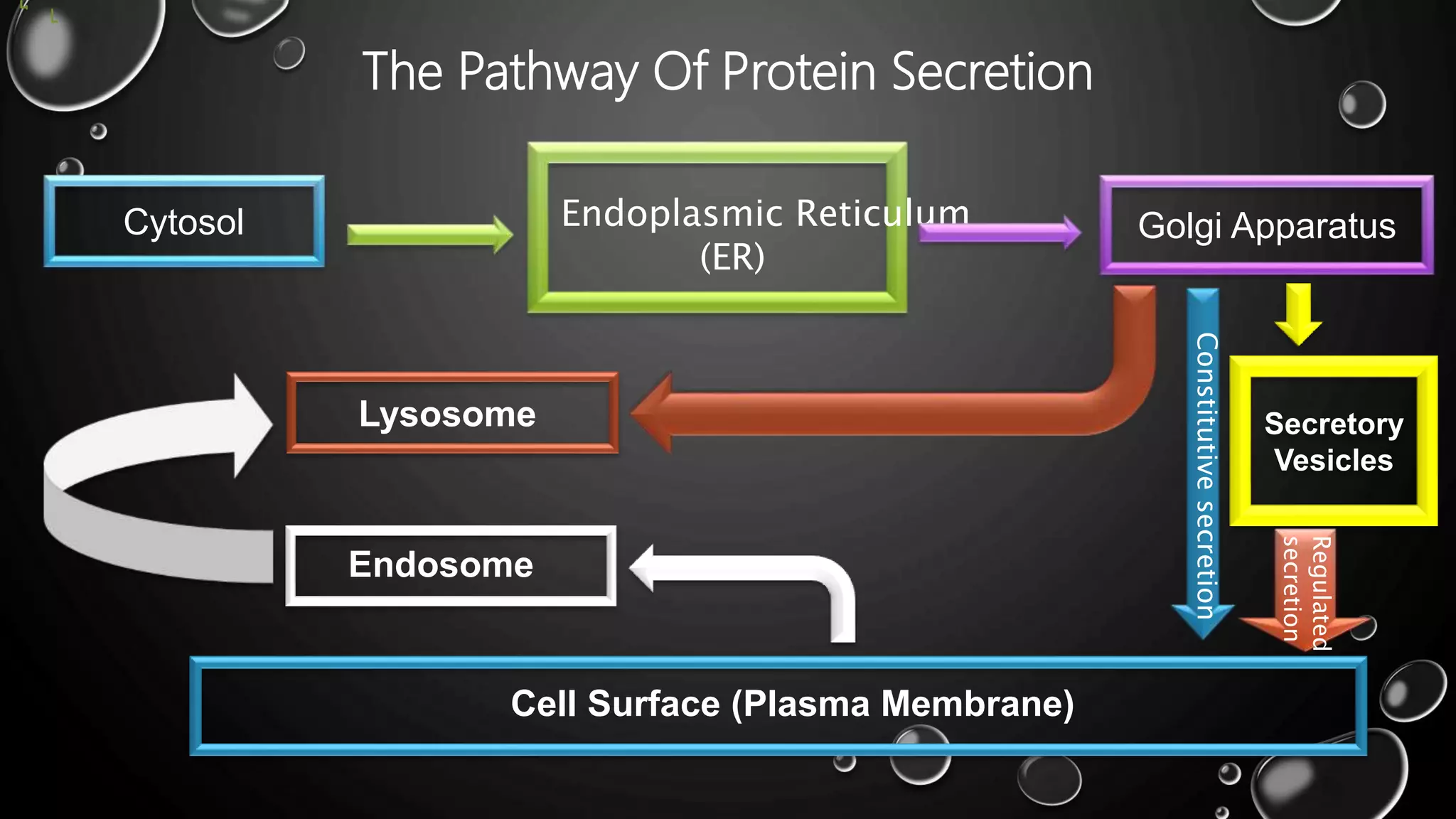
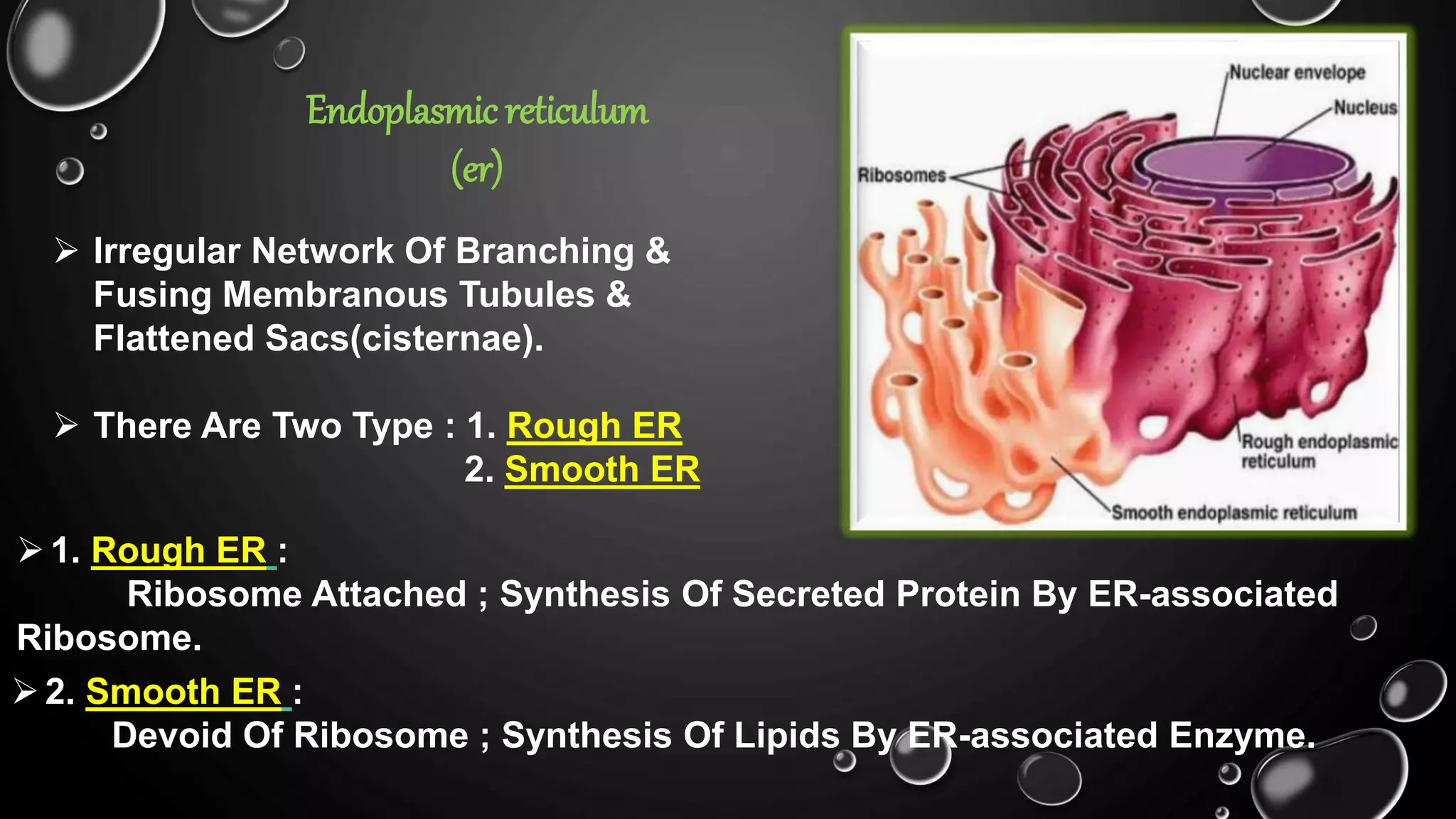
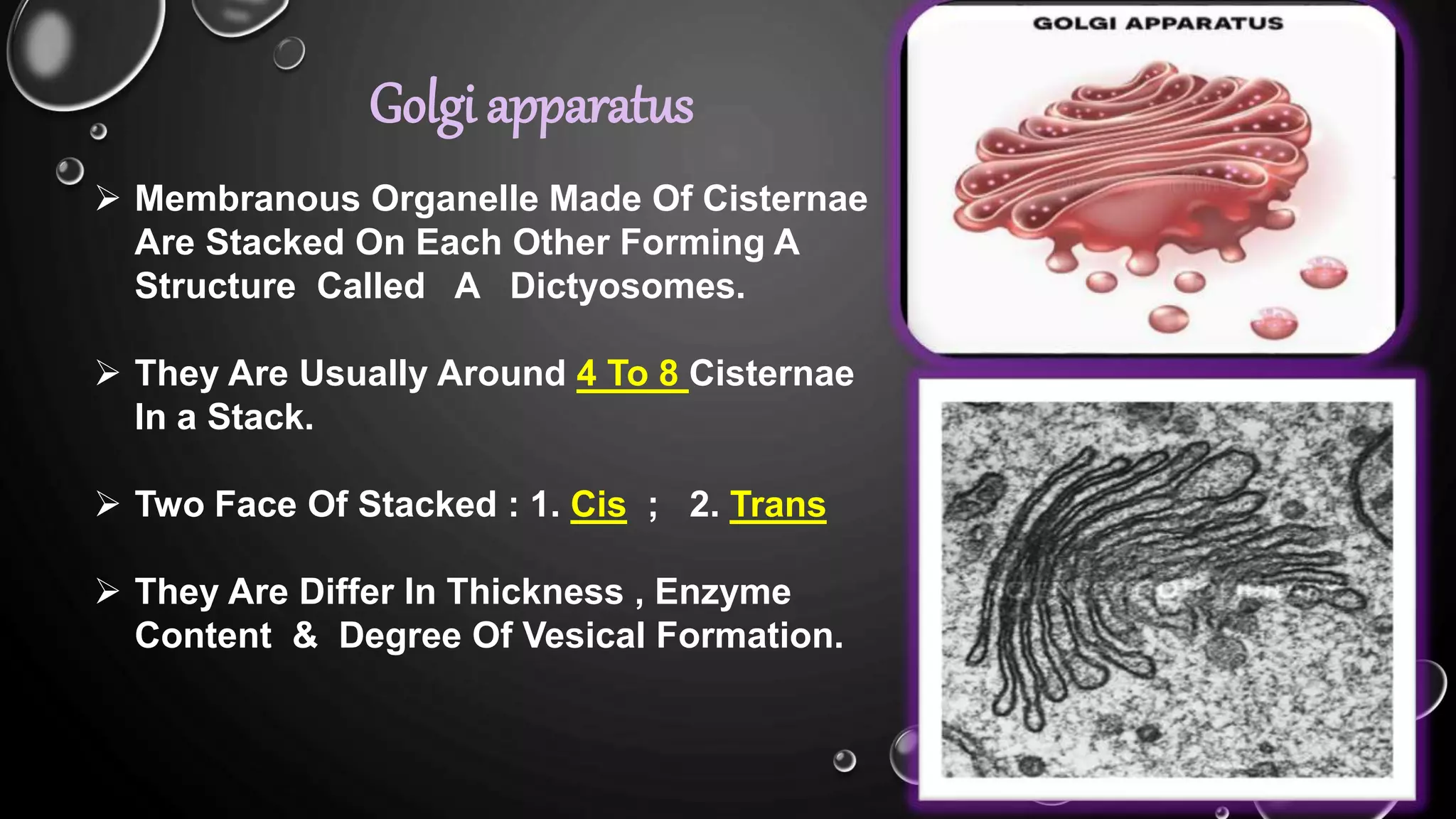
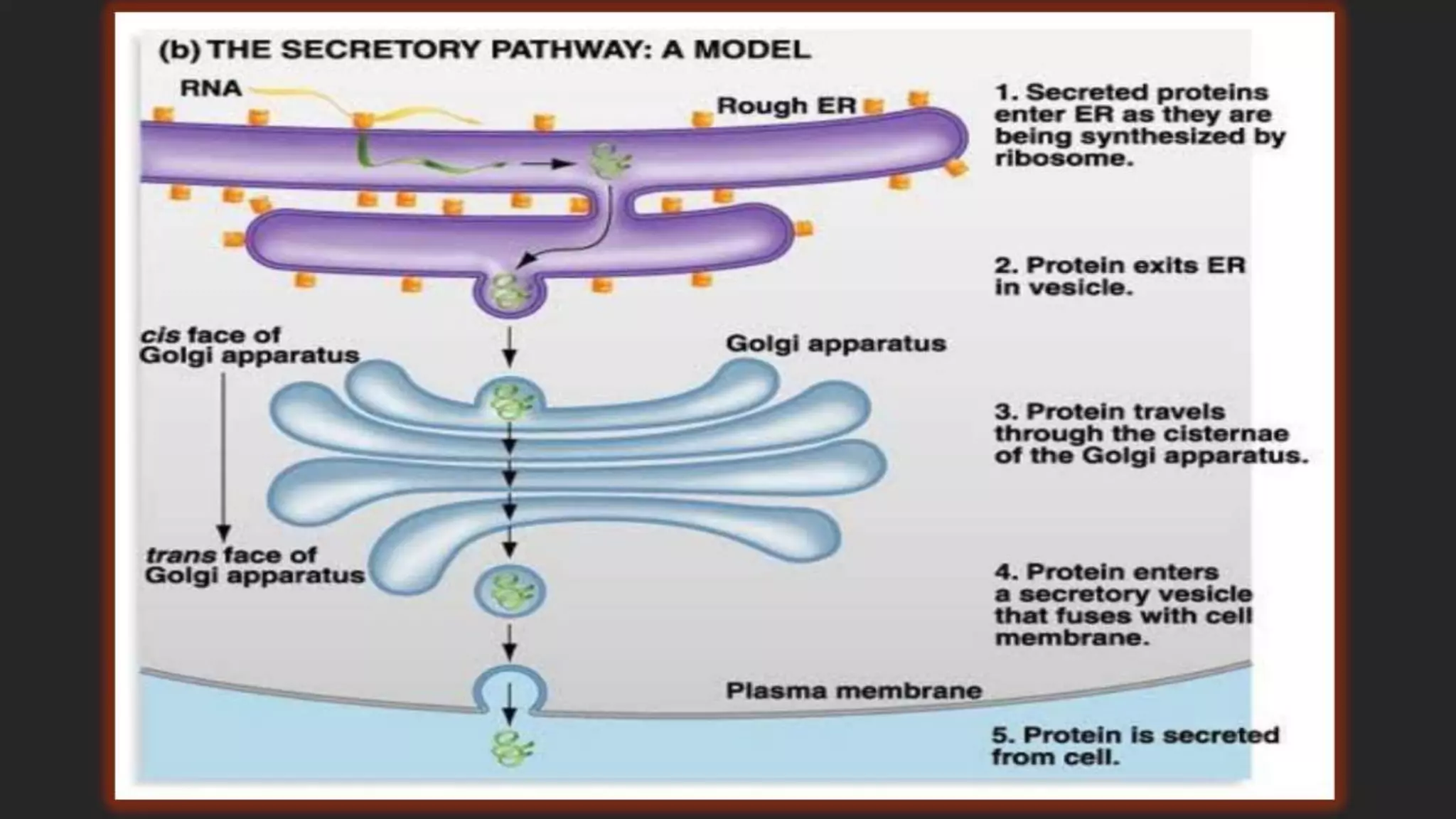
