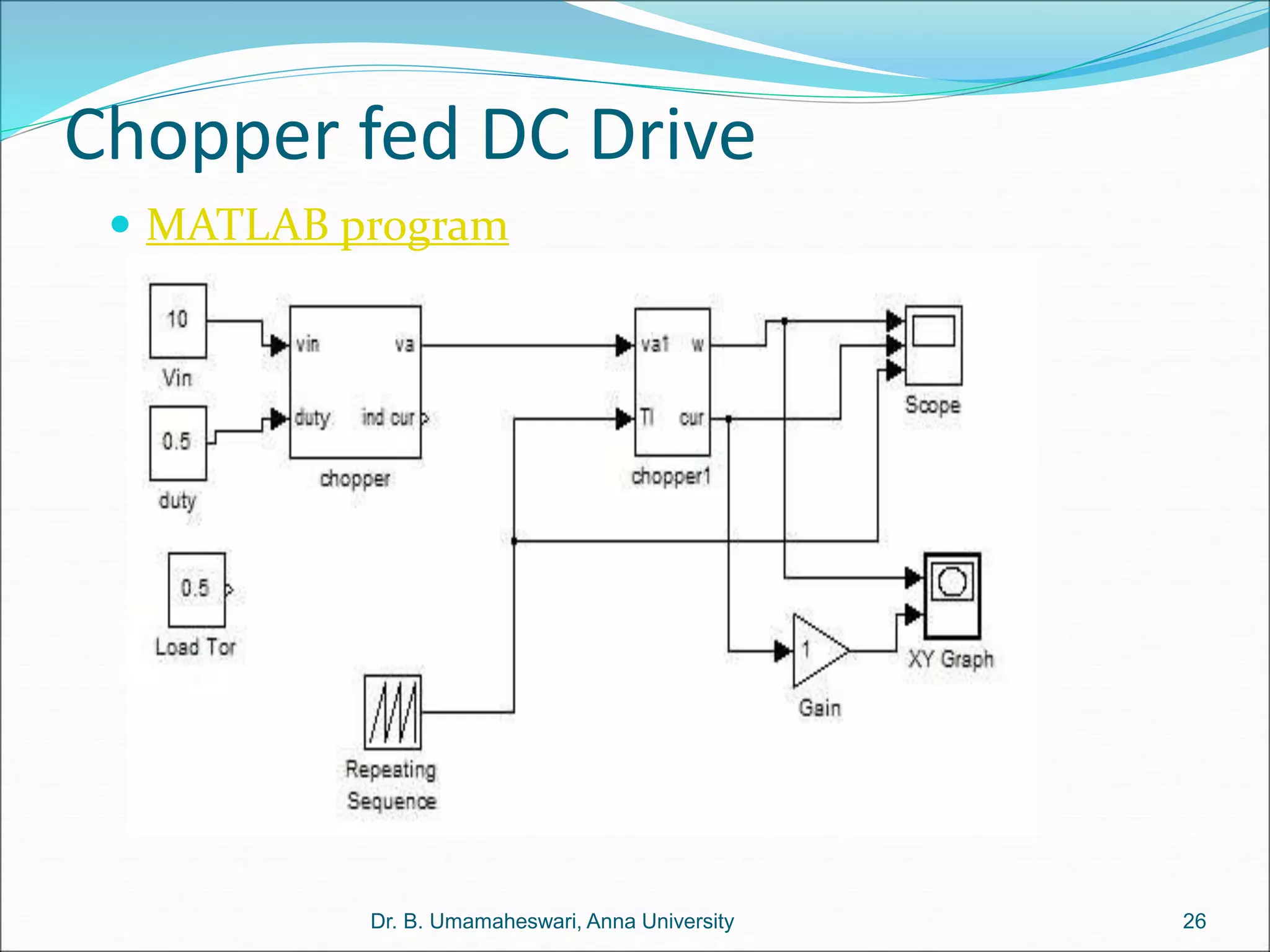
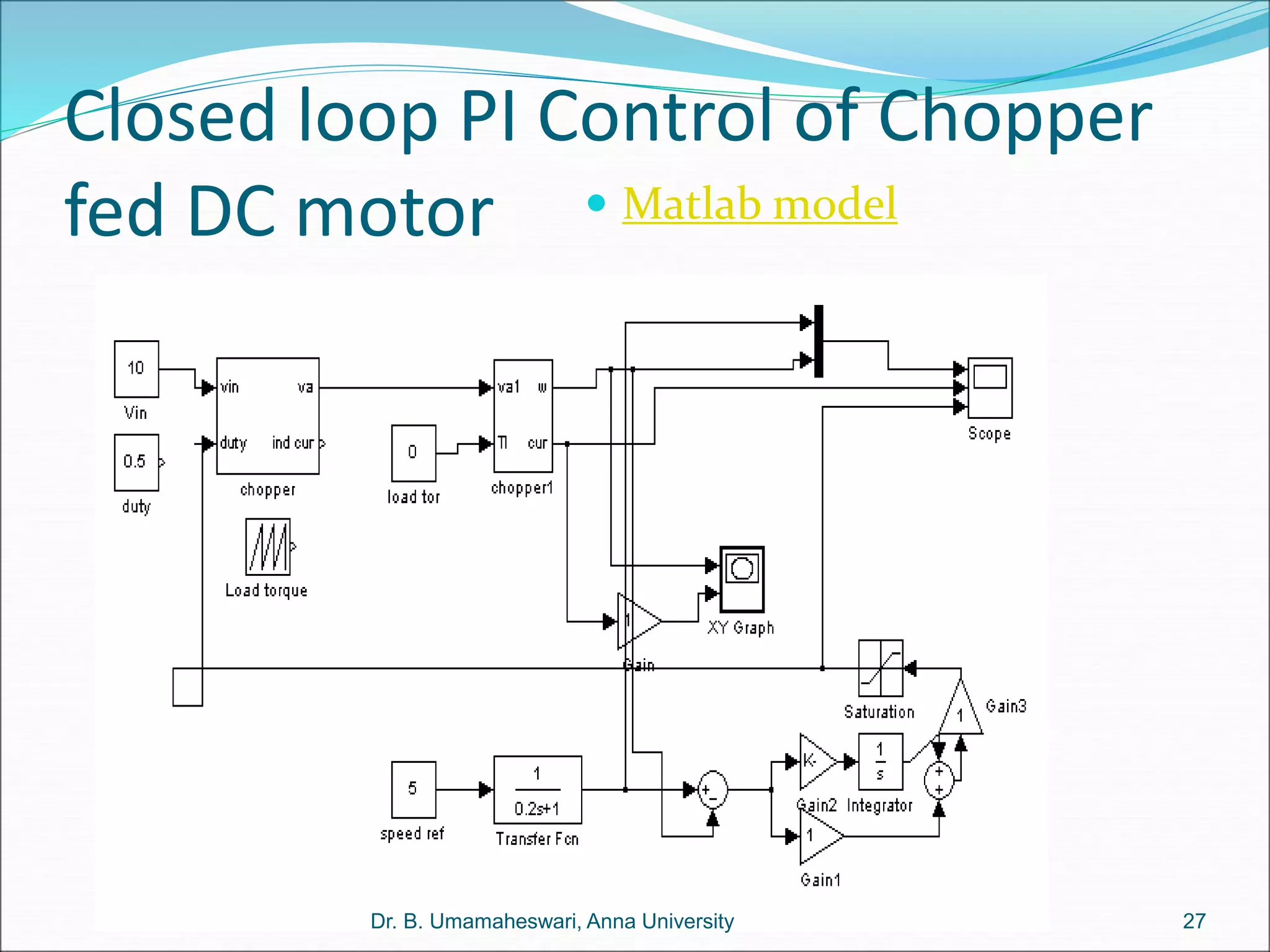
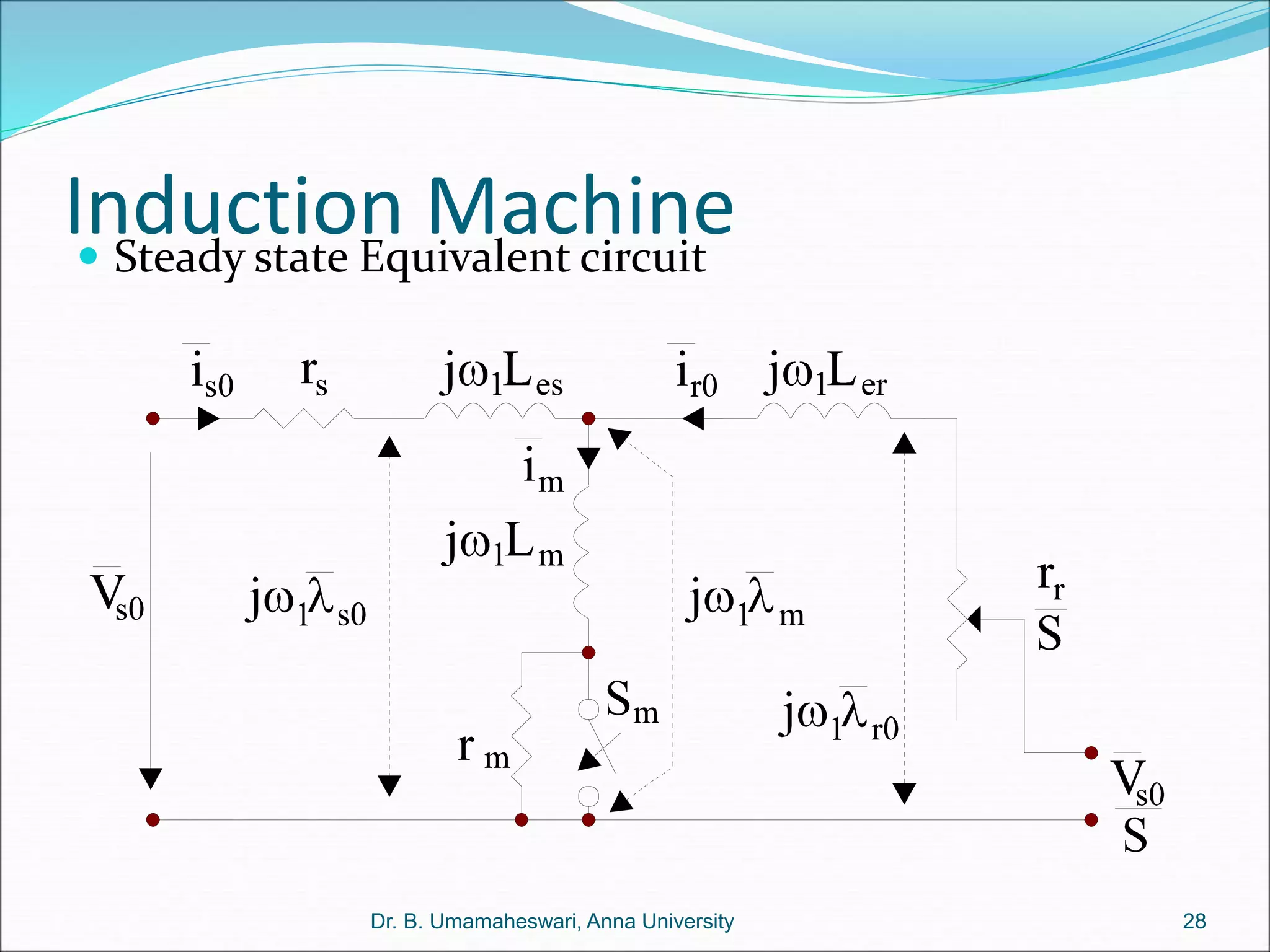
