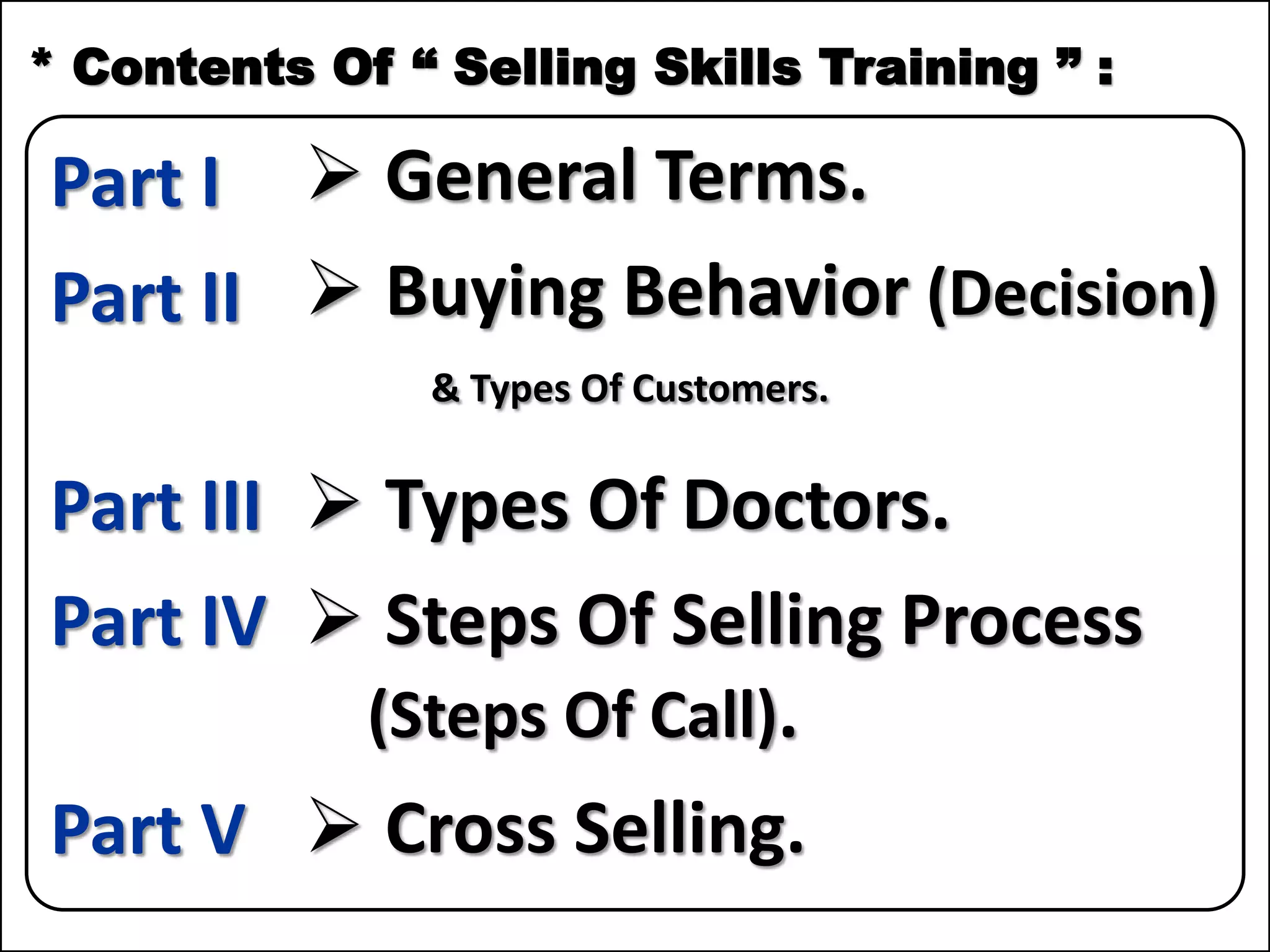
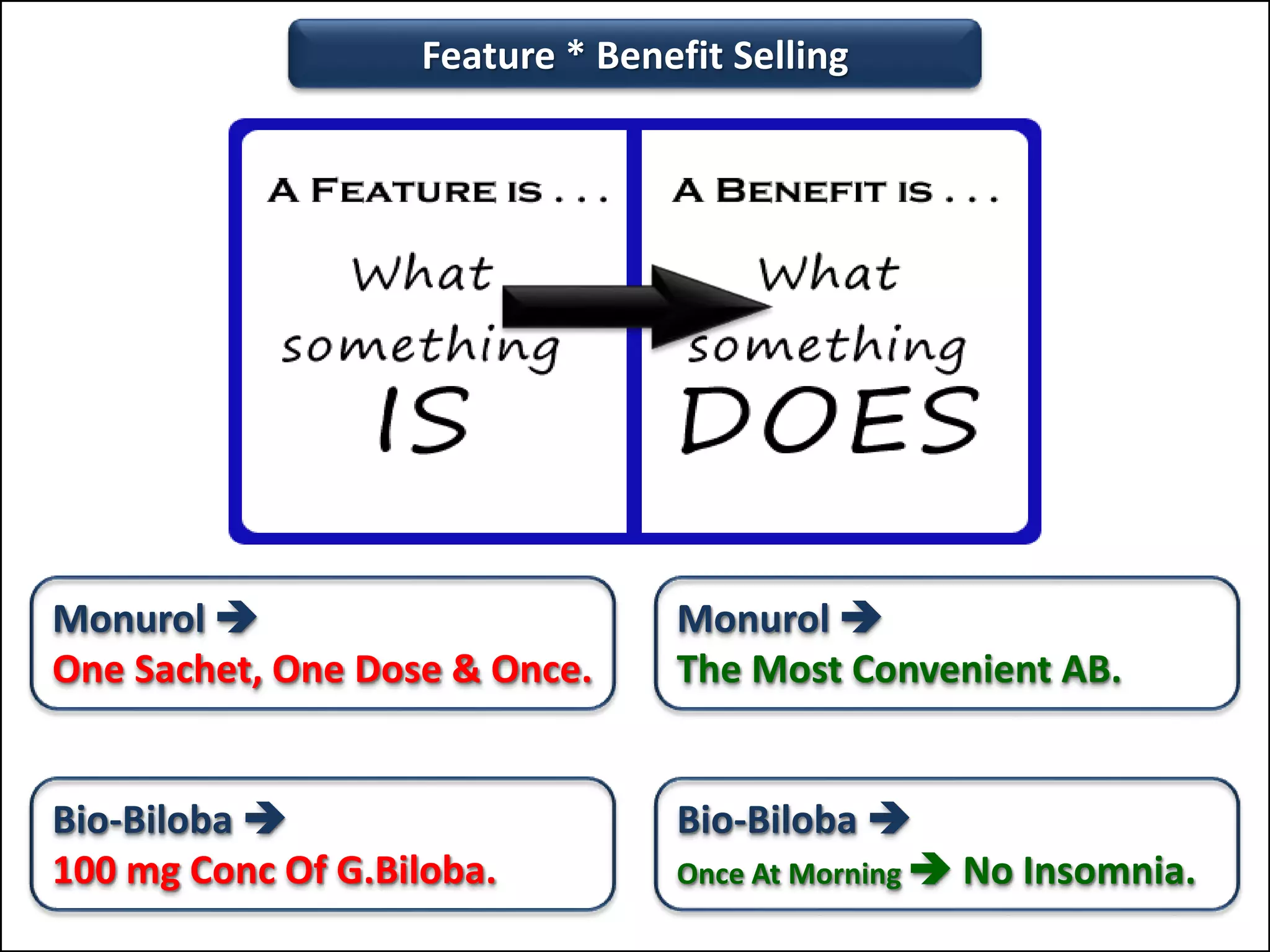
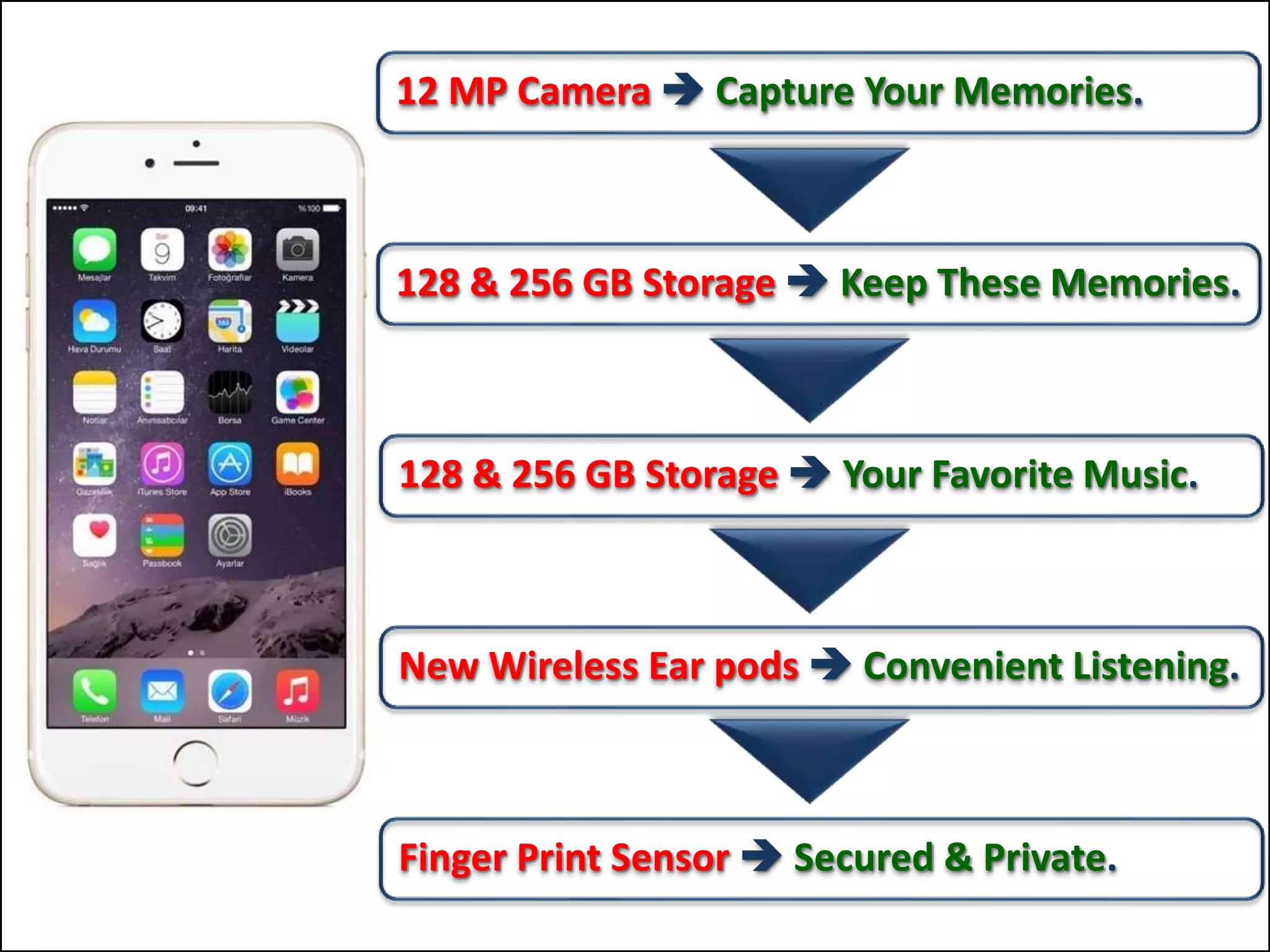
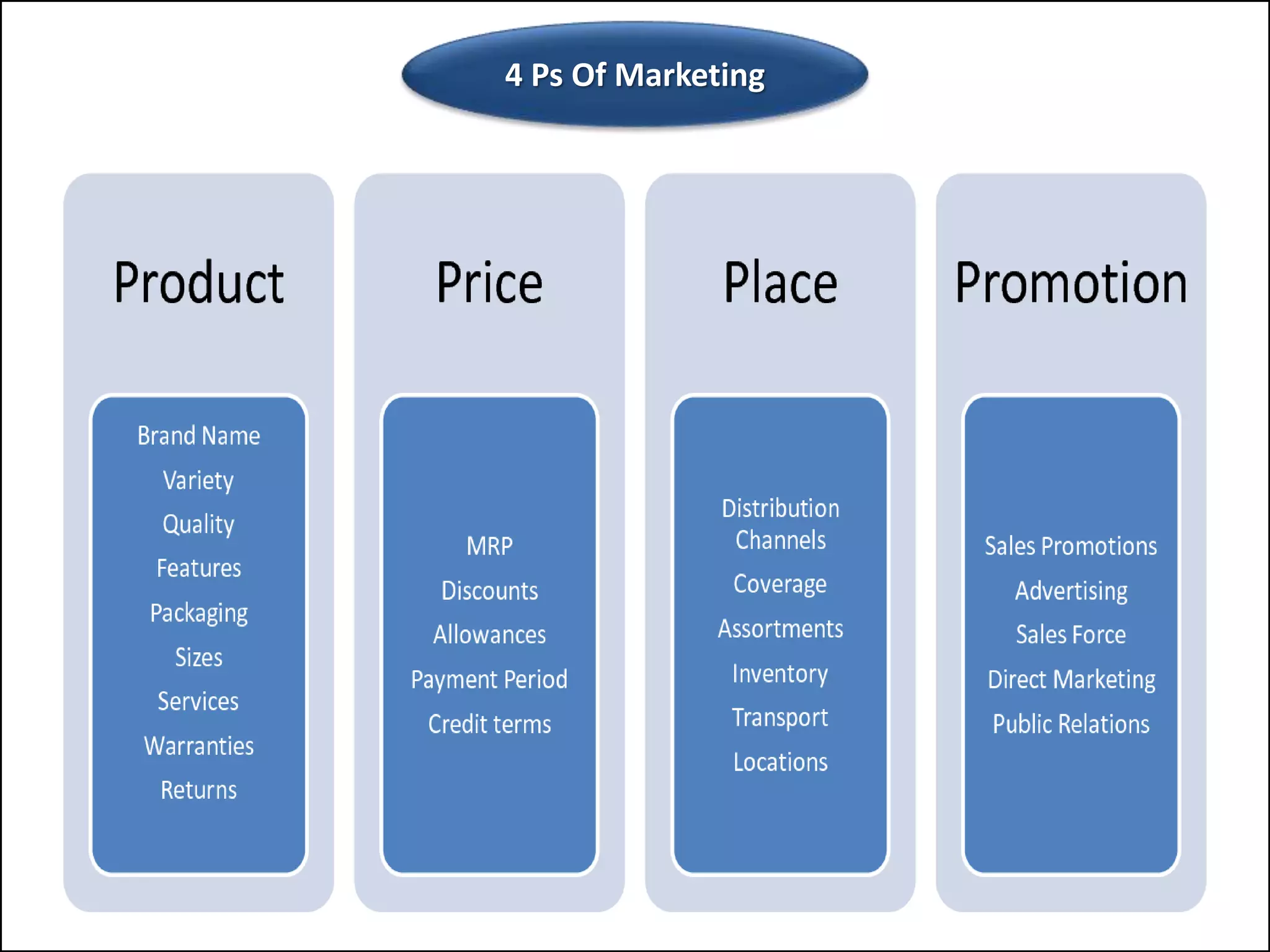
