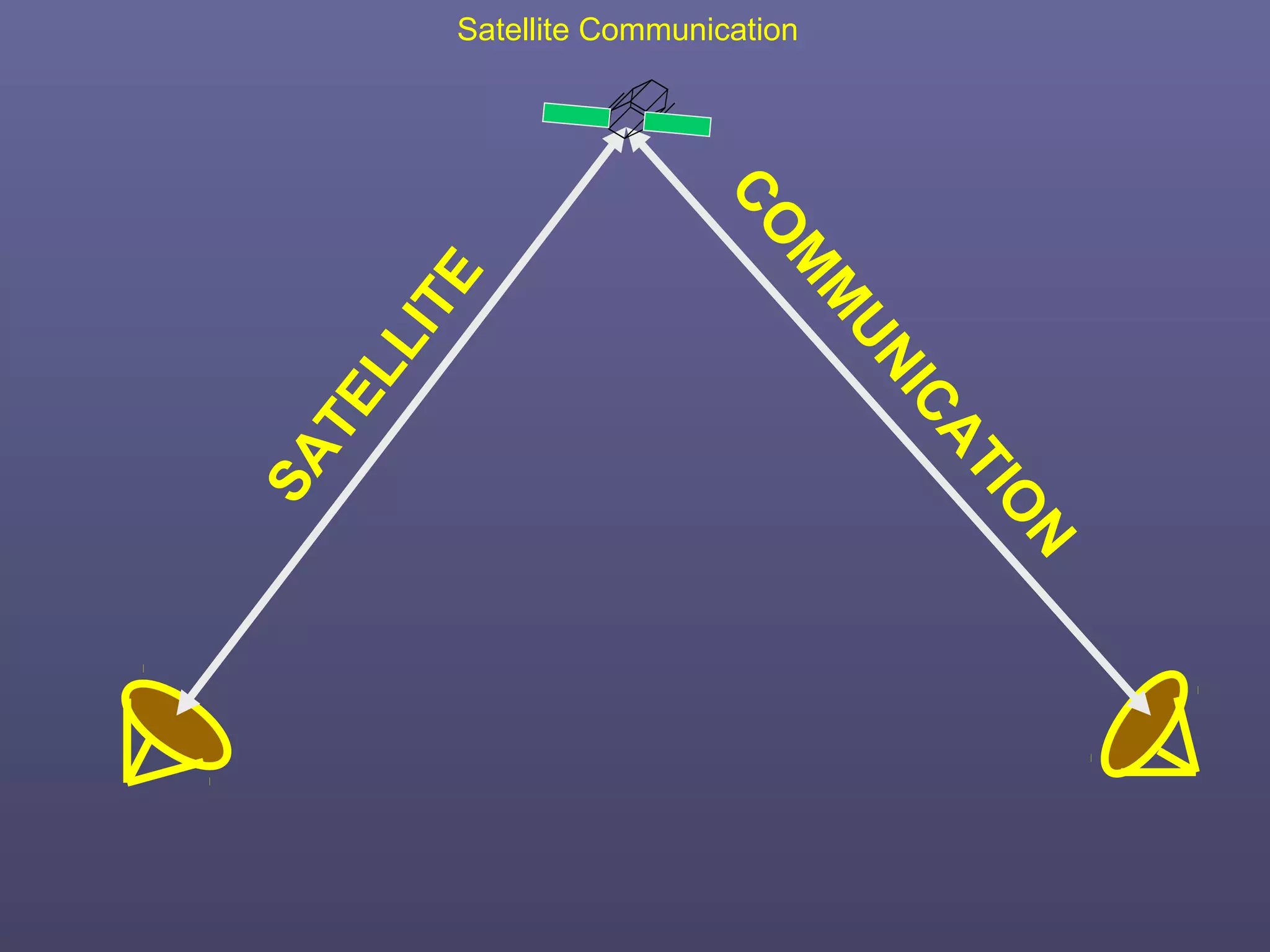
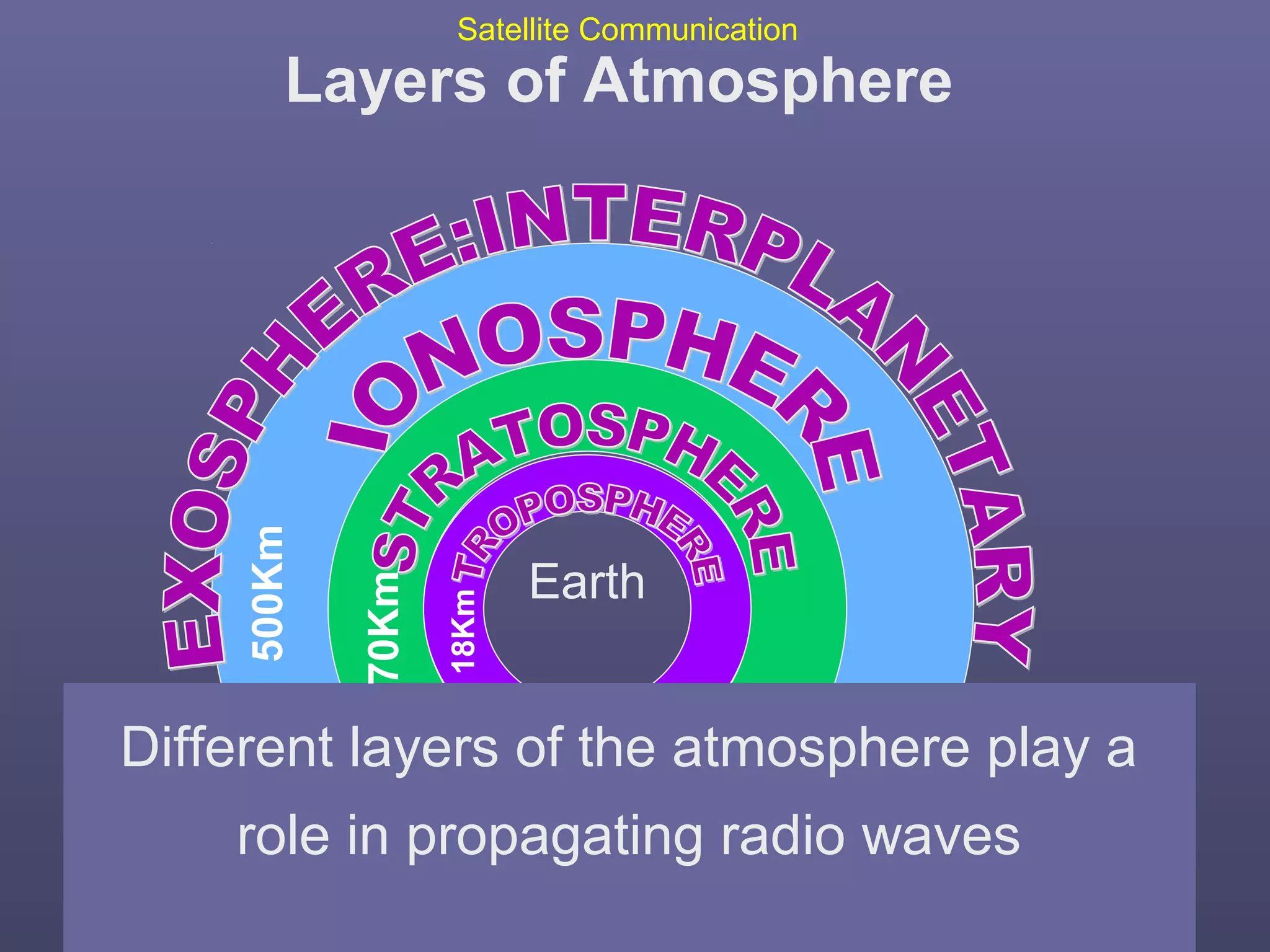