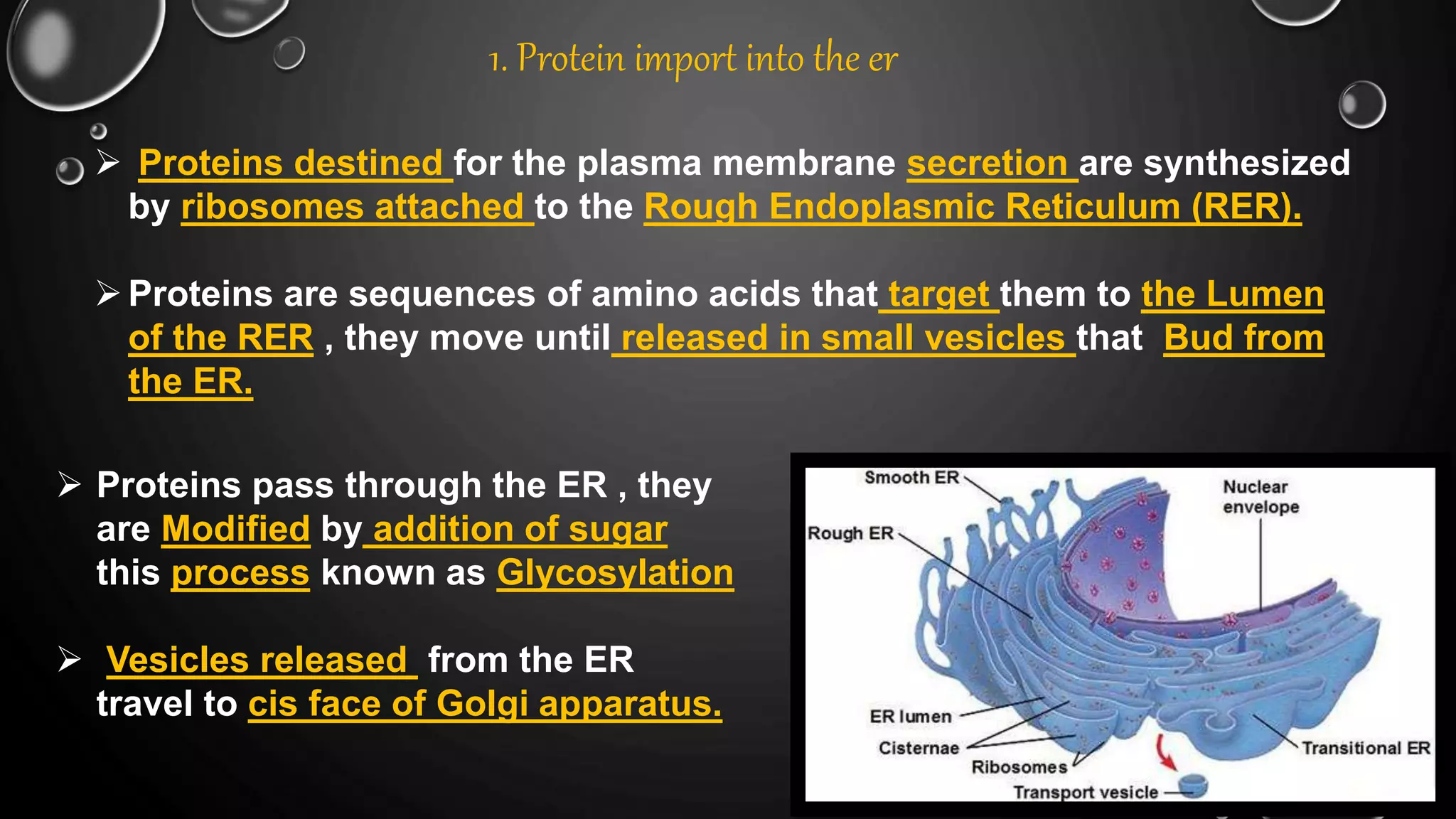
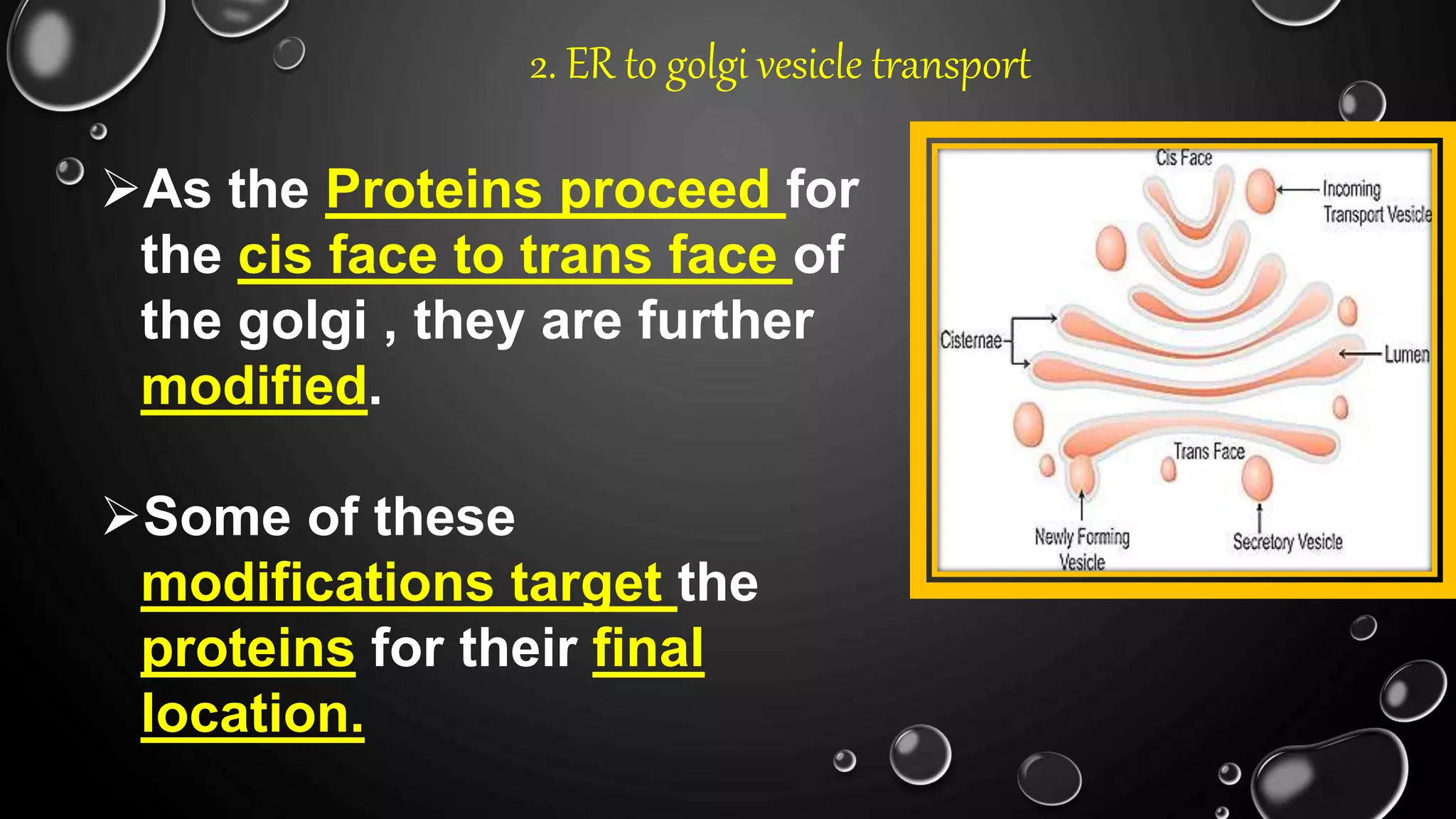
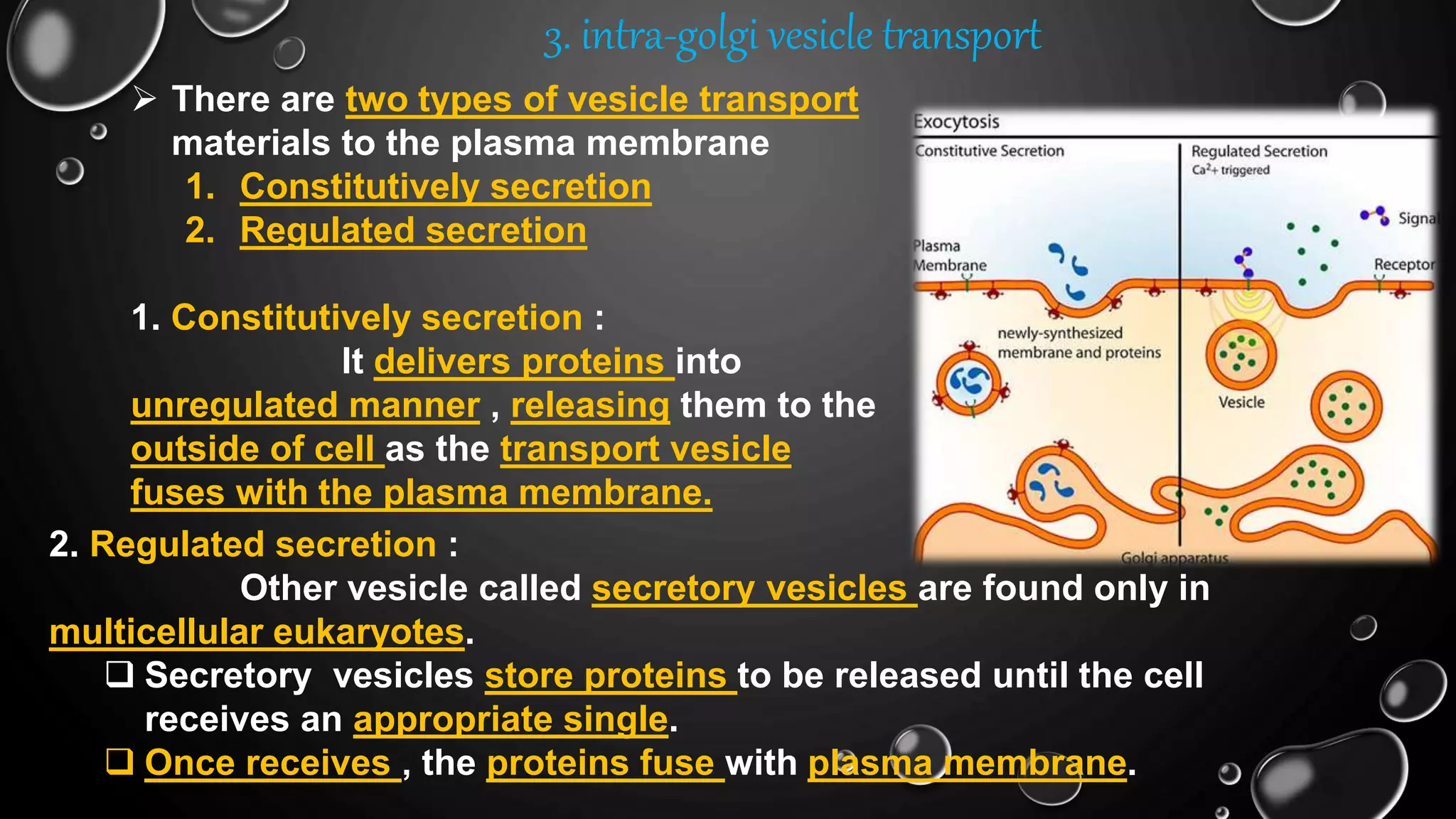
The secretory pathway is the series of steps a cell uses to move proteins from where they are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum out of the cell. There are four main steps: 1) proteins are synthesized and modified in the ER, 2) vesicles bud off from the ER and deliver proteins to the Golgi apparatus, 3) proteins undergo further modification as they are transported between cisternae within the Golgi apparatus, and 4) proteins are packaged into vesicles for transport to their final destination, either to lysosomes for degradation or to the cell surface for secretion or insertion into the plasma membrane. The secretory pathway also has quality control mechanisms to retain and degrade any misfolded proteins.