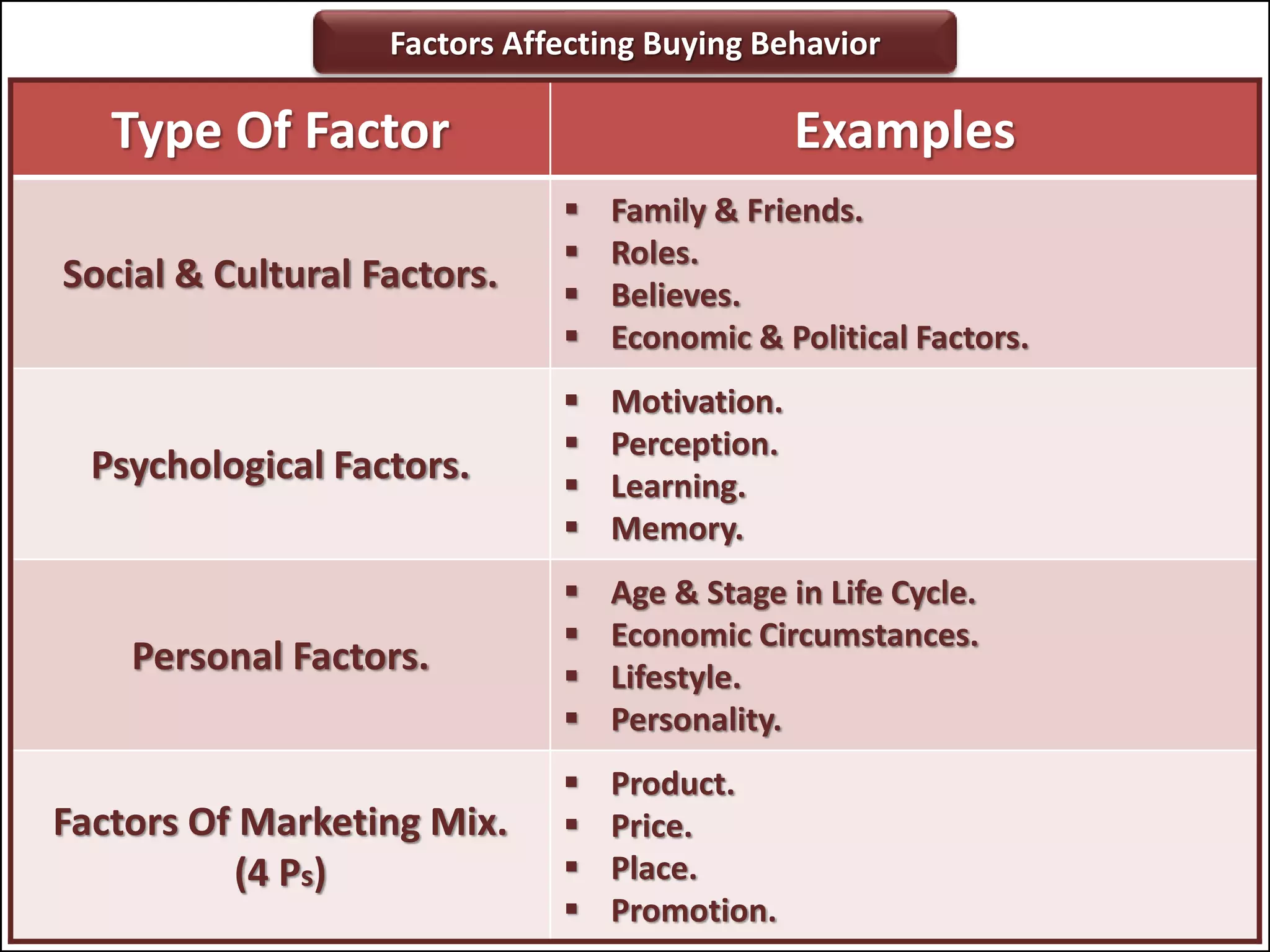
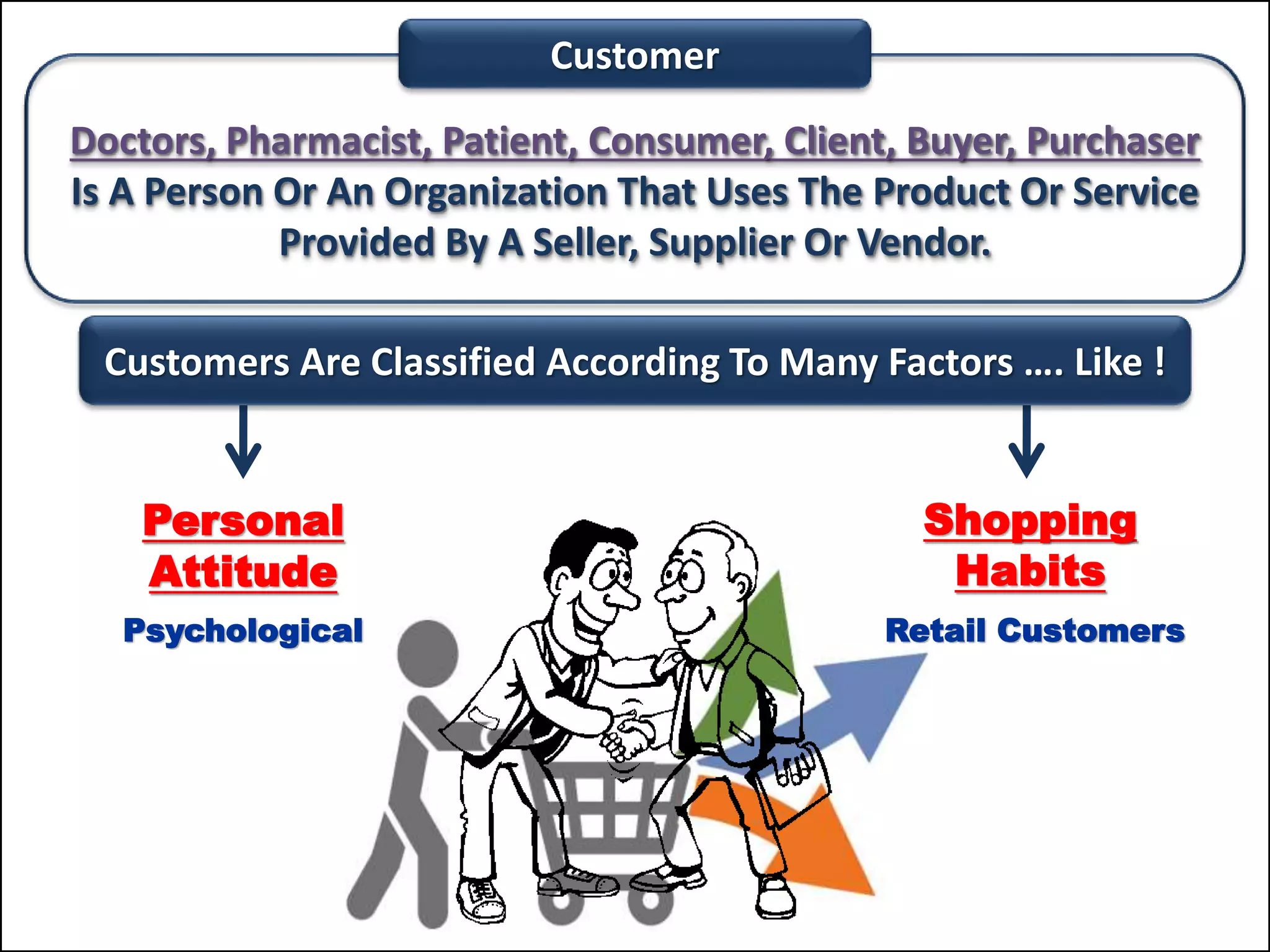
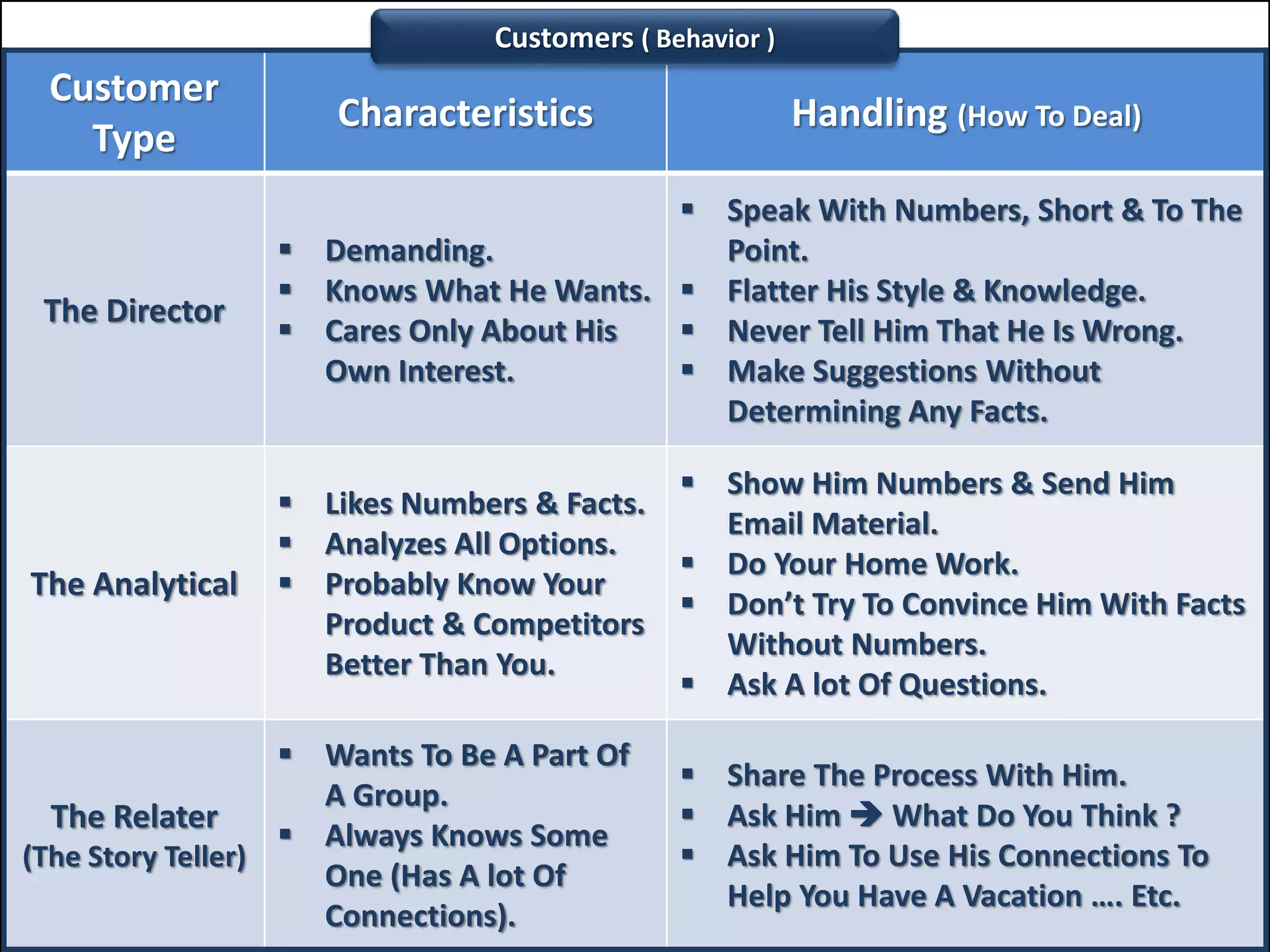