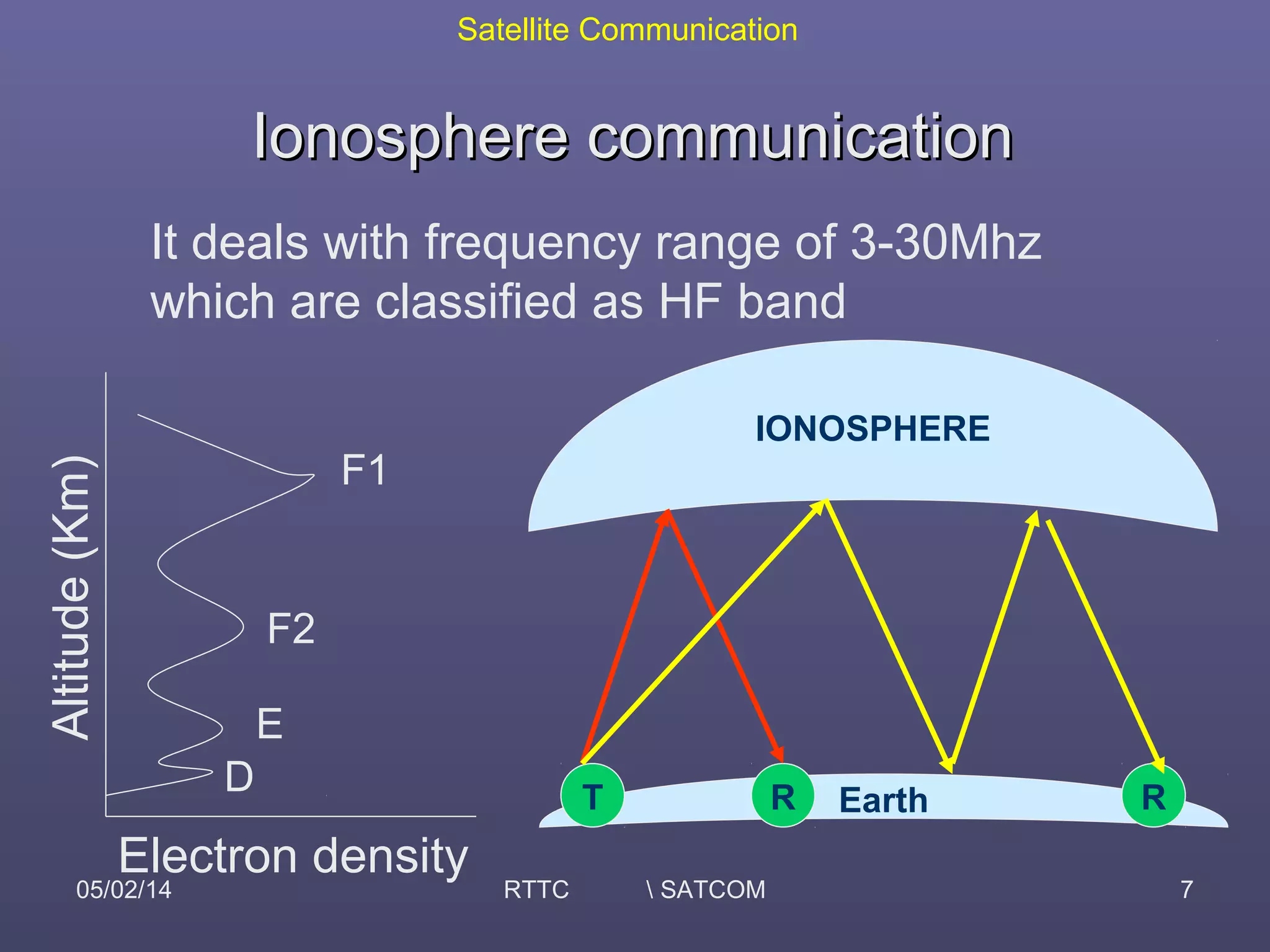
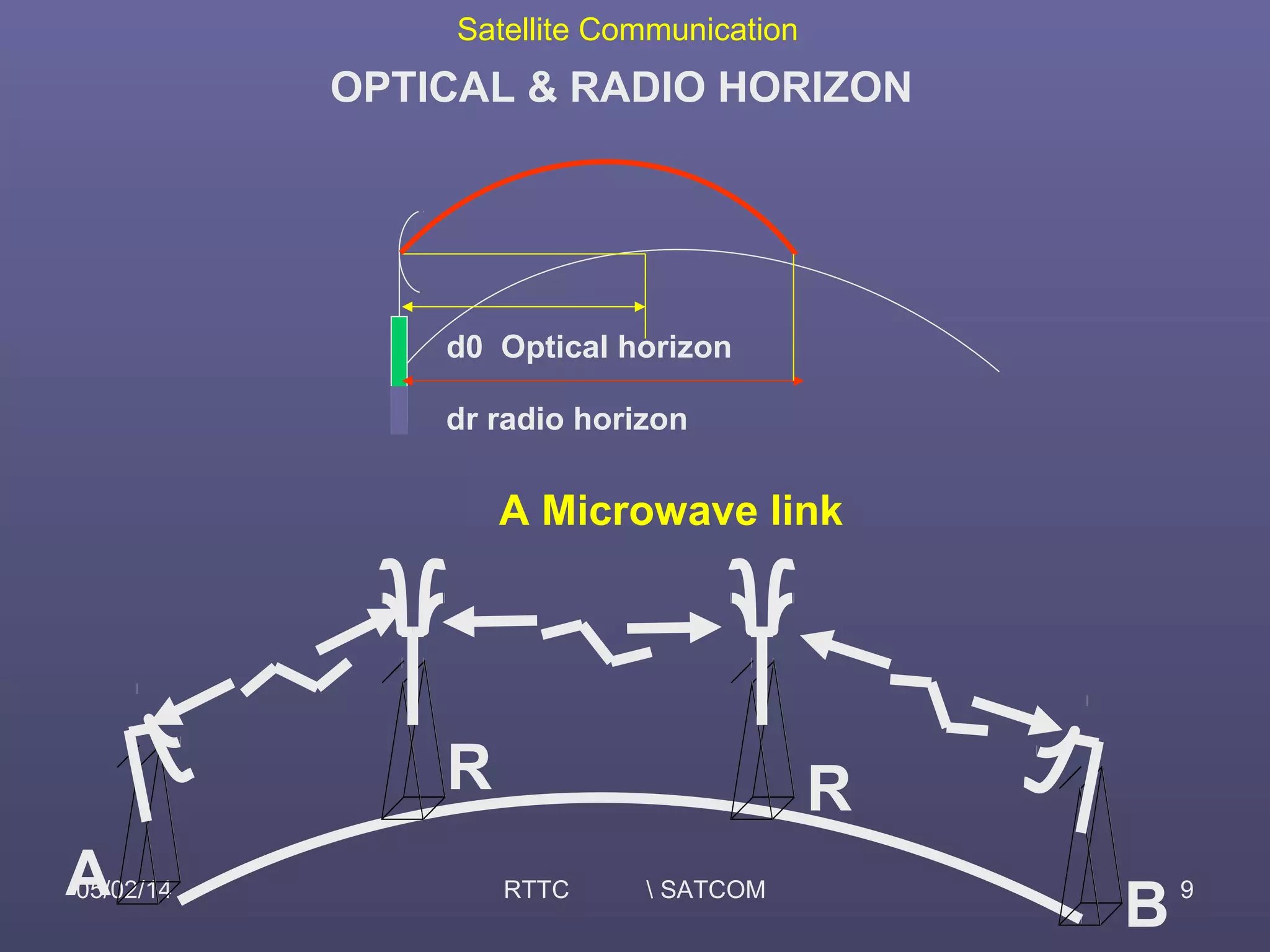
