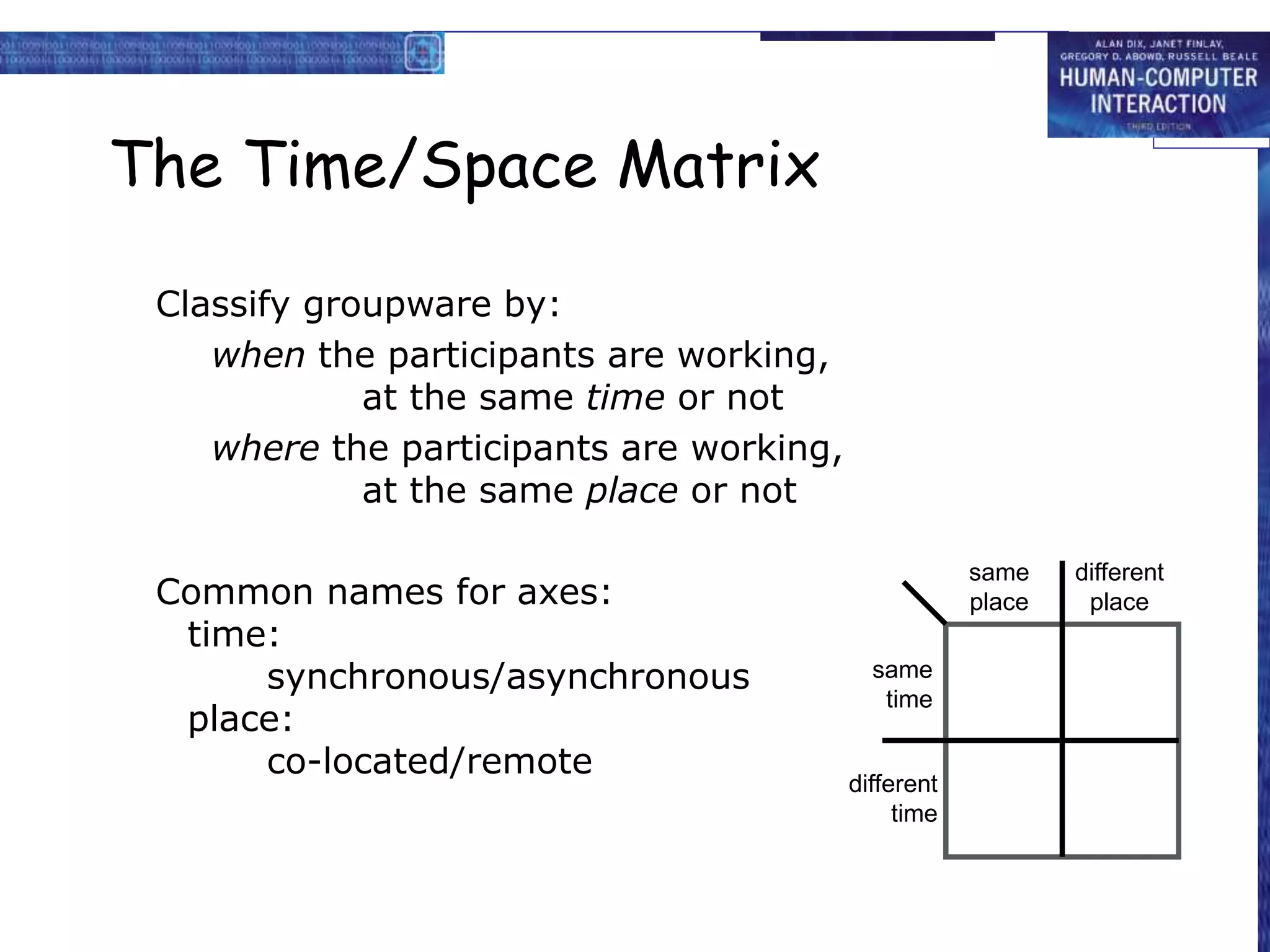
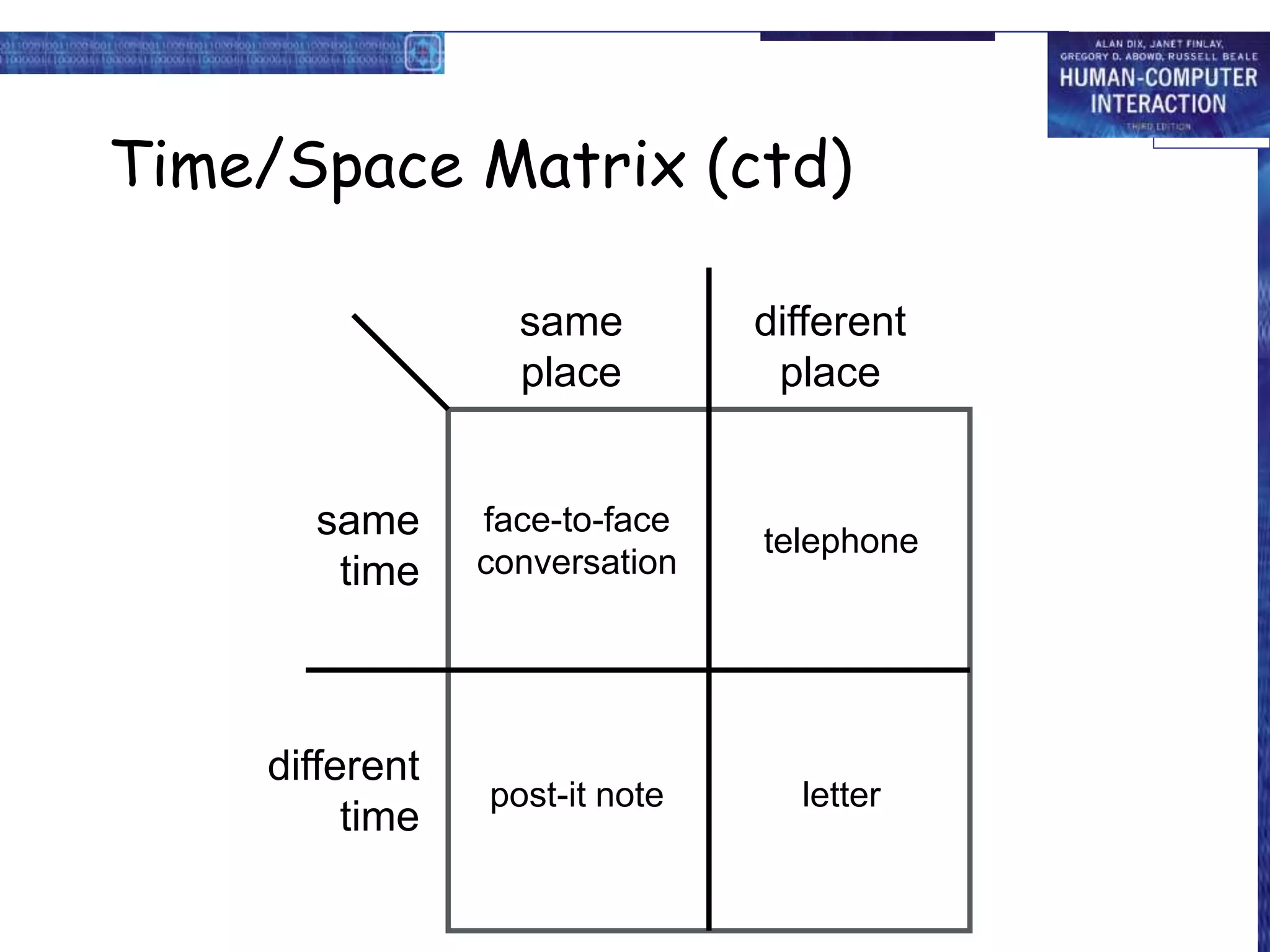
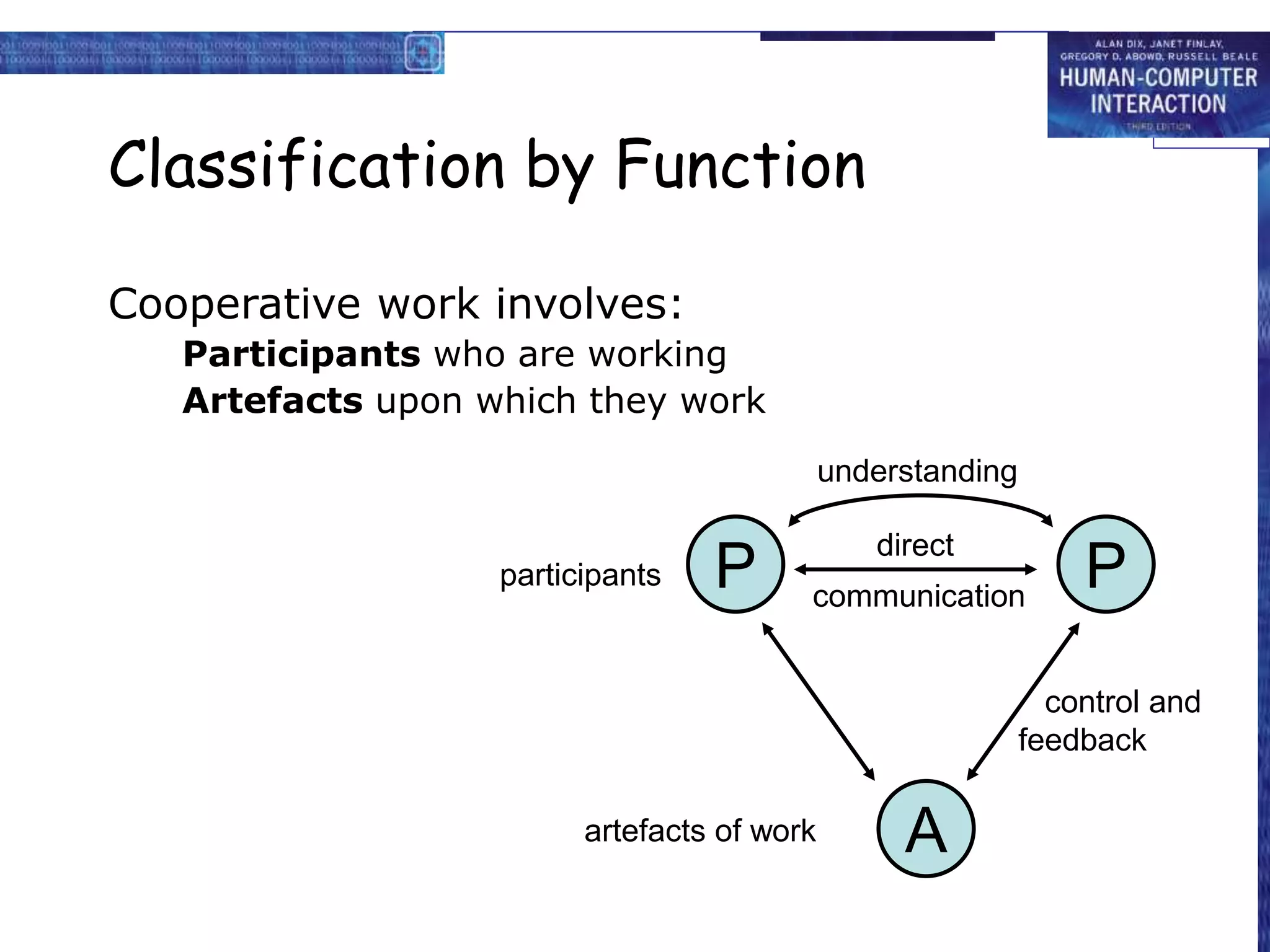
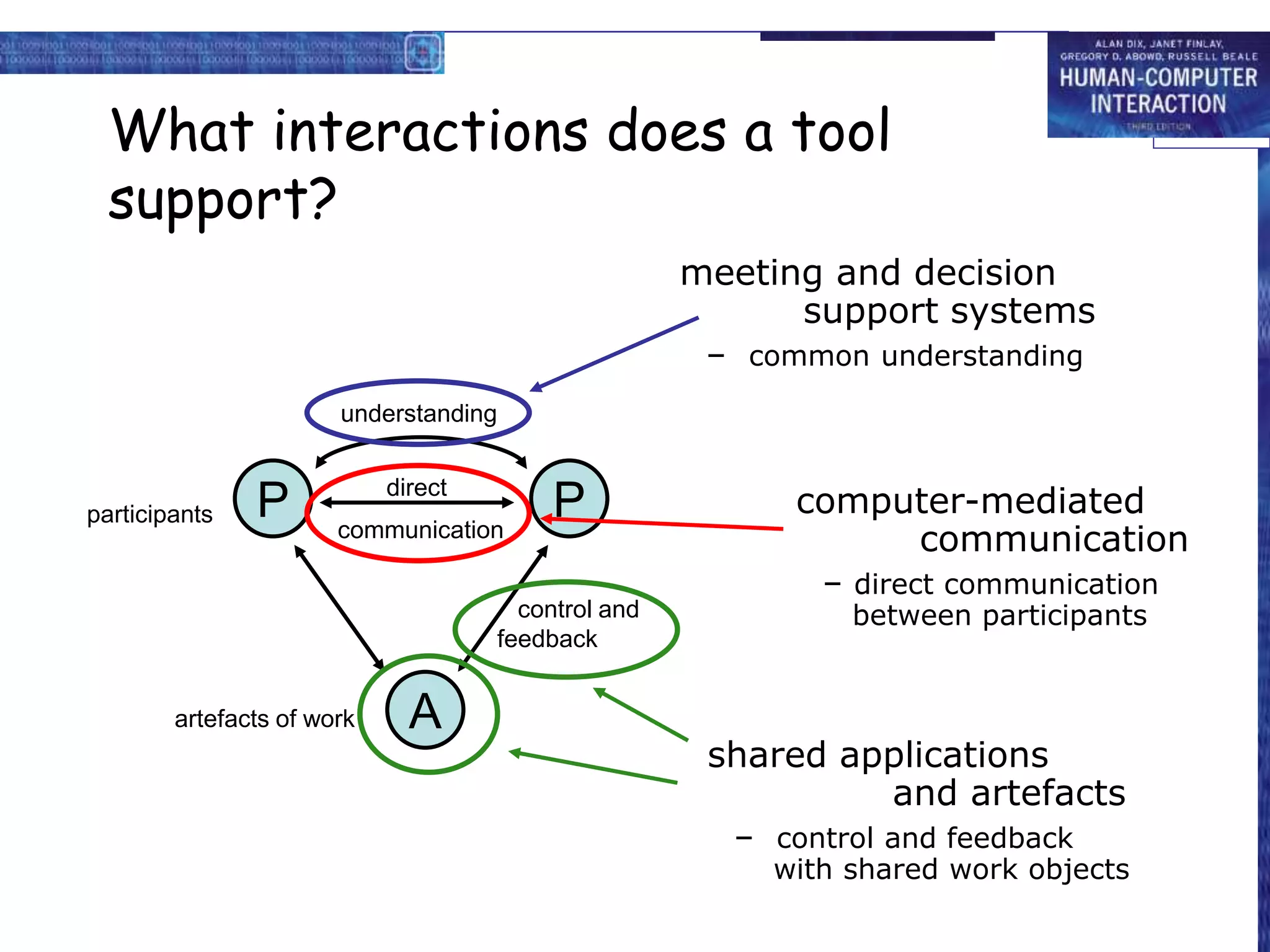
The document discusses groupware, defined as software designed for cooperative work, encompassing various types including computer-mediated communication and meeting support systems. It classifies groupware based on time and place of user interactions, as well as functionality, detailing specific tools like email, instant messaging, and video conferencing. Additionally, it addresses implementation challenges and highlights the evolution and diverse applications of groupware in professional settings.