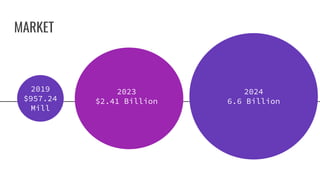
The document discusses the issue of signature forgery, highlighting its impact on financial institutions, legal processes, and personal identification systems, with significant financial losses and legal consequences. It presents statistics indicating that signature forgery contributes to about 9% of occupational fraud cases, with businesses facing average losses of $20,000 per incident. The proposed business model involves a verification service that could charge fees, offer subscriptions, or license technology, aiming to reduce fraud and improve security in various sectors.