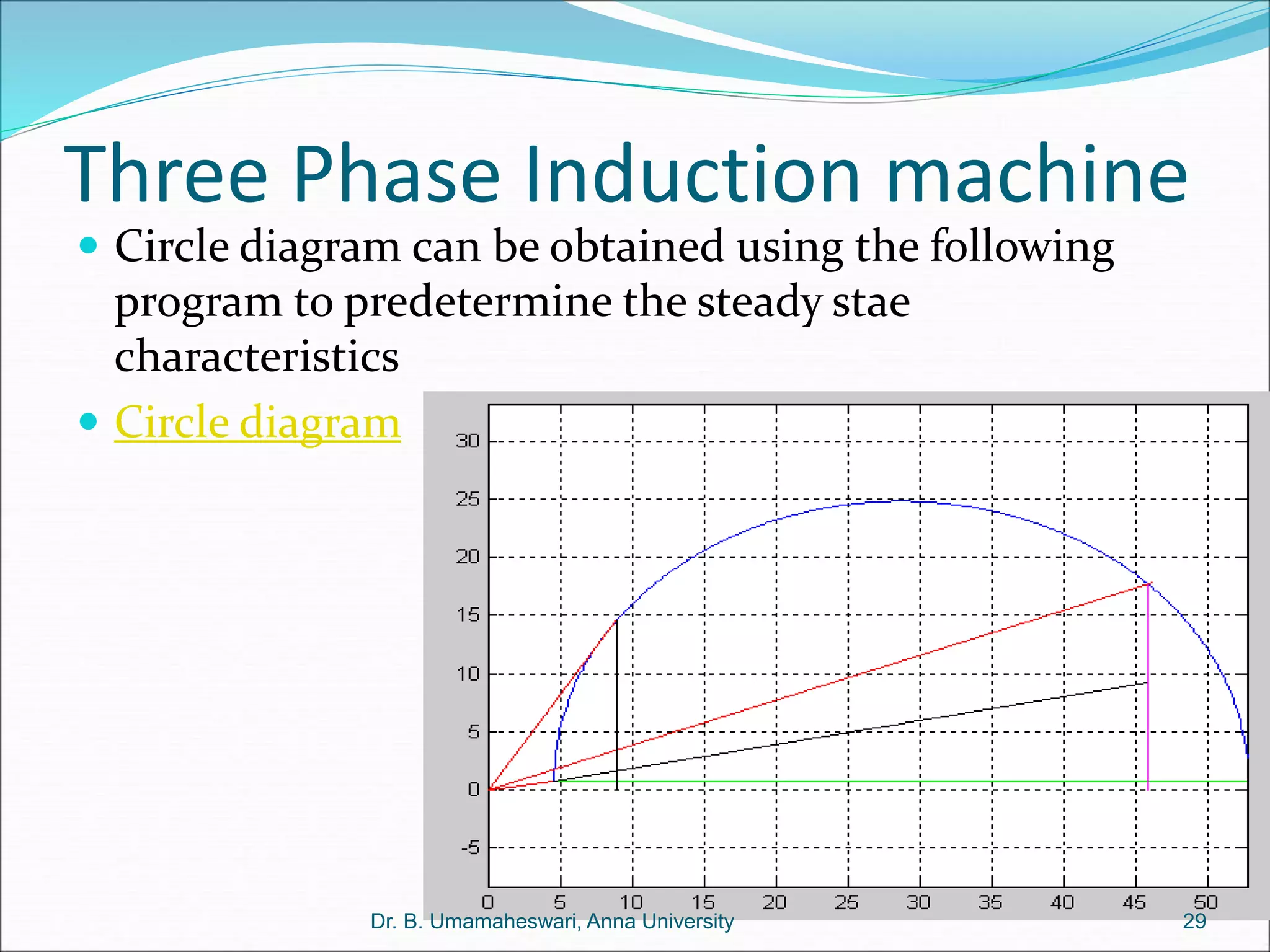
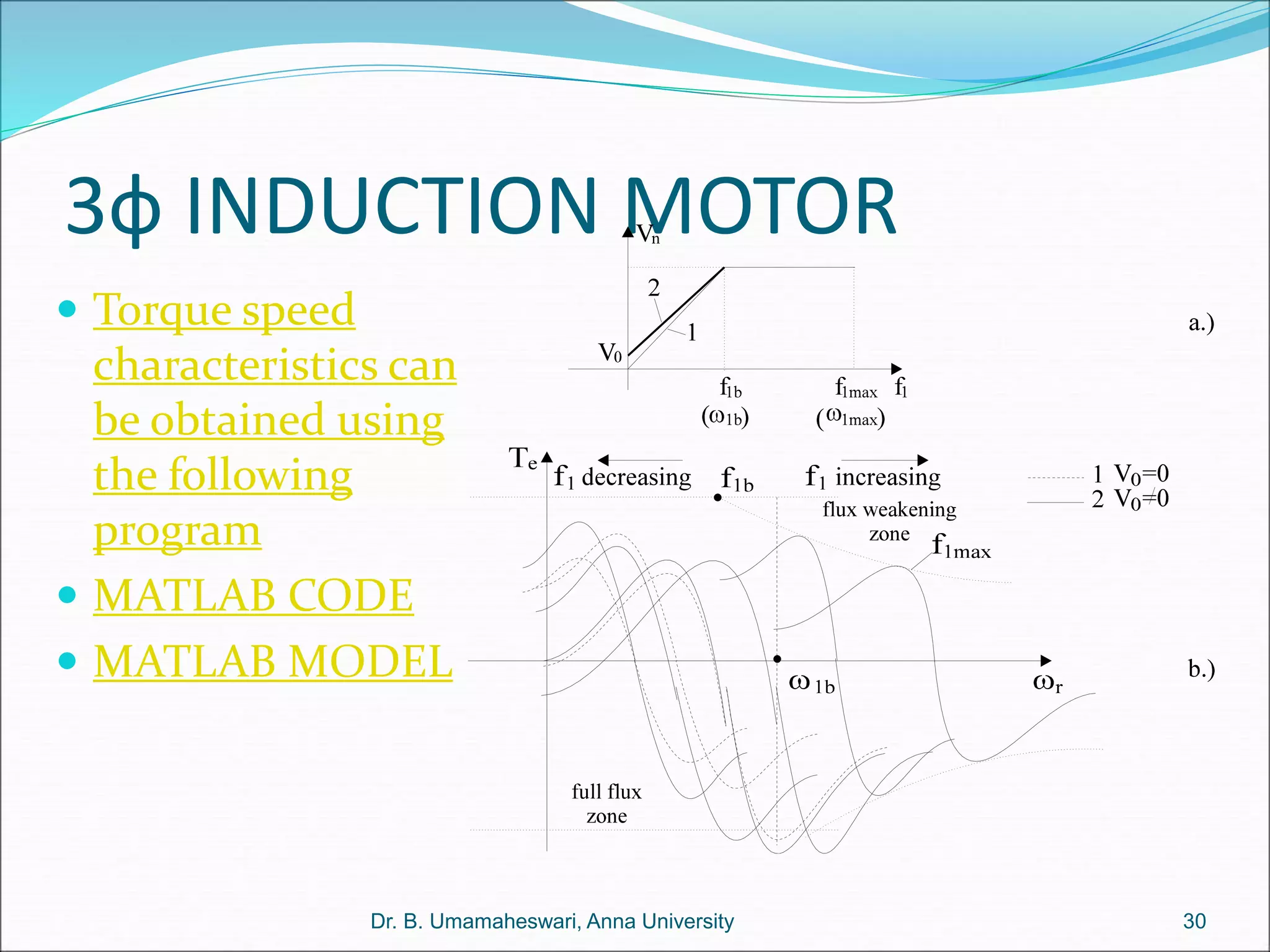
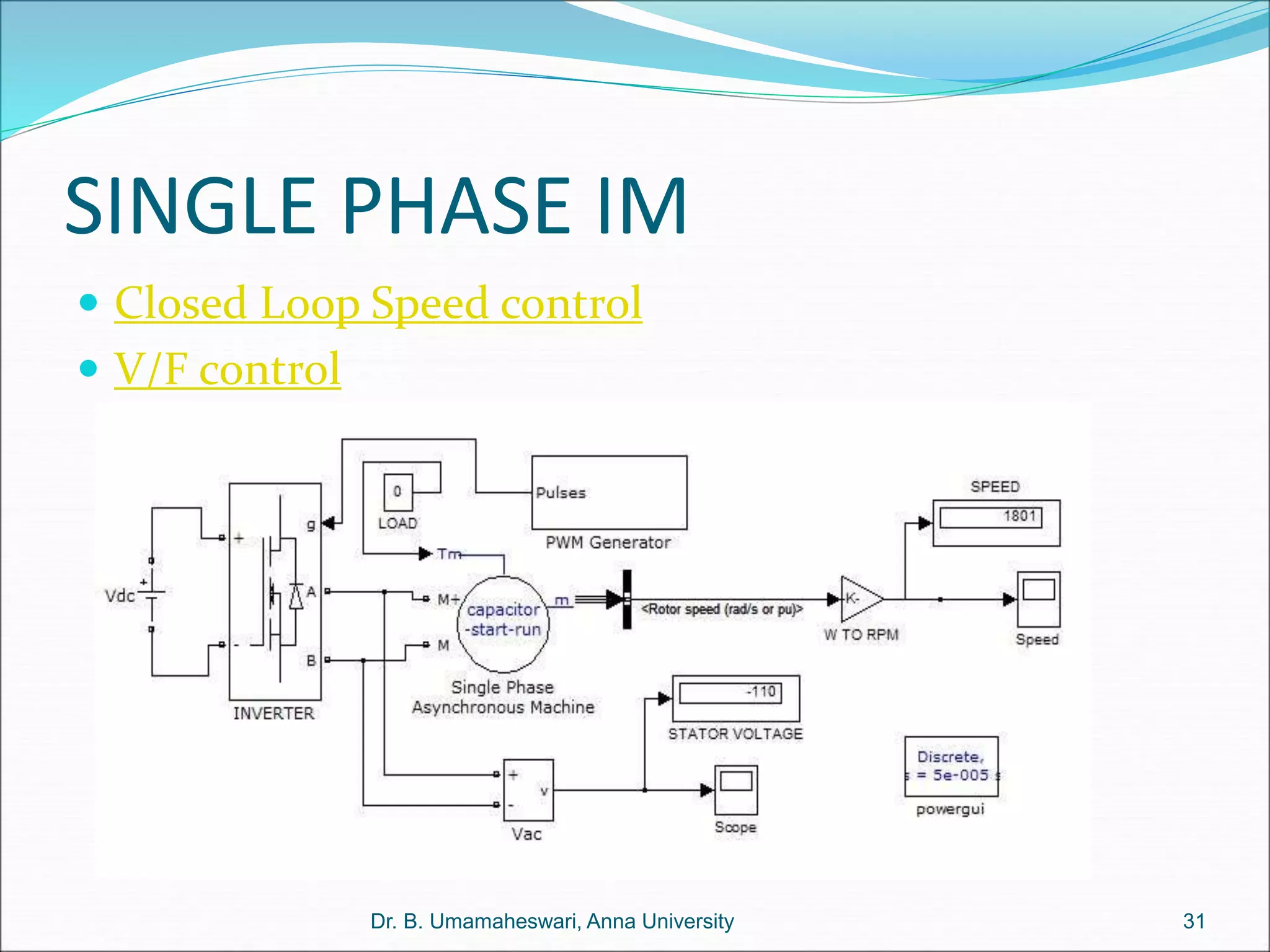
Dr. B. Umamaheswari gives a presentation on using MATLAB and SIMULINK software tools to teach concepts in electrical machines, drives, and control. She discusses 5 topics - electro-magnetics, electro-mechanics, DC machines, induction machines, and references. For each topic, she presents the relevant theory, MATLAB models, codes, and simulations that can help explain the concepts and characterize machine performance under different operating conditions. The goal is to provide students a better understanding and hands-on learning experience with electrical engineering domains.