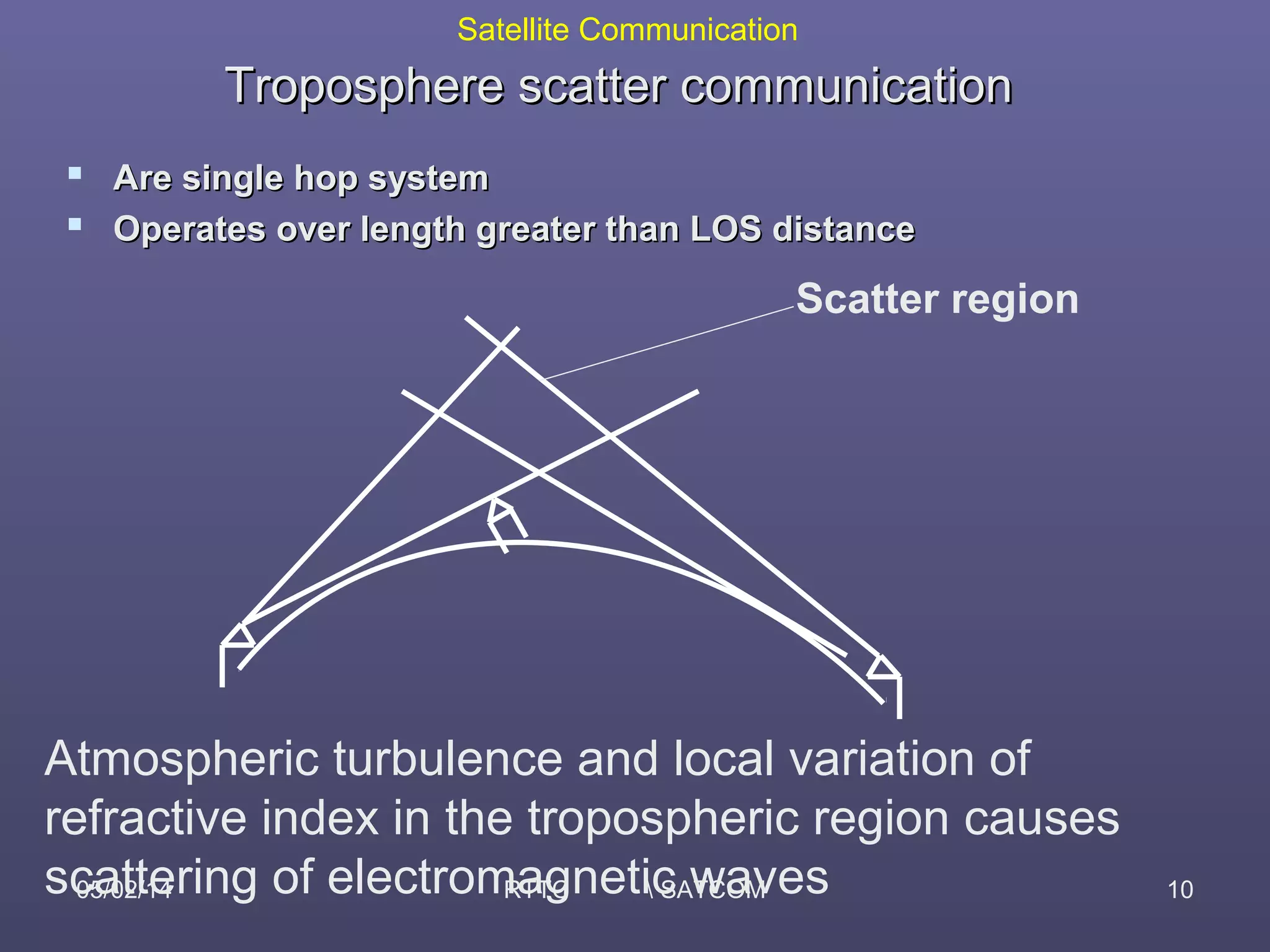
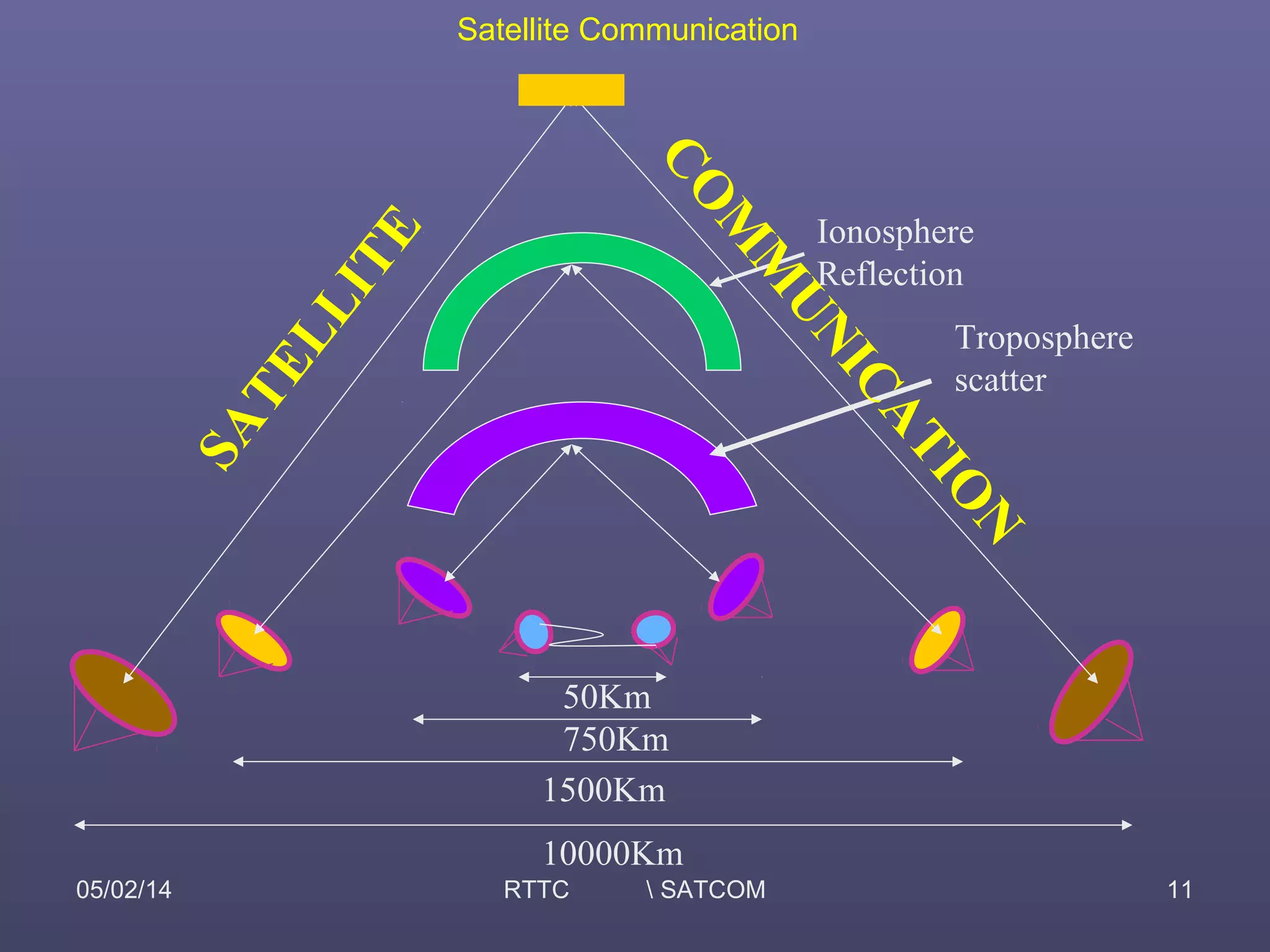
