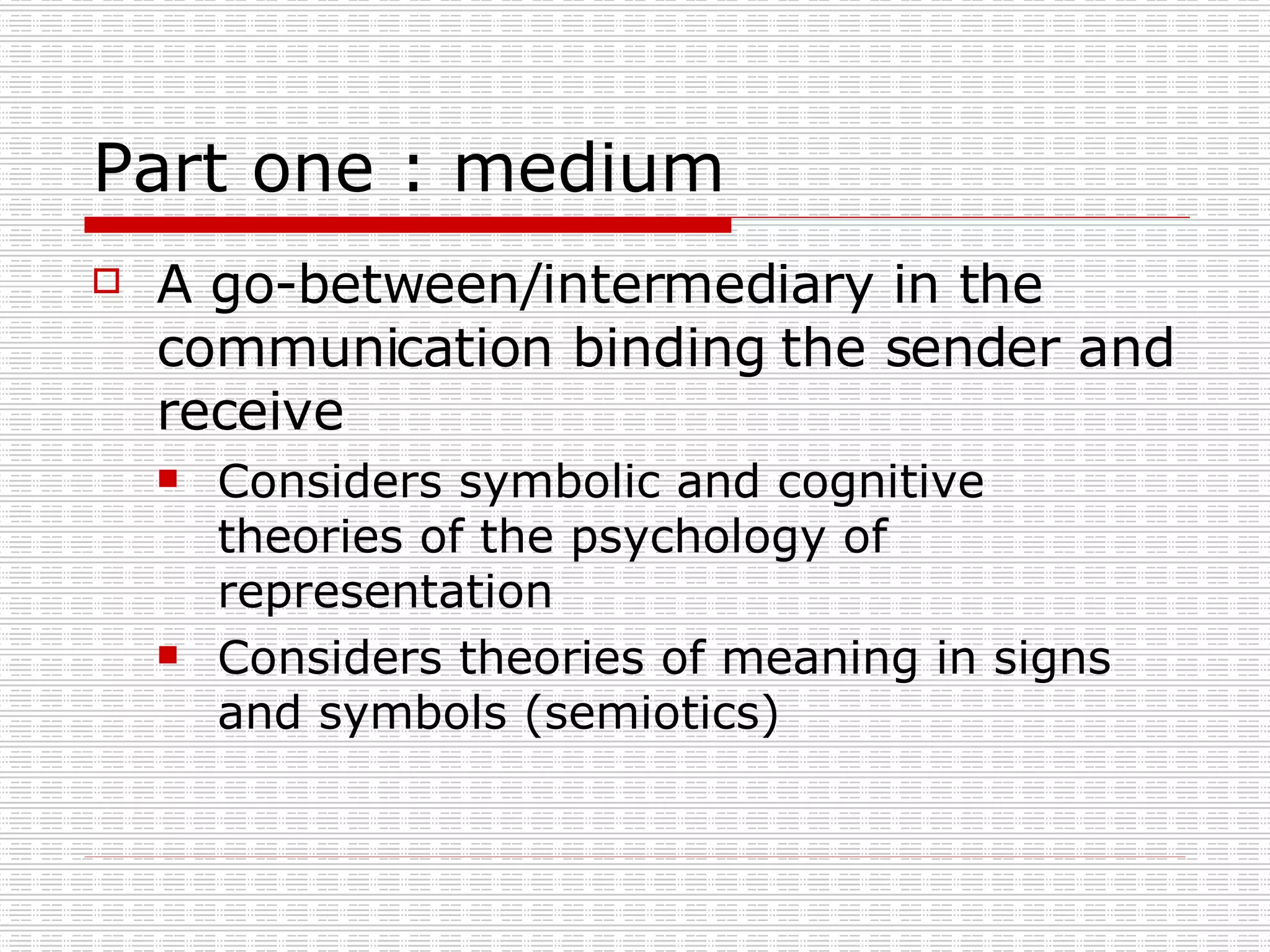
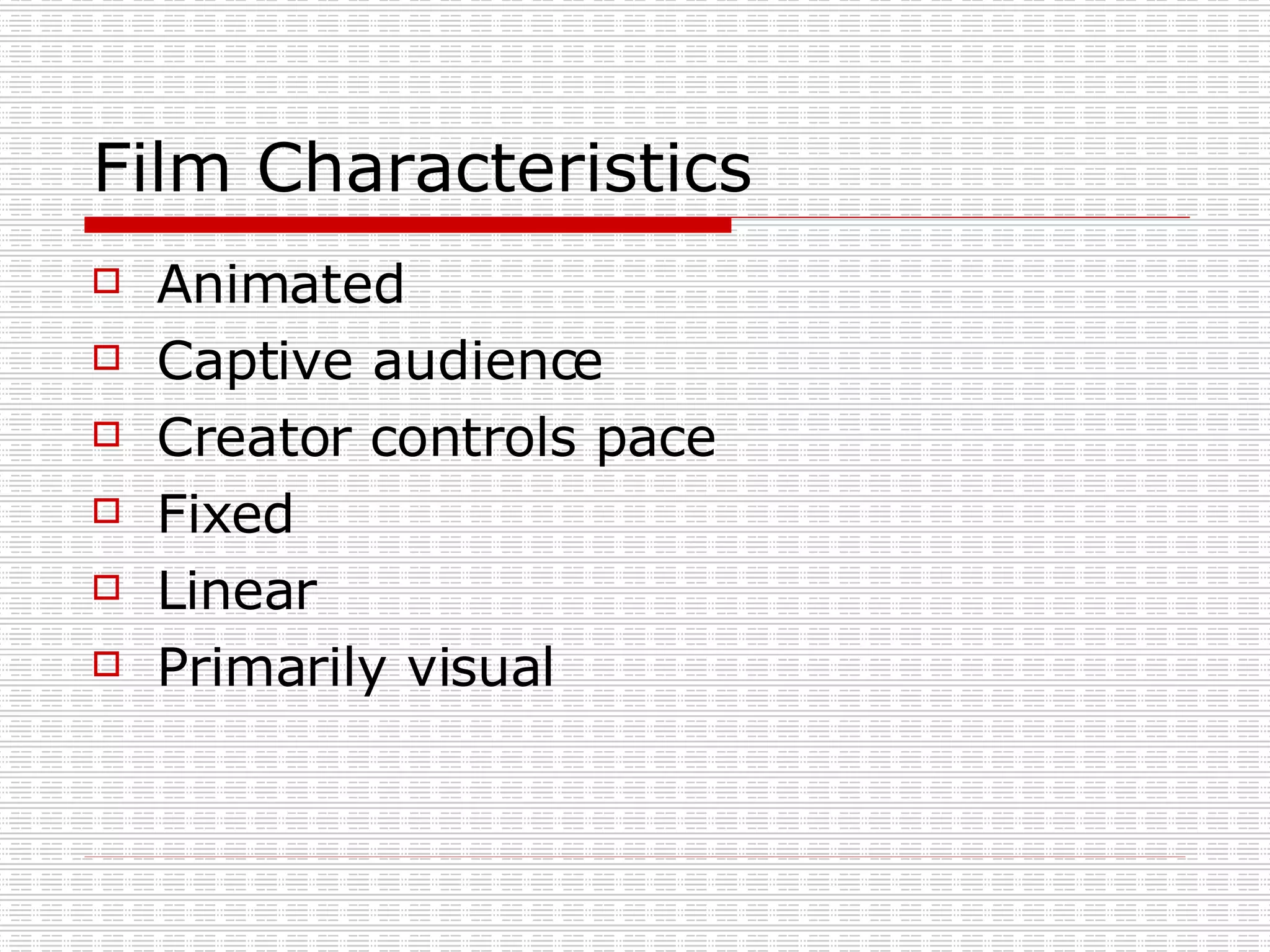
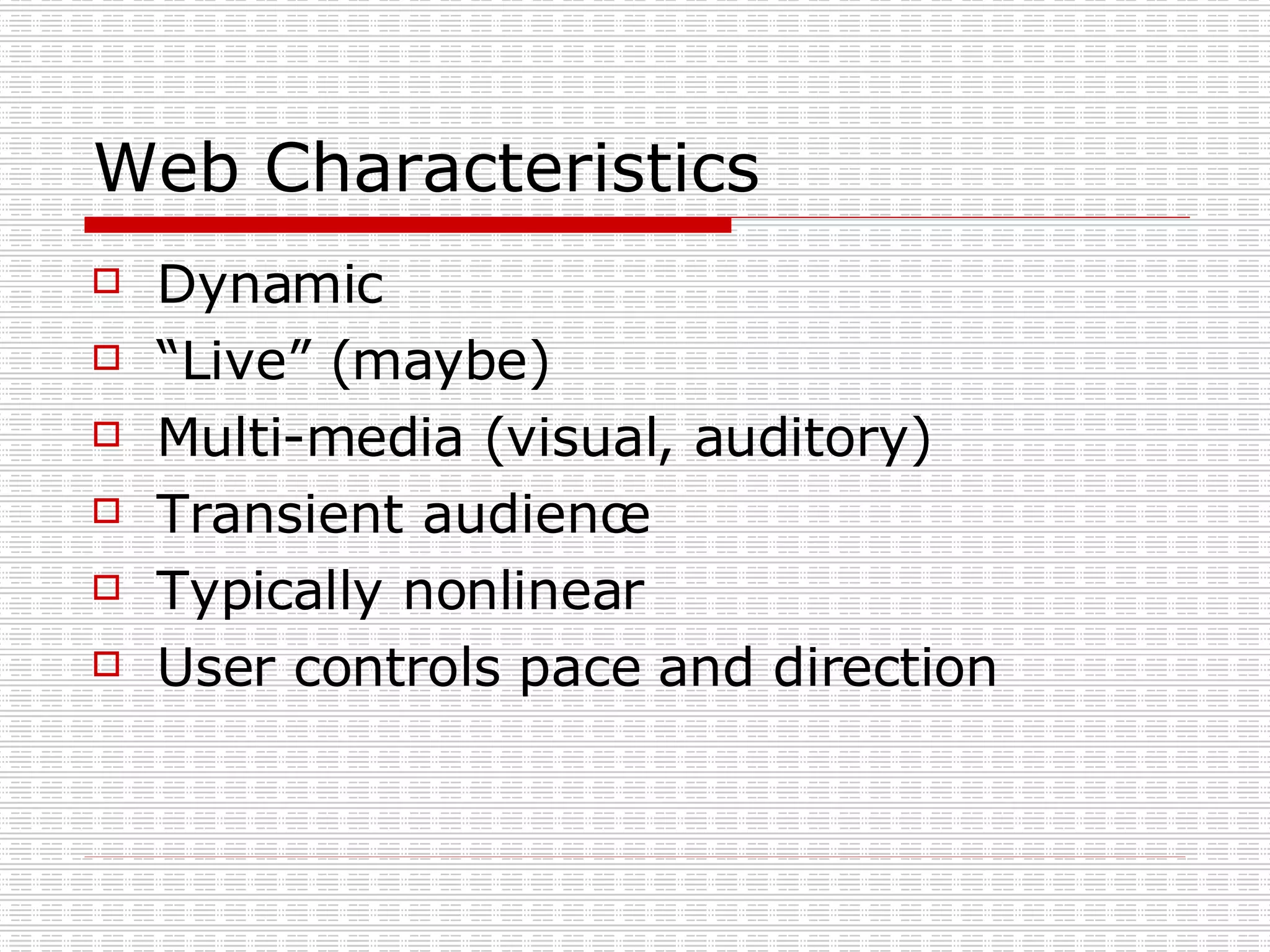
Mediated communication refers to communication that occurs through an intervening agent. New media technologies have changed communication by eliminating constraints of scarcity, time, and space. They allow for new communication channels like the world wide web, email, videoconferencing, and mobile phones. These channels share characteristics of being hardware independent, software independent, allowing information sharing, and giving users control over pace and direction.