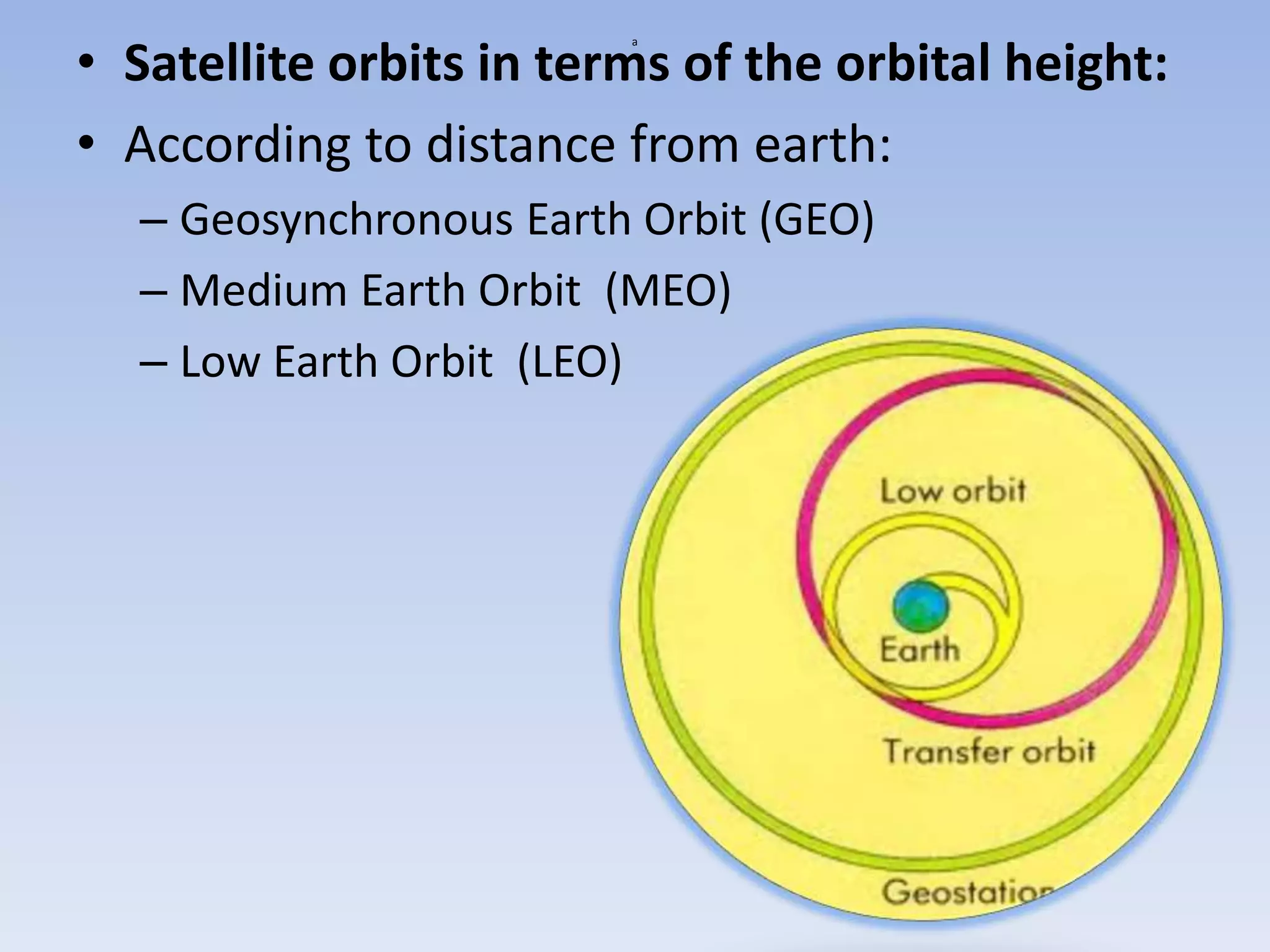
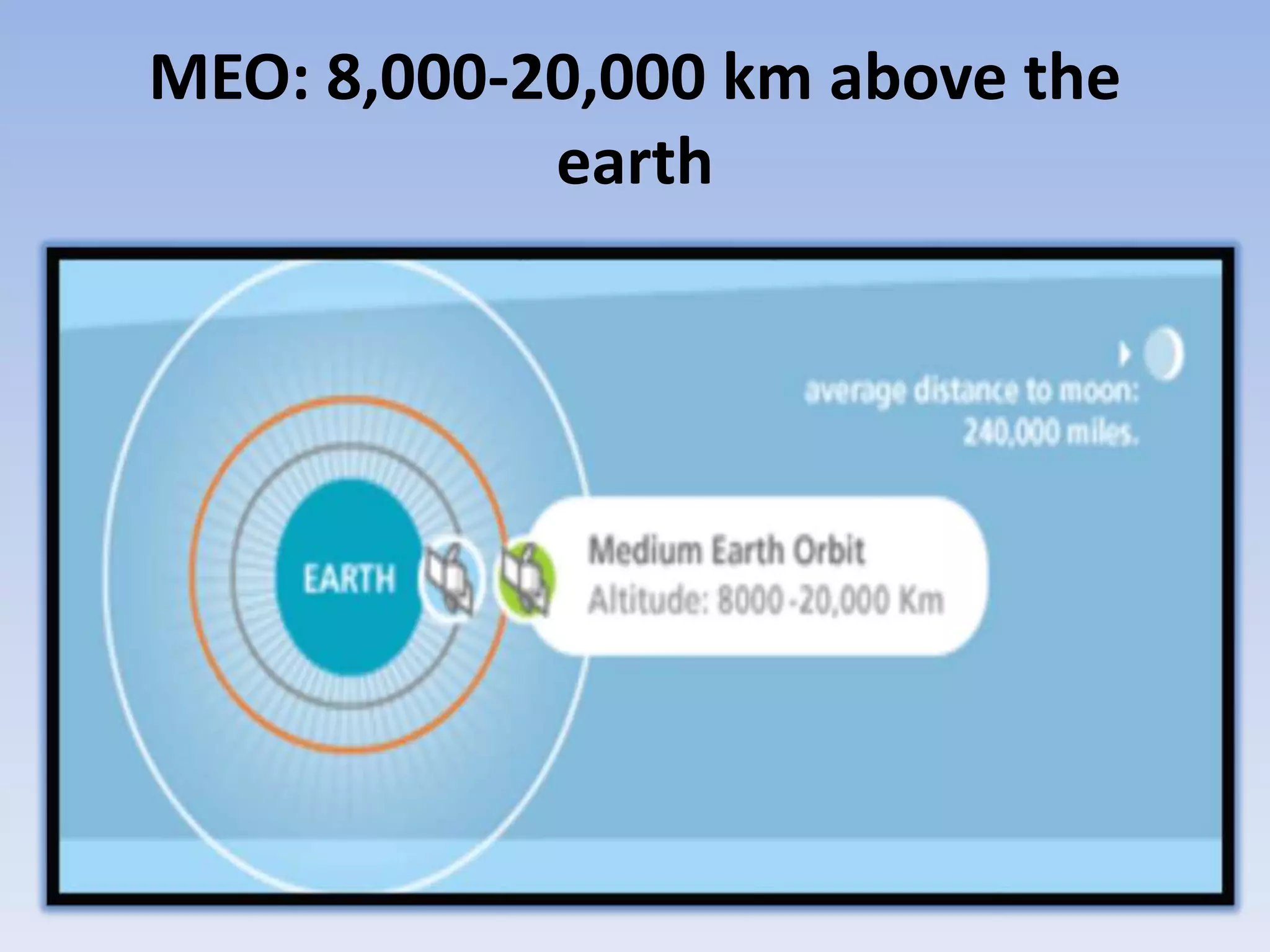
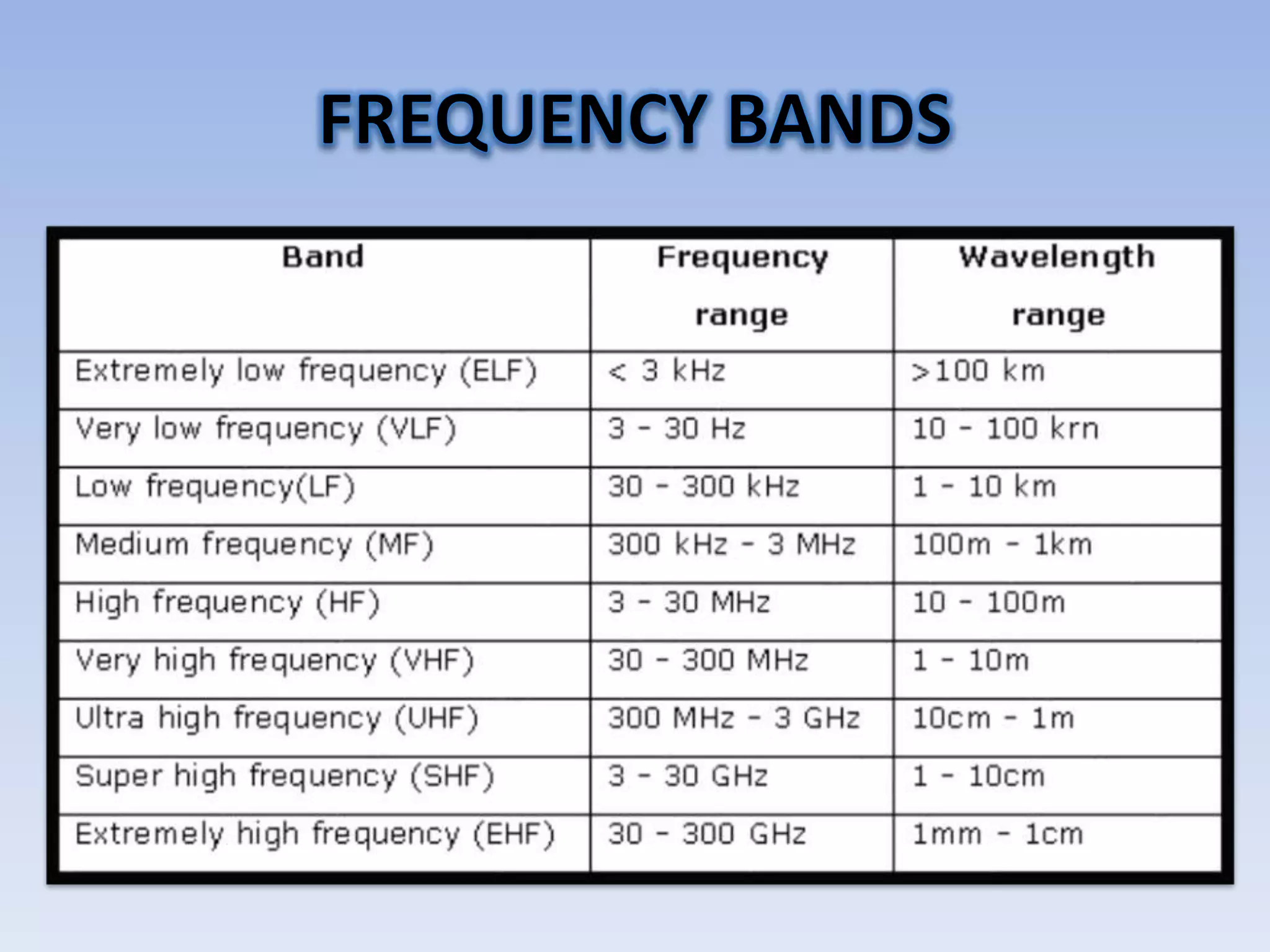
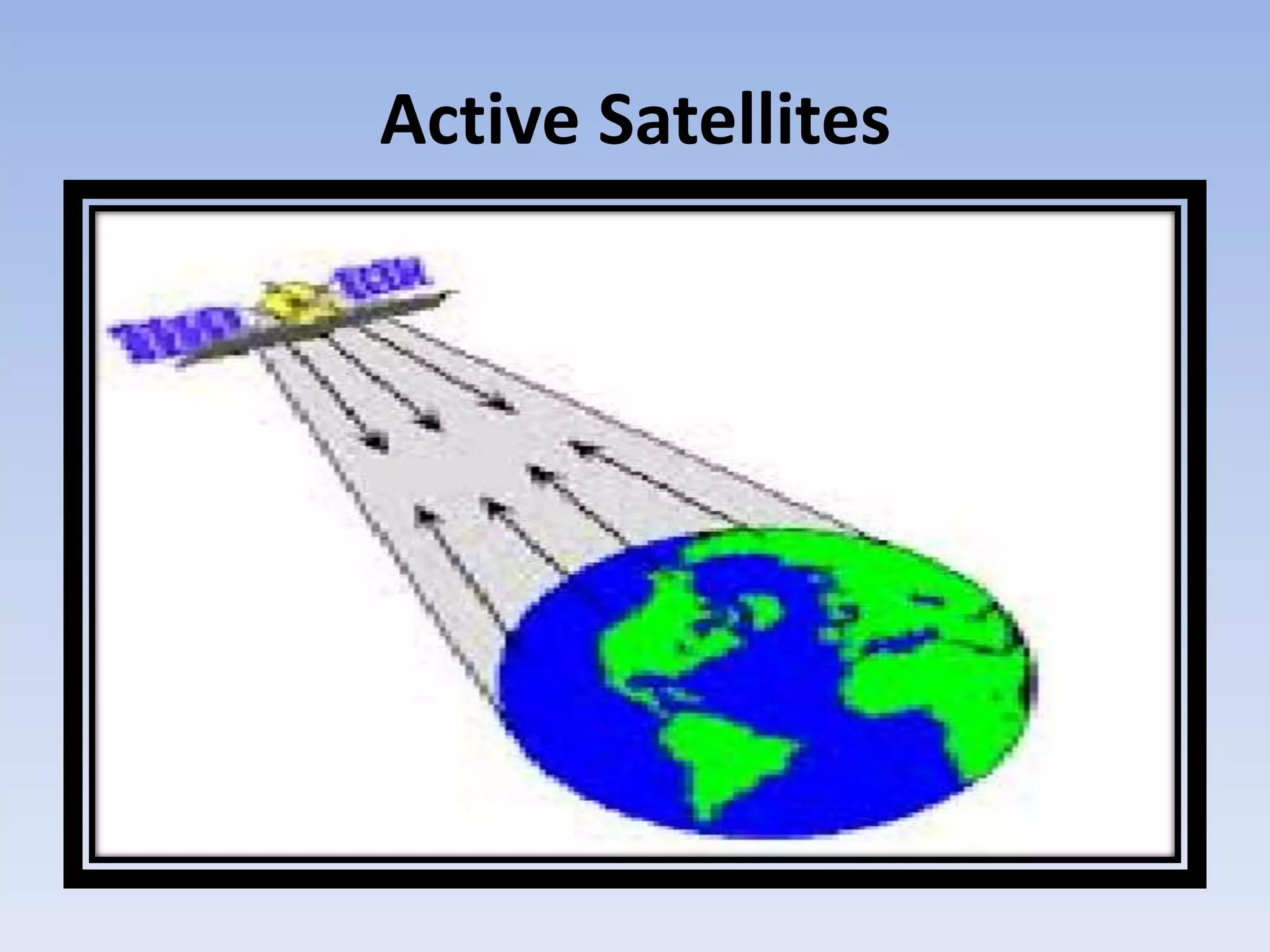
Satellite communication uses satellites in orbit above the Earth to relay analog and digital signals between ground stations. There are about 750 communication satellites currently in orbit. Satellites can provide wide area coverage of the Earth's surface and transmission costs are independent of distance. Satellites are classified based on their orbit, with geostationary orbits providing constant coverage of one location on Earth. Active satellites amplify and retransmit signals, replacing earlier passive satellites that only reflected signals.