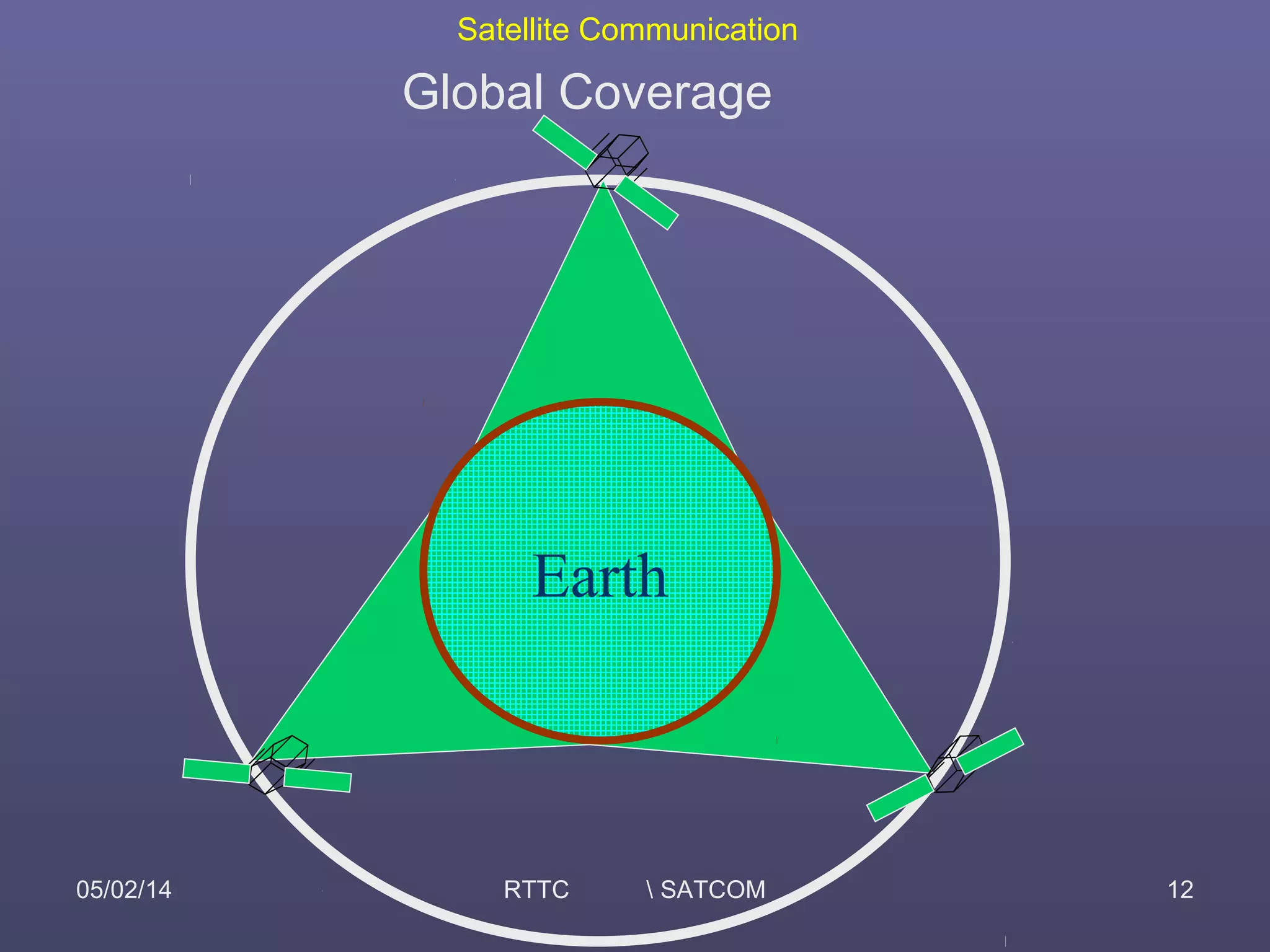
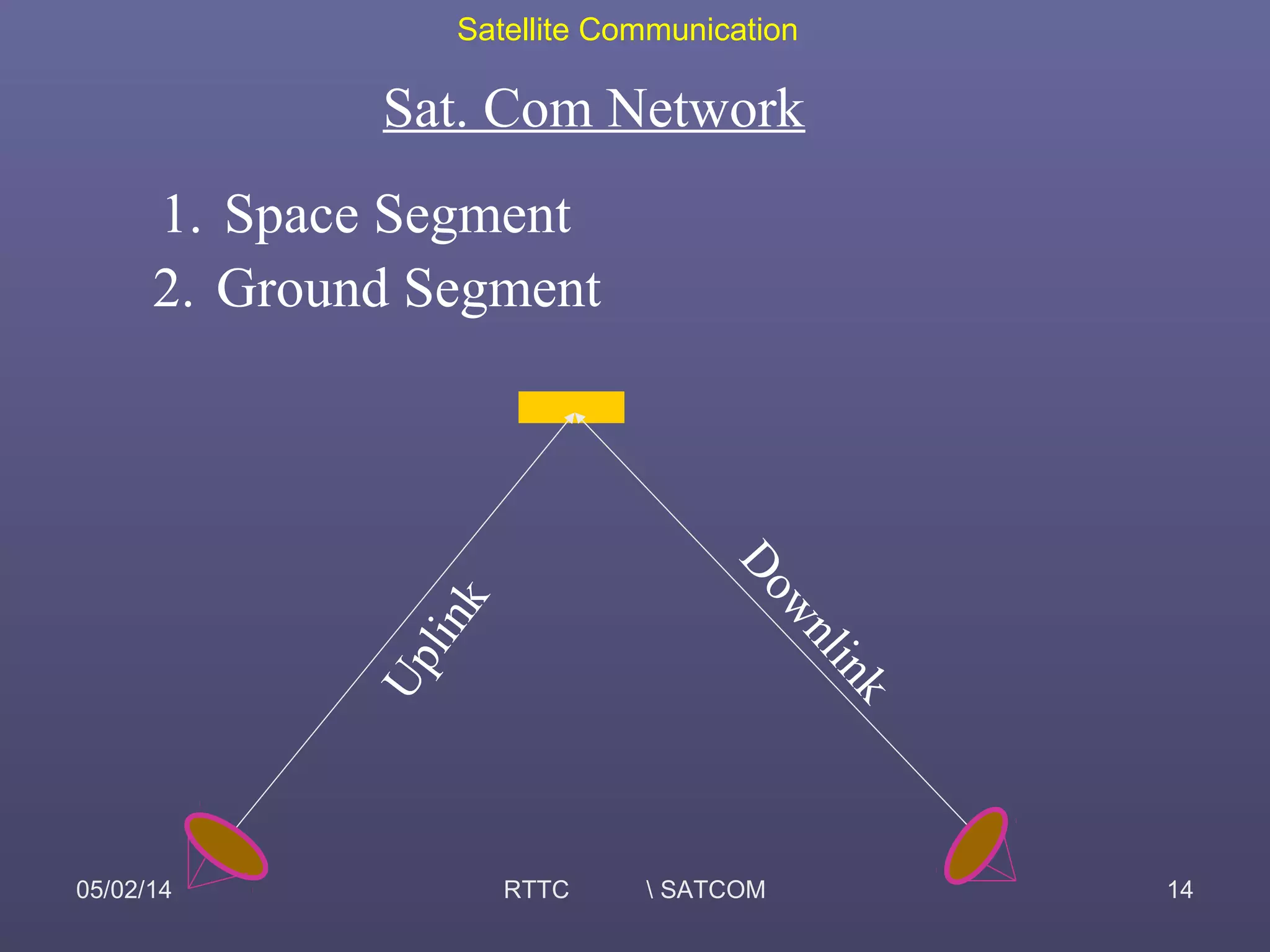
