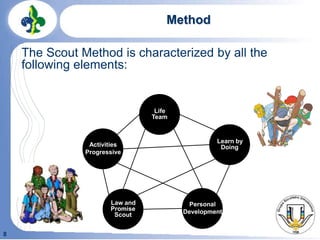
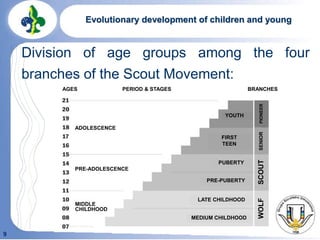
Robert Baden-Powell founded the scouting movement after holding an experimental camp on Brownsea Island in 1907. Scouting aims to help young people develop physically, intellectually, socially, emotionally and spiritually through activities, a progressive program, and teamwork according to the Scout Law and Promise. Scouting is divided into branches for different age groups including Wolf Cubs, Scouts, and Senior Scouts. Scouts greet each other with specific handshakes and insignia represent their progression through the branches.