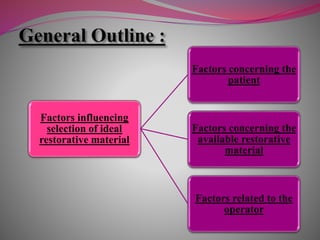
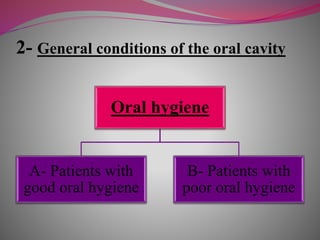
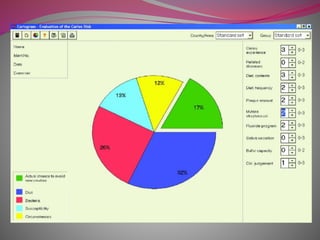
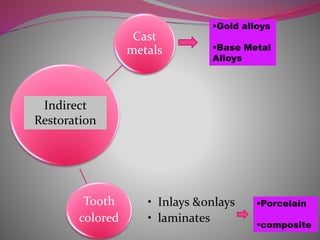
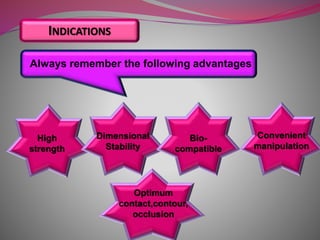
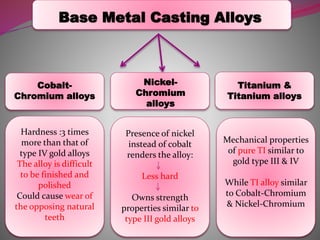
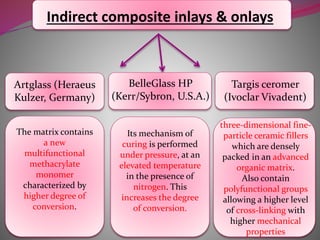
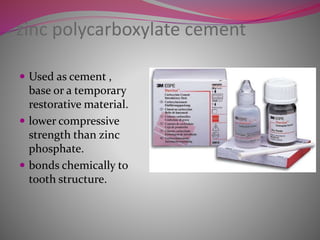
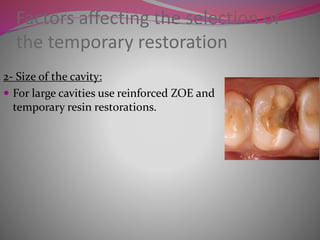
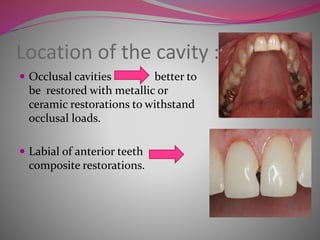
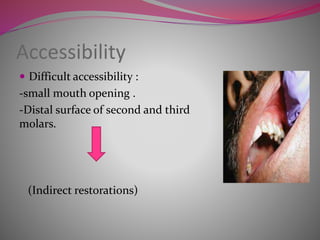
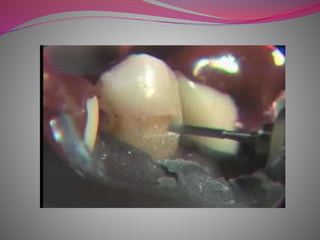
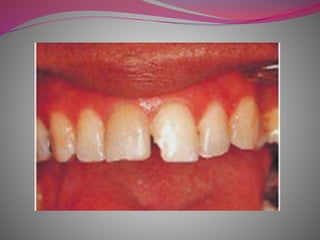
The document discusses factors to consider when selecting a restorative material. It covers factors related to the patient, such as medical history, oral hygiene and caries risk. It also discusses tooth-related factors like position, mobility and remaining structure. Material-related factors include the advantages and disadvantages of different direct and indirect options like amalgam, composite, glass ionomer and cast metals. Proper selection depends on balancing the clinical situation and material properties.