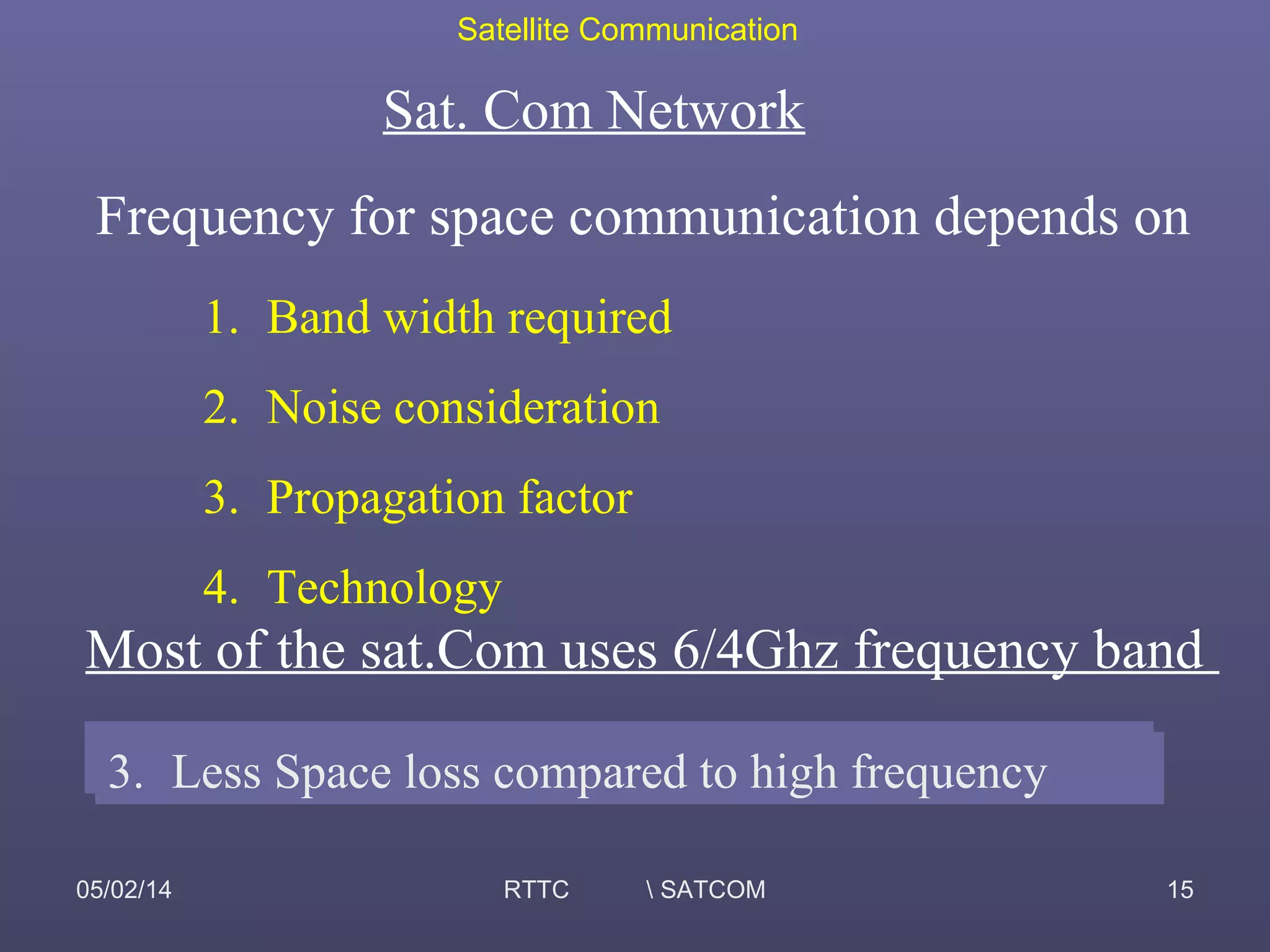
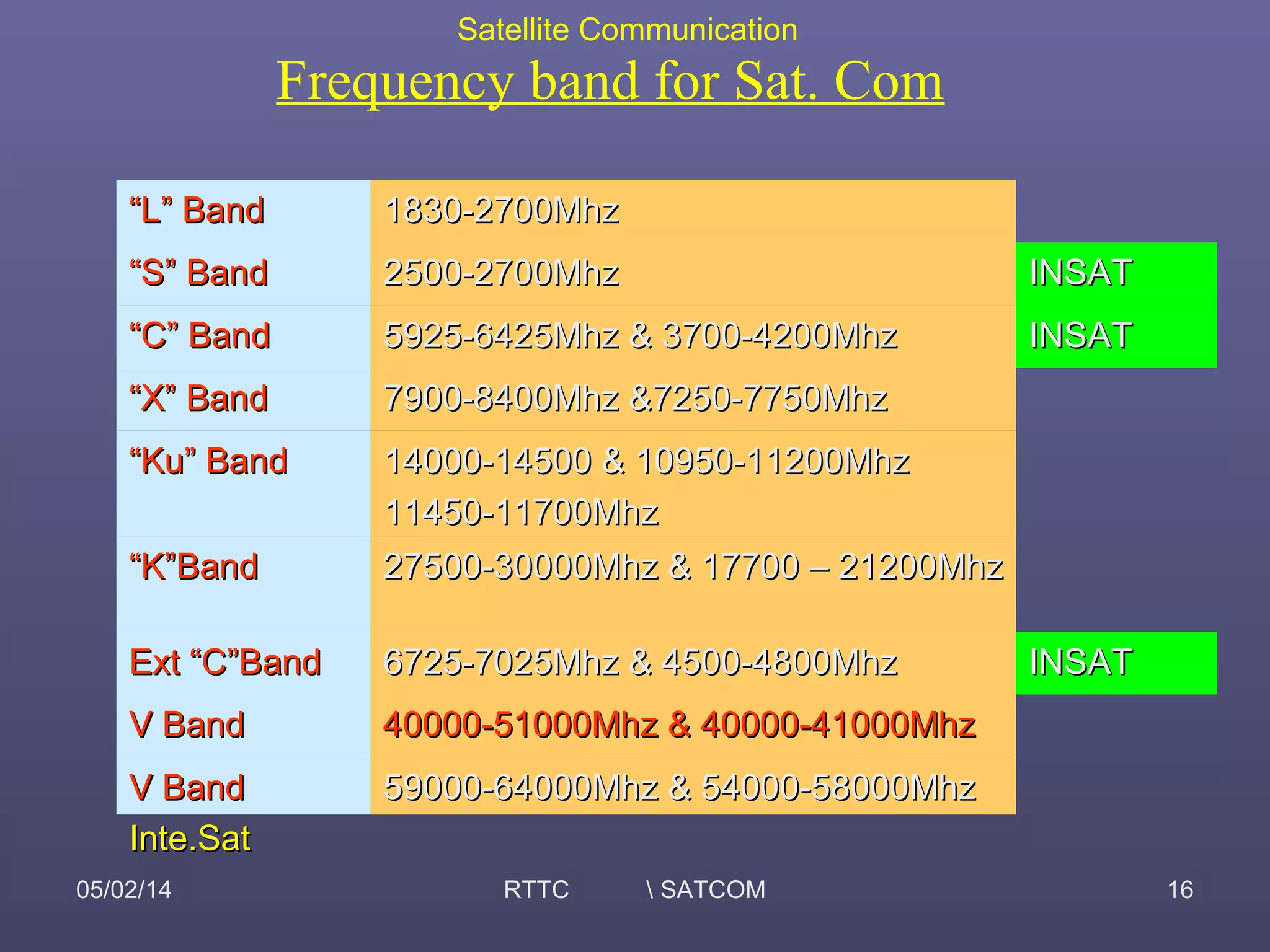
