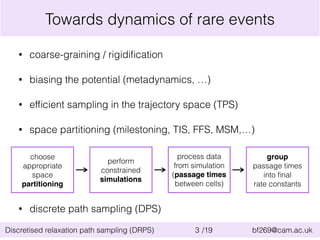
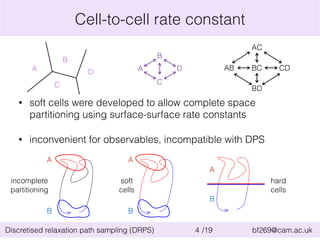
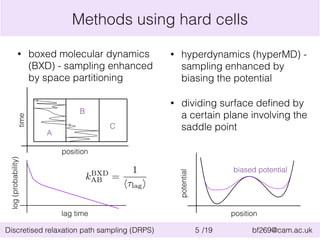
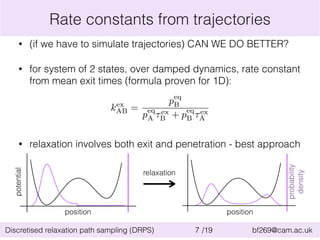
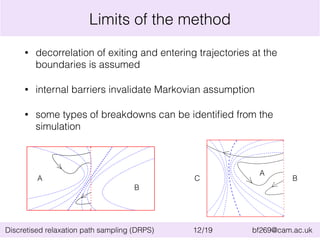
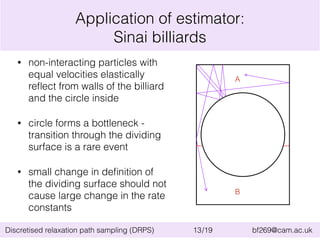
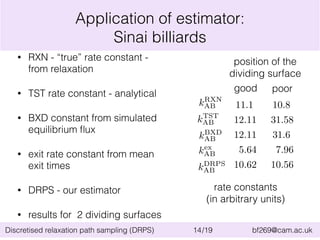
This document summarizes the discretised relaxation path sampling (DRPS) method for simulating rare events. DRPS partitions configuration space into cells and propagates response functions describing the relaxation between cells to obtain rate constants. The method was tested on Sinai billiards and a cluster of Lennard-Jones disks, obtaining good agreement with other methods. Future applications discussed include polymer reversal in nanopores and biomolecular folding.

![Limits of TST
• transition state theory - rate constant = equilibrium flux /
equilibrium population
kTST
AB =
flux
population
= hP(x) [n(x) · v]i@A
hP(x)iA
=
@tpA(0)
pA(0)
• the rate constant is very sensitive to definition of the dividing
time
population in A
A A
time
population in A
surface
Discretised relaxation path sampling (DRPS) 6 /19 bf269@cam.ac.uk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkdurhamfackovec2014-141022175859-conversion-gate01/85/Simulating-dynamics-of-rare-events-using-discretised-relaxation-path-sampling-6-320.jpg)
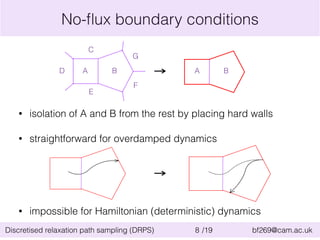
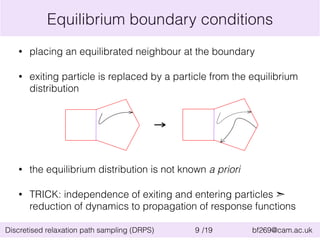
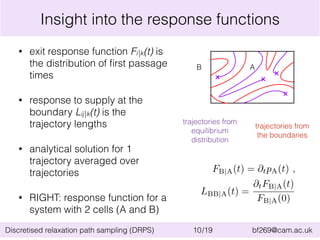
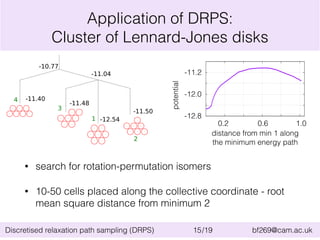
![Application of DRPS:
Cluster of Lennard-Jones disks
0.6
simul
0.2
k fit
k equil
-0.6
1.00
0.95
0.90
0.85
0.80
0.75
0.70
-1.0
0.9
0.8
0.0 0.4 0.8 0.2 0.6
0.65
in A
free energy
Discretised relaxation path sampling (DRPS) 16
/19 bf269@cam.ac.uk
Rate constants
box 2 box 5 box 10 TPS DPS
ln(k12/⌧0) -28.9 ± 0.3 -29.6 ± 0.5 -30.5 ± 1.0 -28.7 -26.9
ln(k21/⌧0) -9.3 ± 0.2 -9.4 ± 0.3 -9.7 ± 0.7 -7.2 -9.2
0.60
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
population
time / [τ0]
population time distance from min 2
1.0
0.7
-0.2
0.2 0.6 1.0 0.4 0.8 1.0
fit
propagation
equilibrium value
TST
MC
DRPS small cell
DRPS large cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkdurhamfackovec2014-141022175859-conversion-gate01/85/Simulating-dynamics-of-rare-events-using-discretised-relaxation-path-sampling-16-320.jpg)