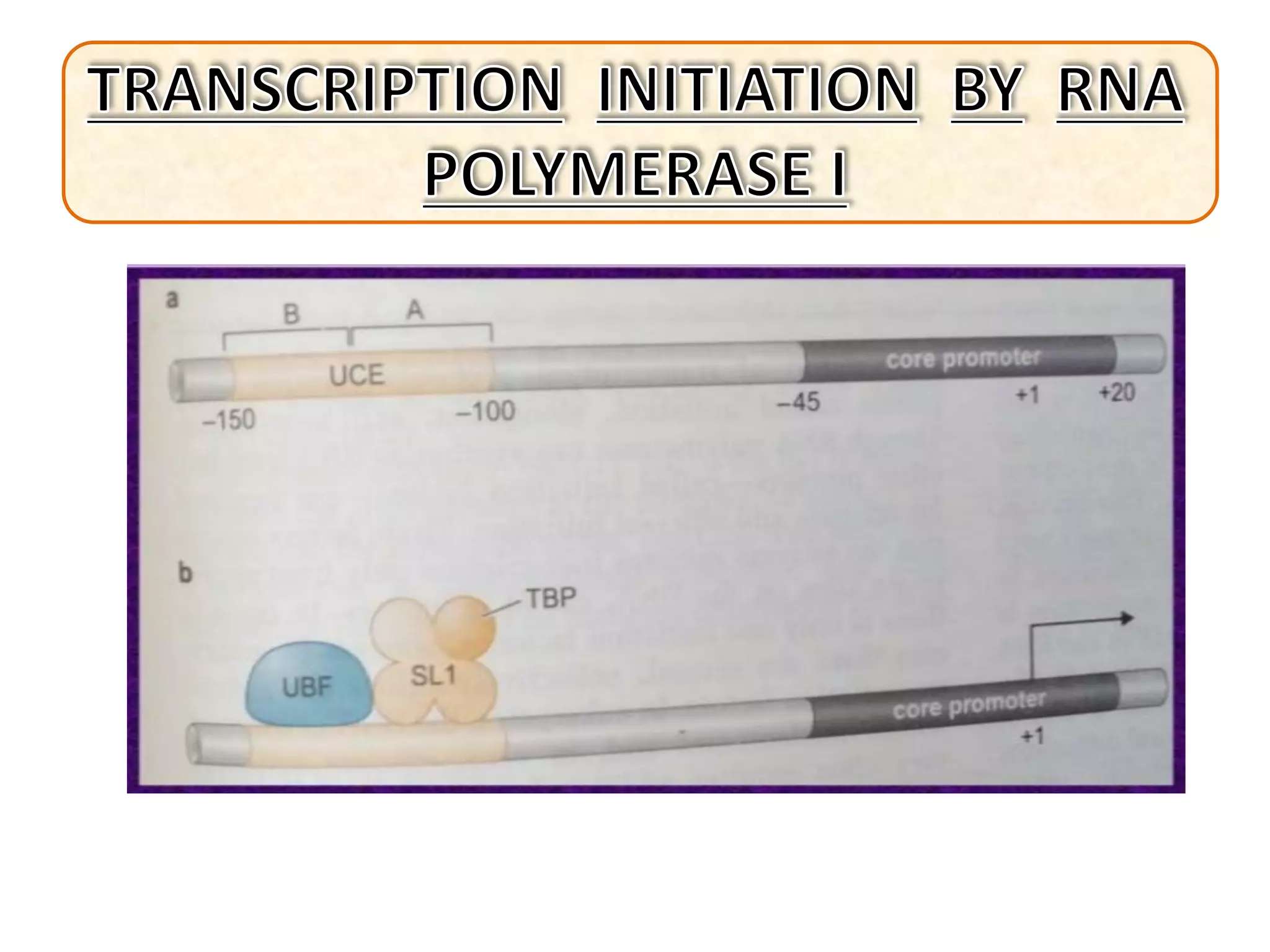
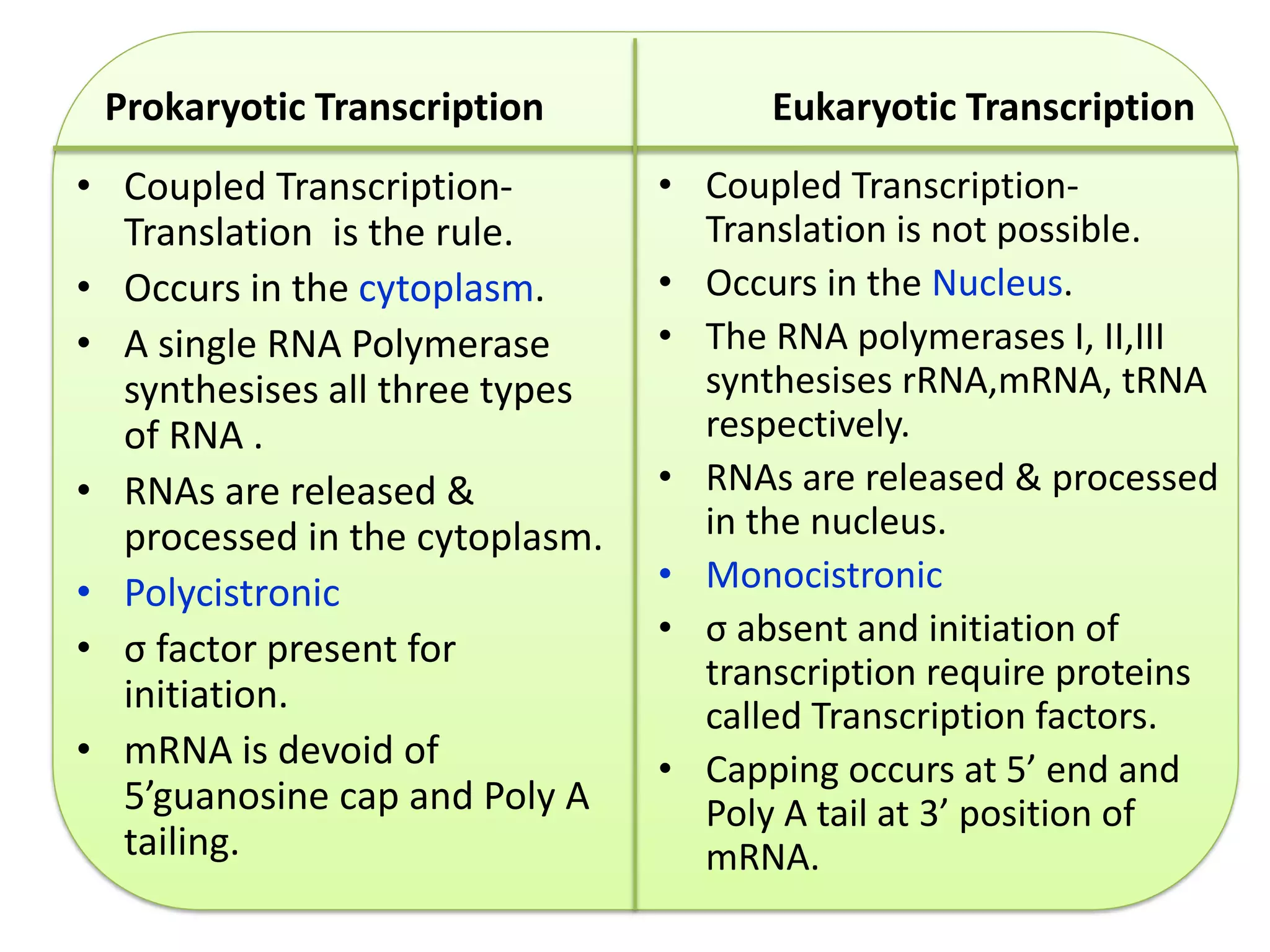
Transcription in eukaryotes is carried out by three RNA polymerases that synthesize different RNA molecules. RNA polymerase II initiates transcription through assembly of general transcription factors and a mediator complex at DNA promoter sequences. Initiation is followed by elongation and termination steps. Additional factors are required at each step to facilitate efficient transcription. The resulting RNA transcripts undergo processing including capping, polyadenylation, and export from the nucleus. Prokaryotic transcription differs in that it occurs in the cytoplasm and involves a single RNA polymerase, while eukaryotic transcription takes place in the nucleus and requires multiple RNA polymerases and transcription factors.