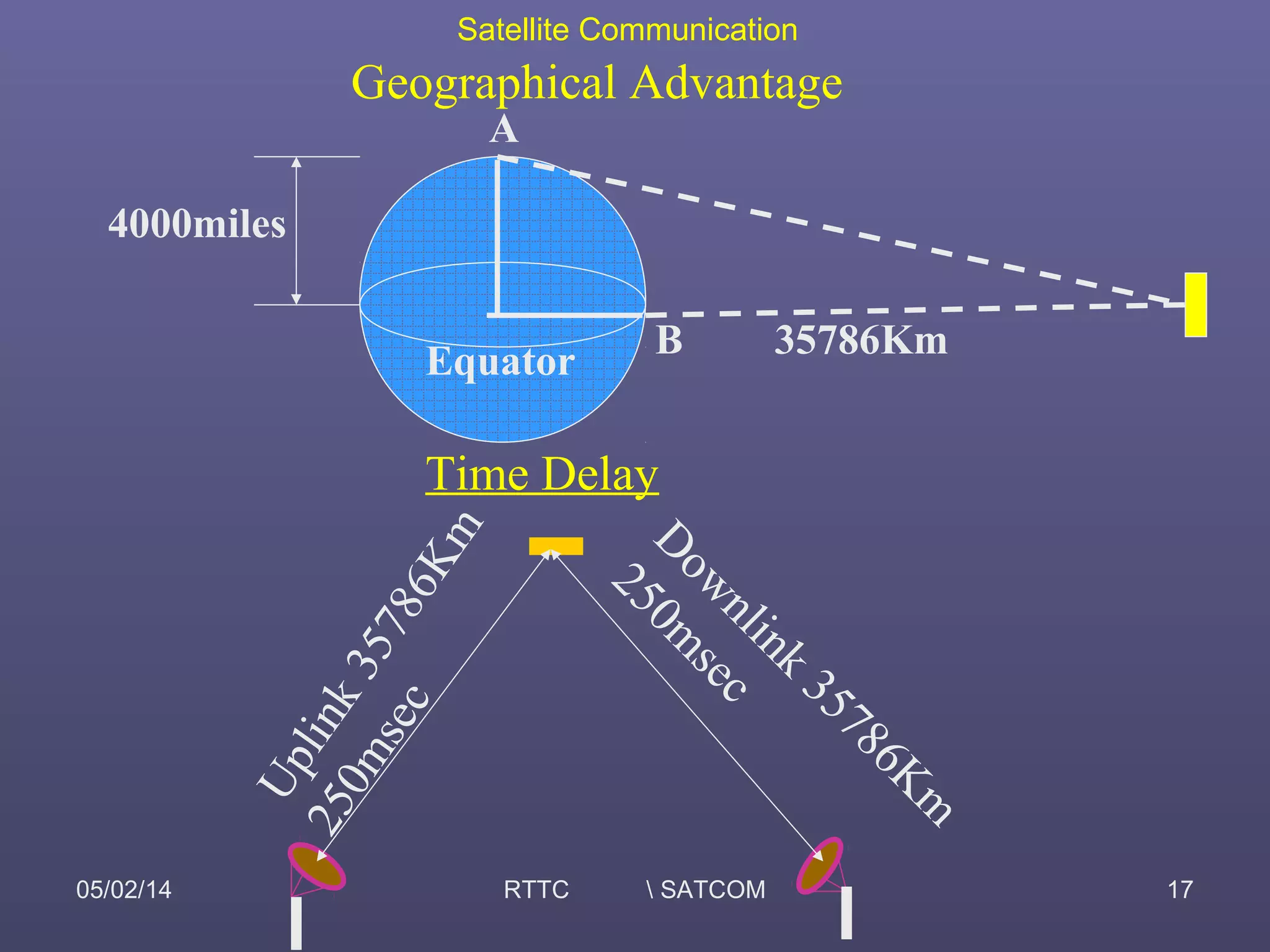
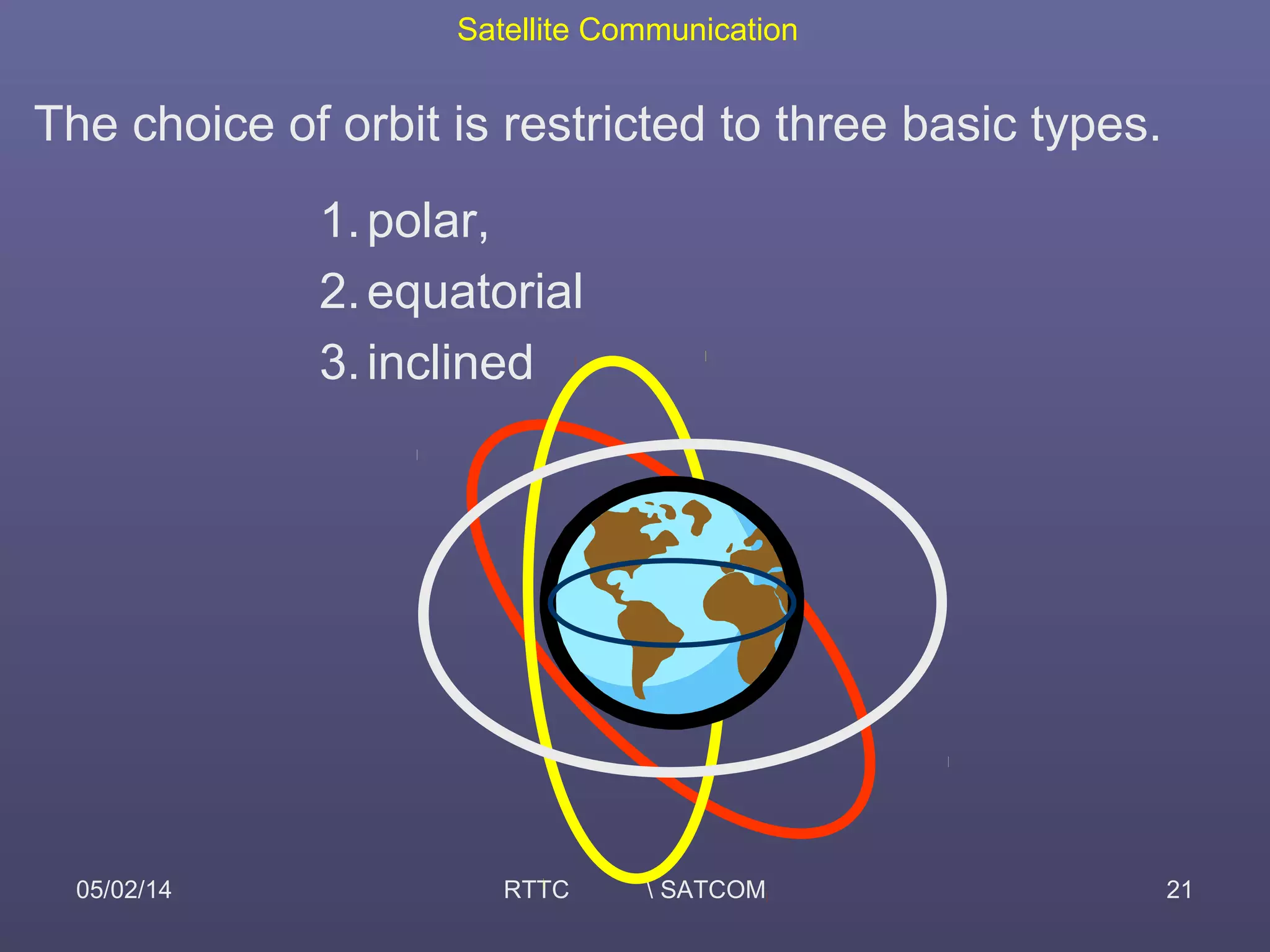
