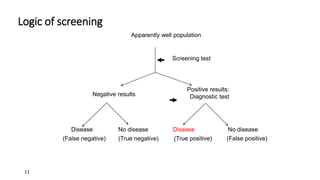
Screening tests are used to identify individuals at risk for a disease who are apparently well, sorting them from those who do not have risk factors. The main elements of an effective screening program are that it targets a disease with significant burden and effective treatment, uses a valid, precise, low-cost and low-risk screening test, and screens a population with high disease prevalence and compliance with follow-up testing and treatment. Examples of common screening tests include mammography, fecal occult blood tests, and Pap smears. Screening can be mass screening of all individuals or selective based on factors like age and sex. The goal of screening is to diagnose disease earlier through a series of tests.