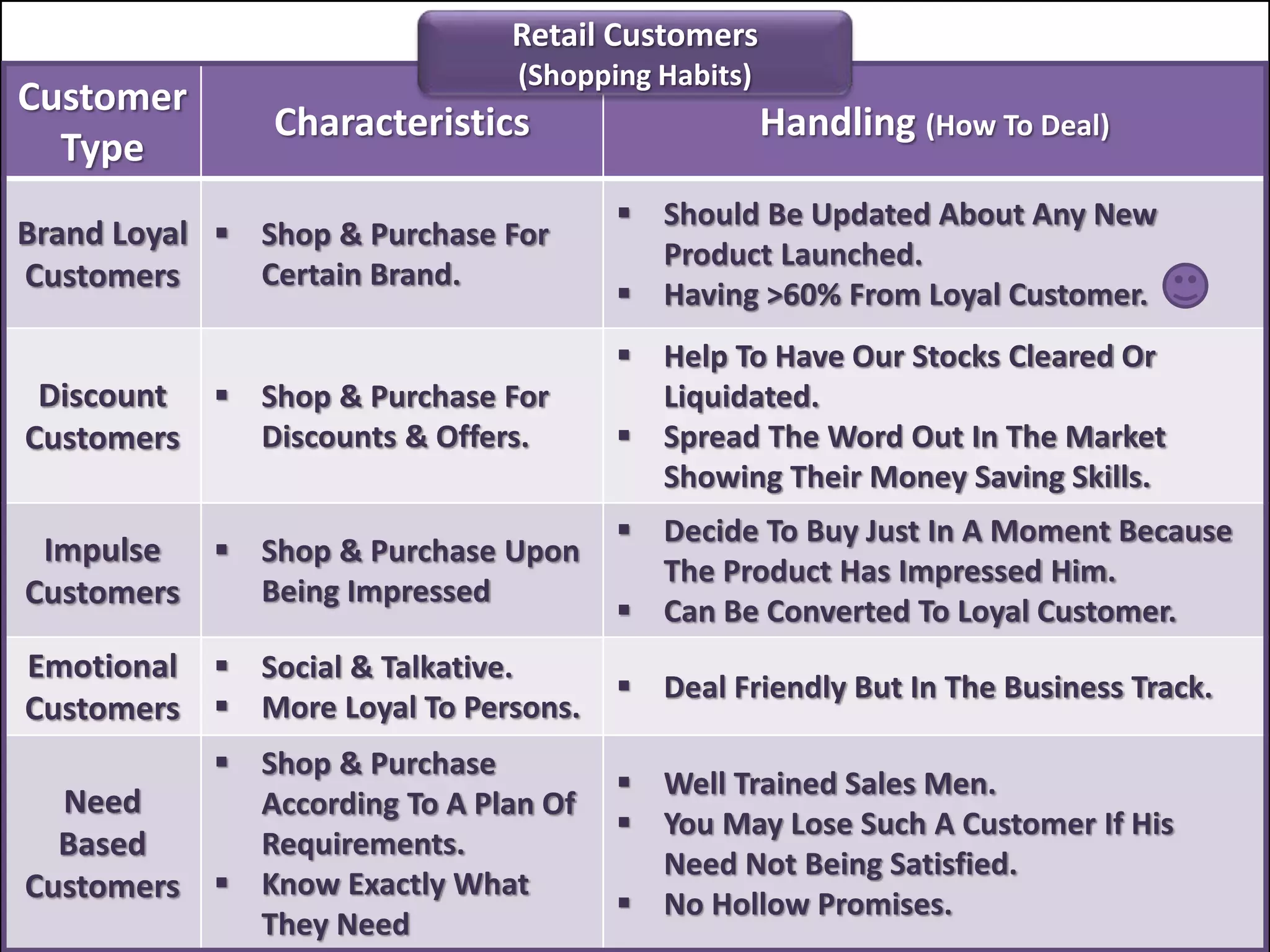
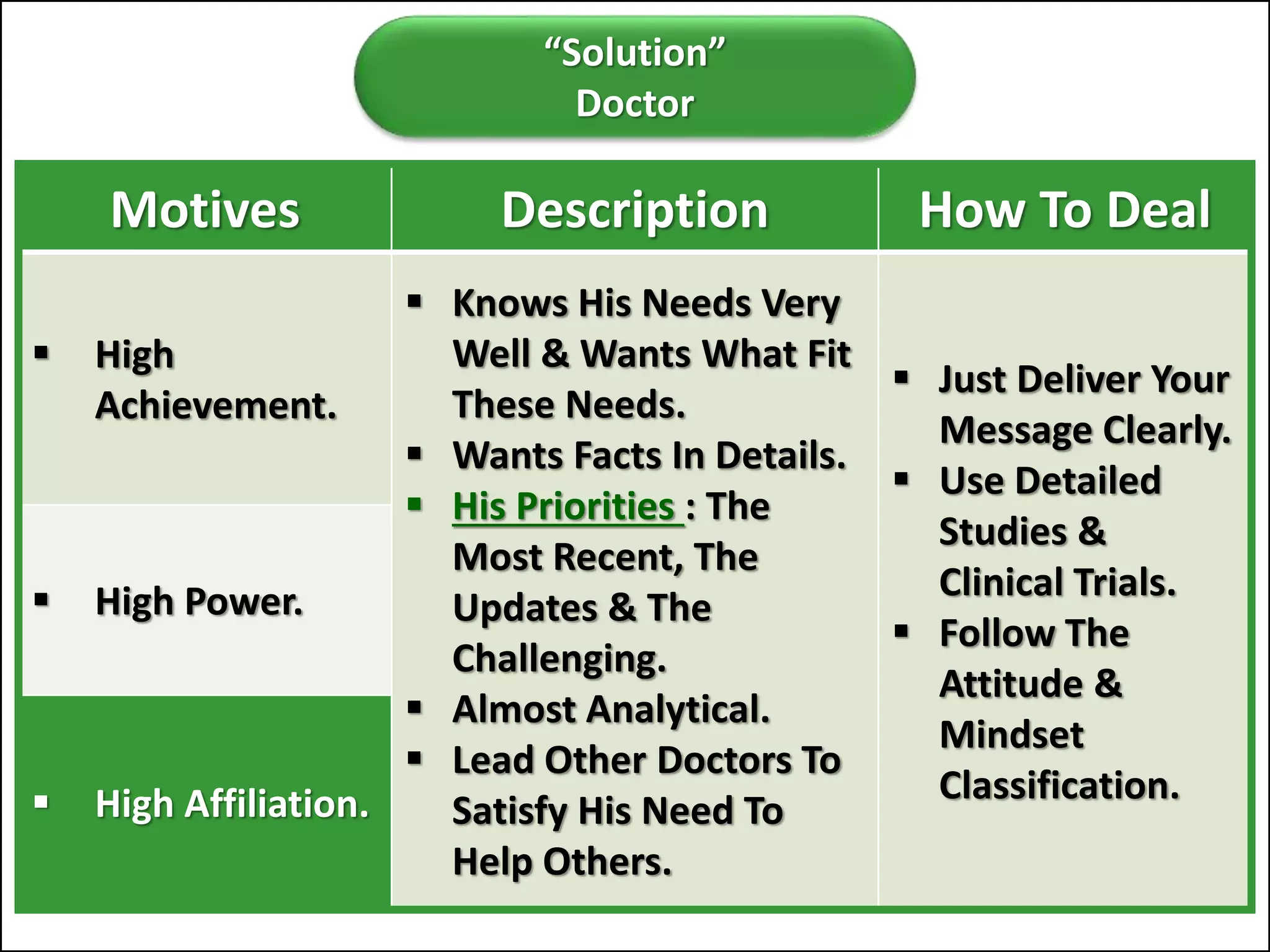
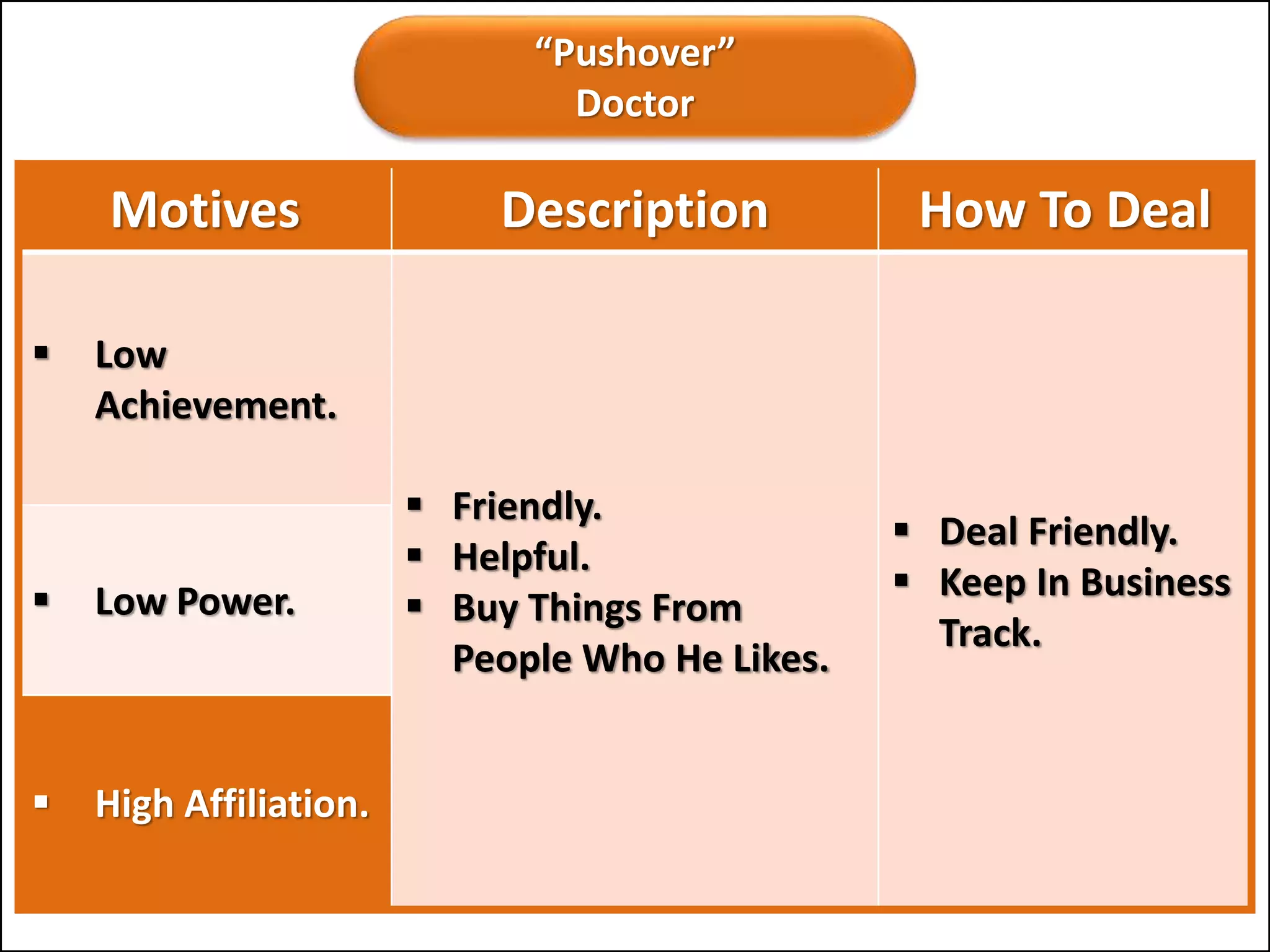
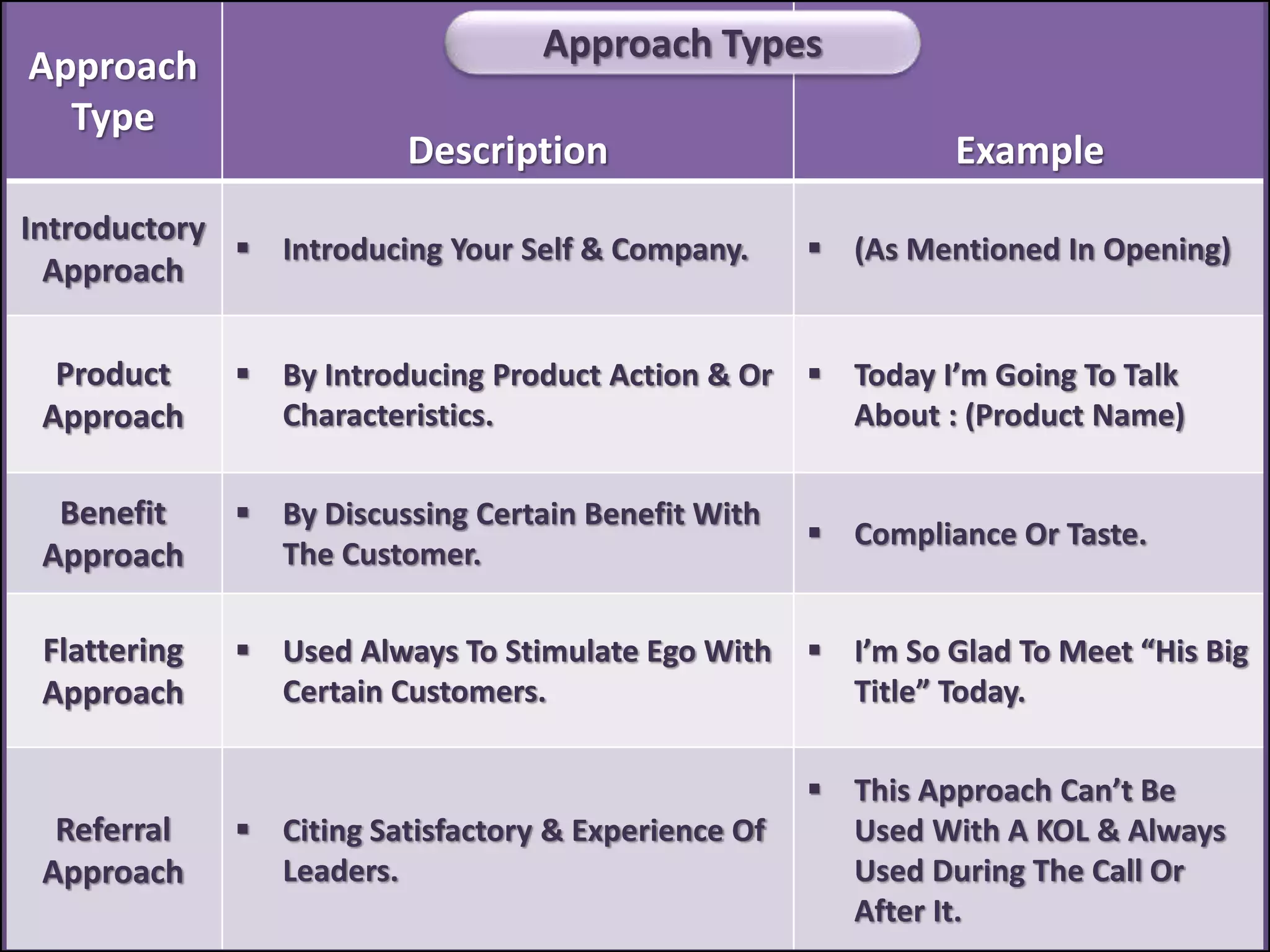
