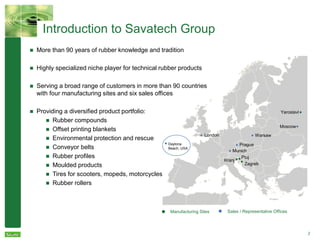
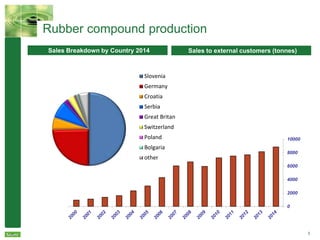
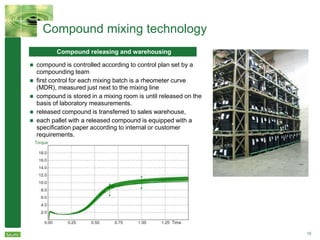
Savatech Group is a highly specialized rubber compound manufacturer with over 90 years of experience. It has four manufacturing sites and six sales offices serving customers in over 90 countries. The document discusses Savatech's product range including rubber compounds, their market position as a leading supplier in Slovenia and the Balkans, and their strengths in R&D and quality management systems to meet customer requirements. Savatech has a history dating back to 1920 and has undergone ownership changes over the decades to become part of the CGS Group in 2013.