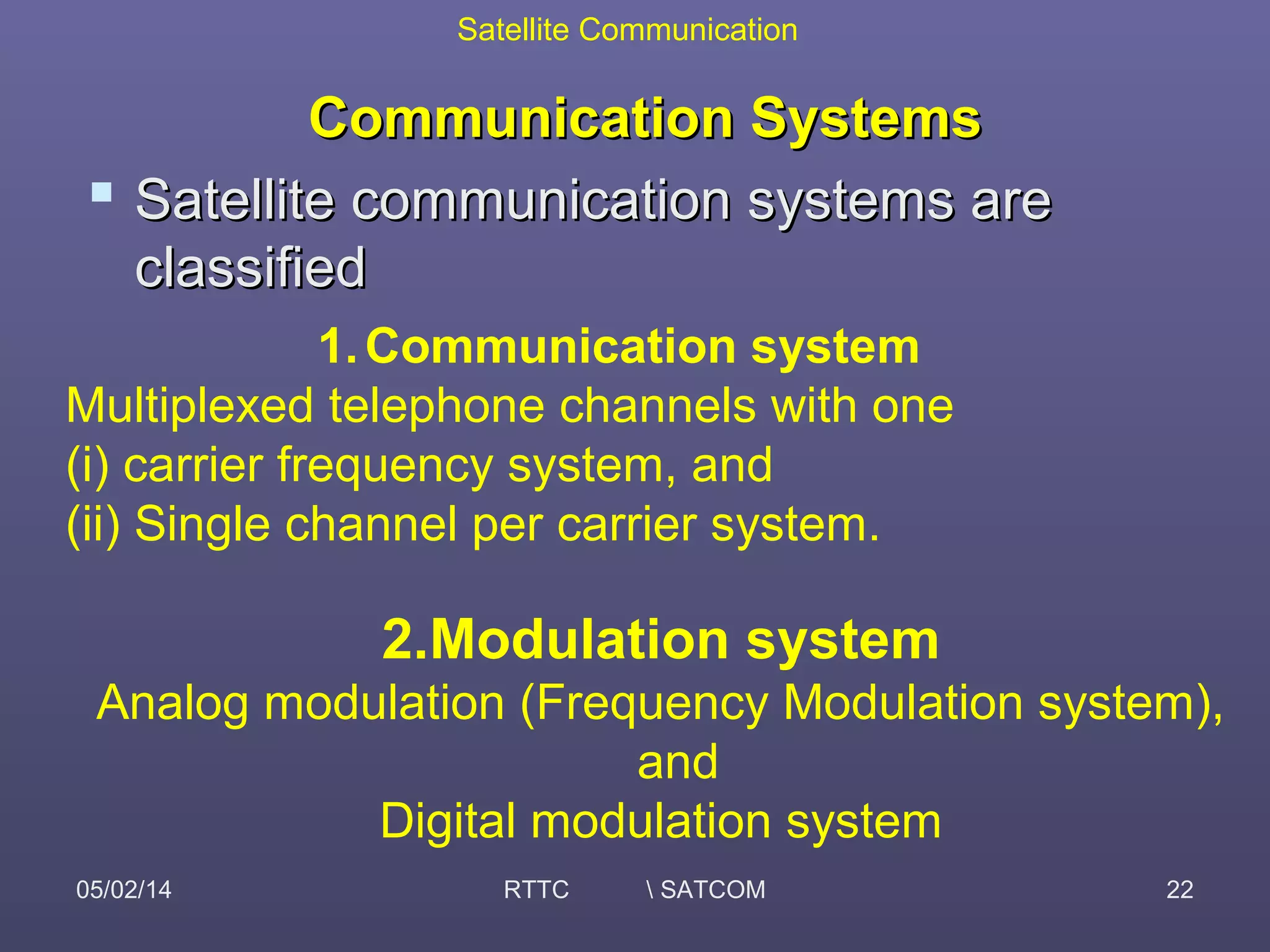
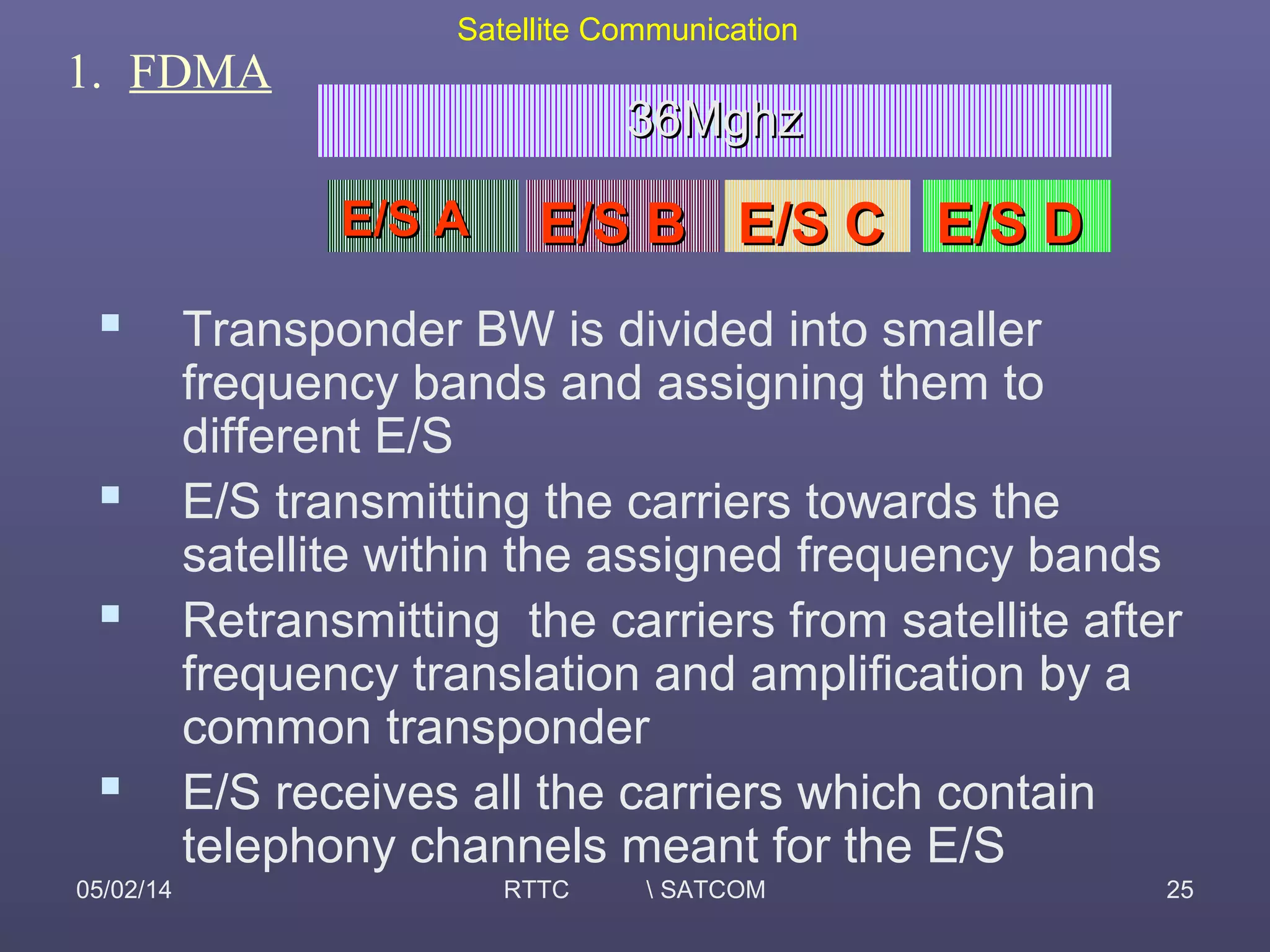