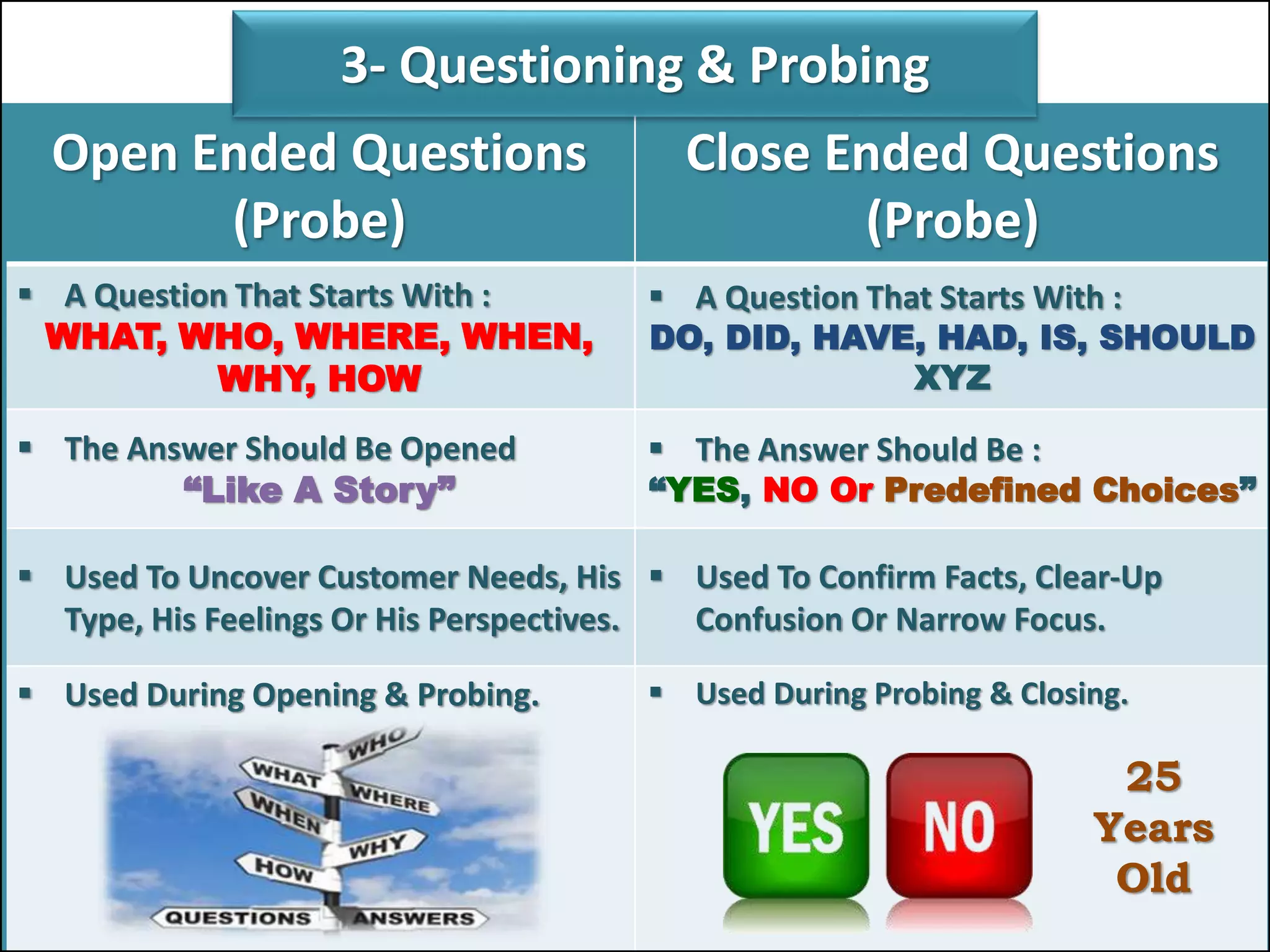
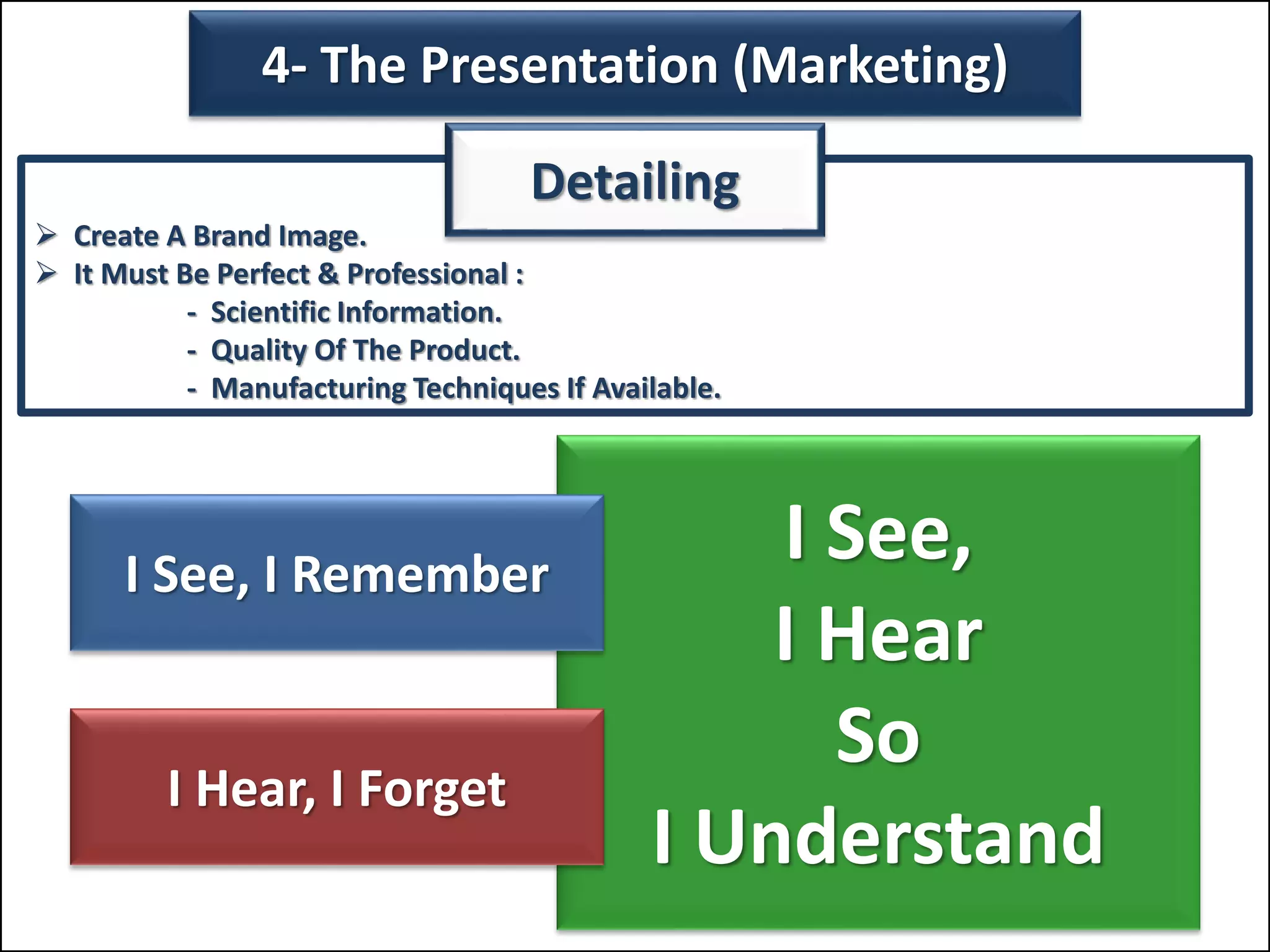
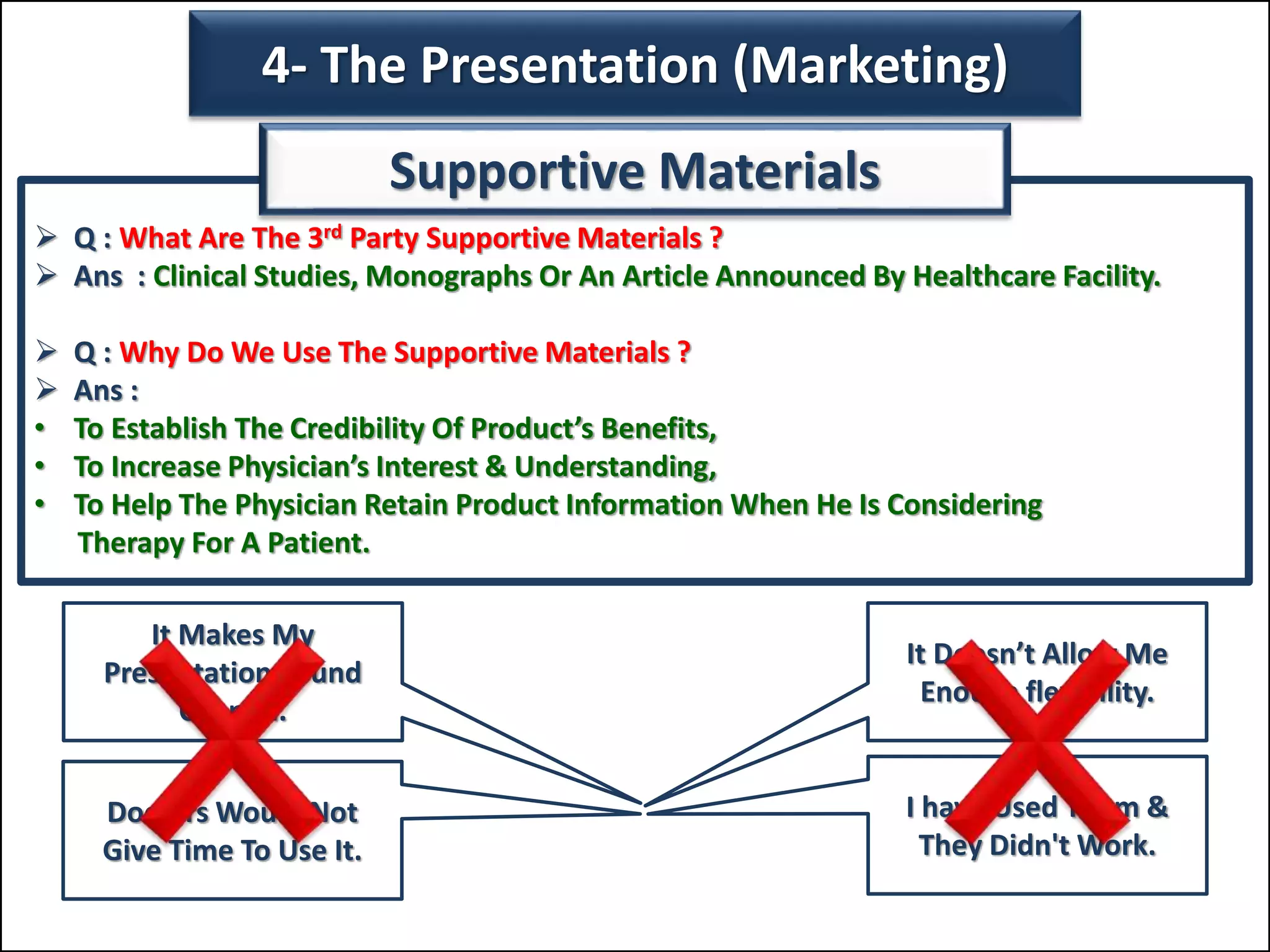
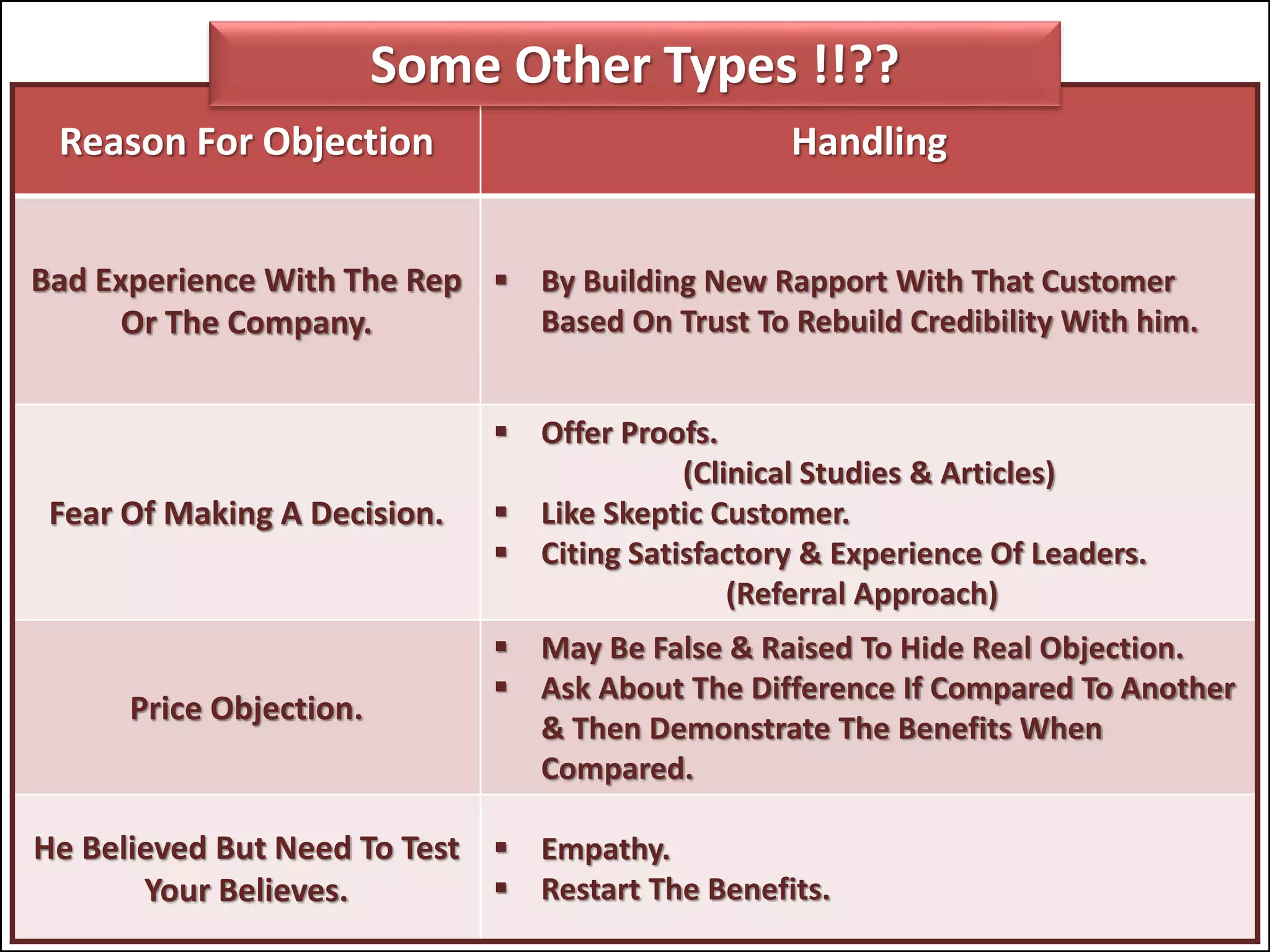
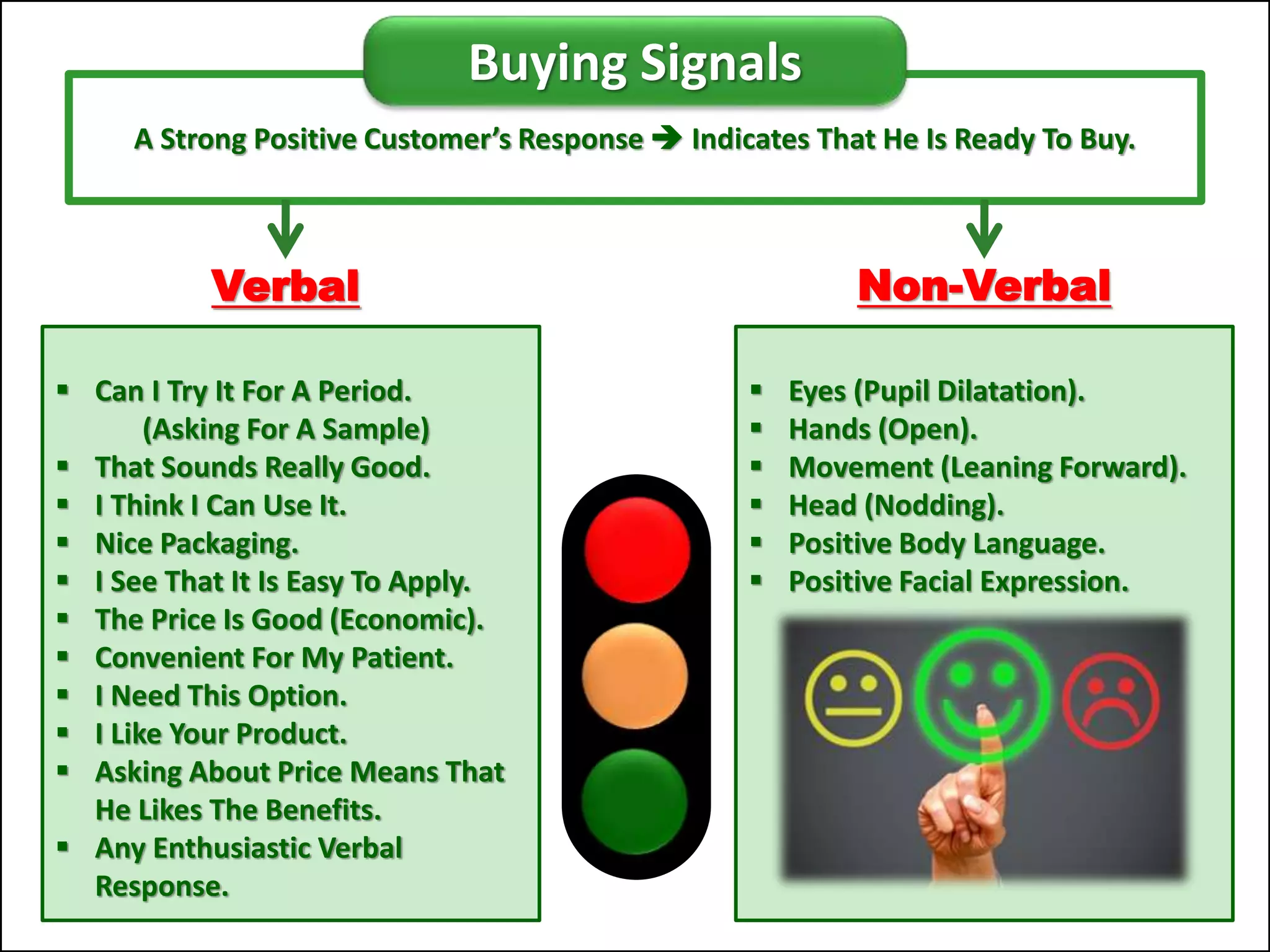
The document outlines a comprehensive training program aimed at enhancing selling skills and professionalism, focusing on various aspects of marketing and customer behavior. It covers essential topics like the selling process, types of customers, and effective communication strategies tailored to different customer profiles, especially in the medical field. Furthermore, it emphasizes understanding customer needs, identifying product benefits, and utilizing unique selling points to improve sales outcomes.