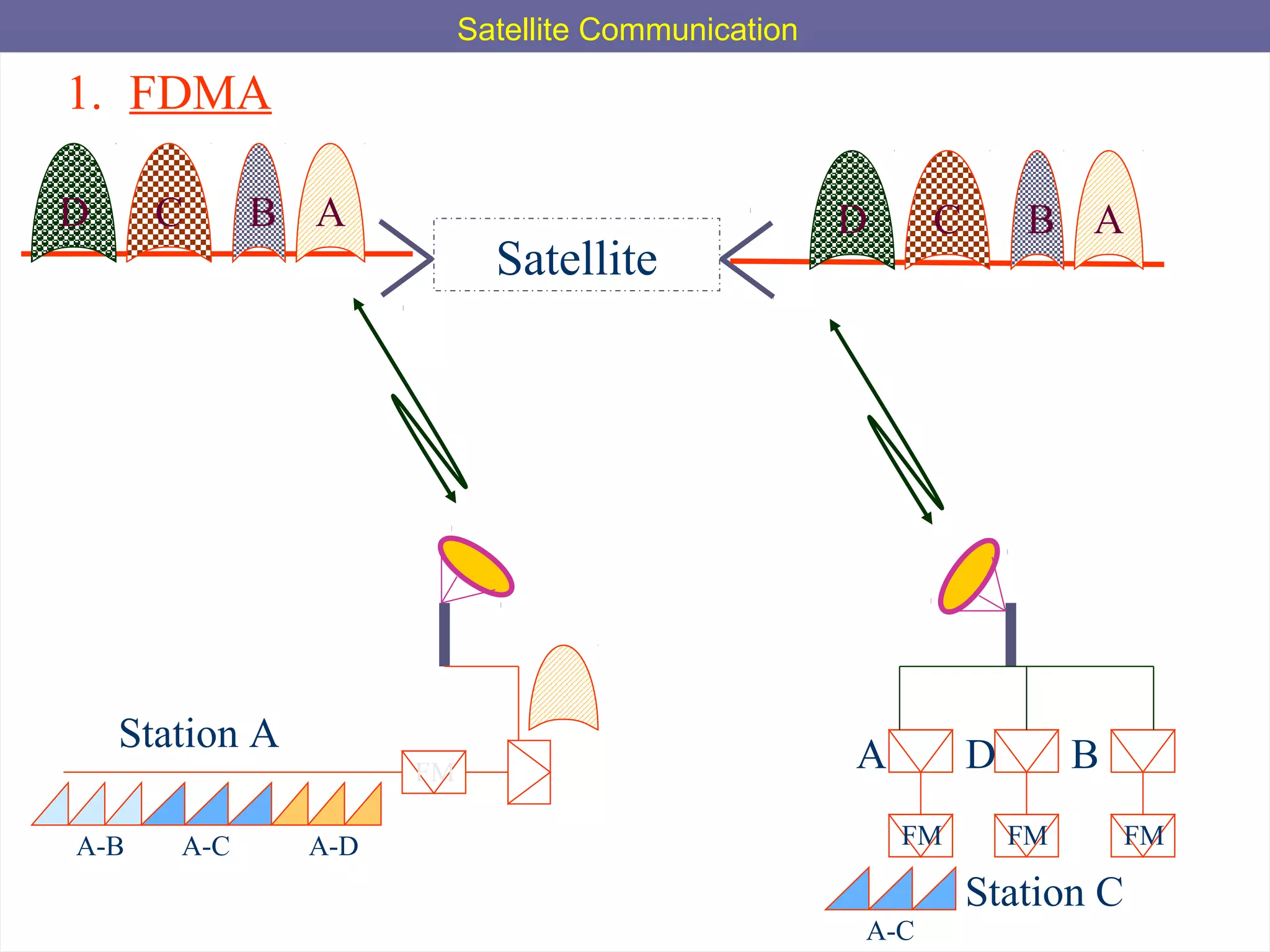
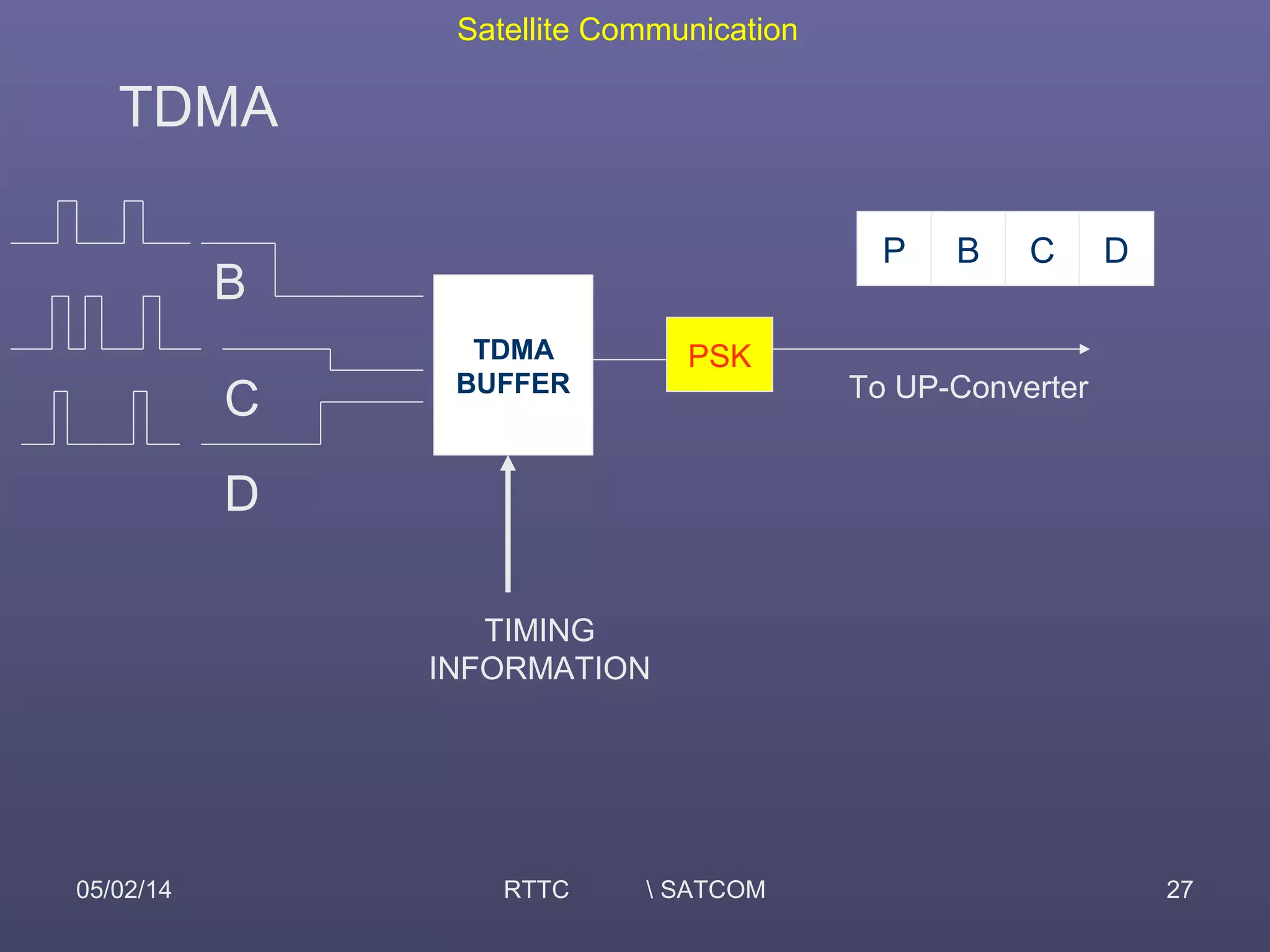
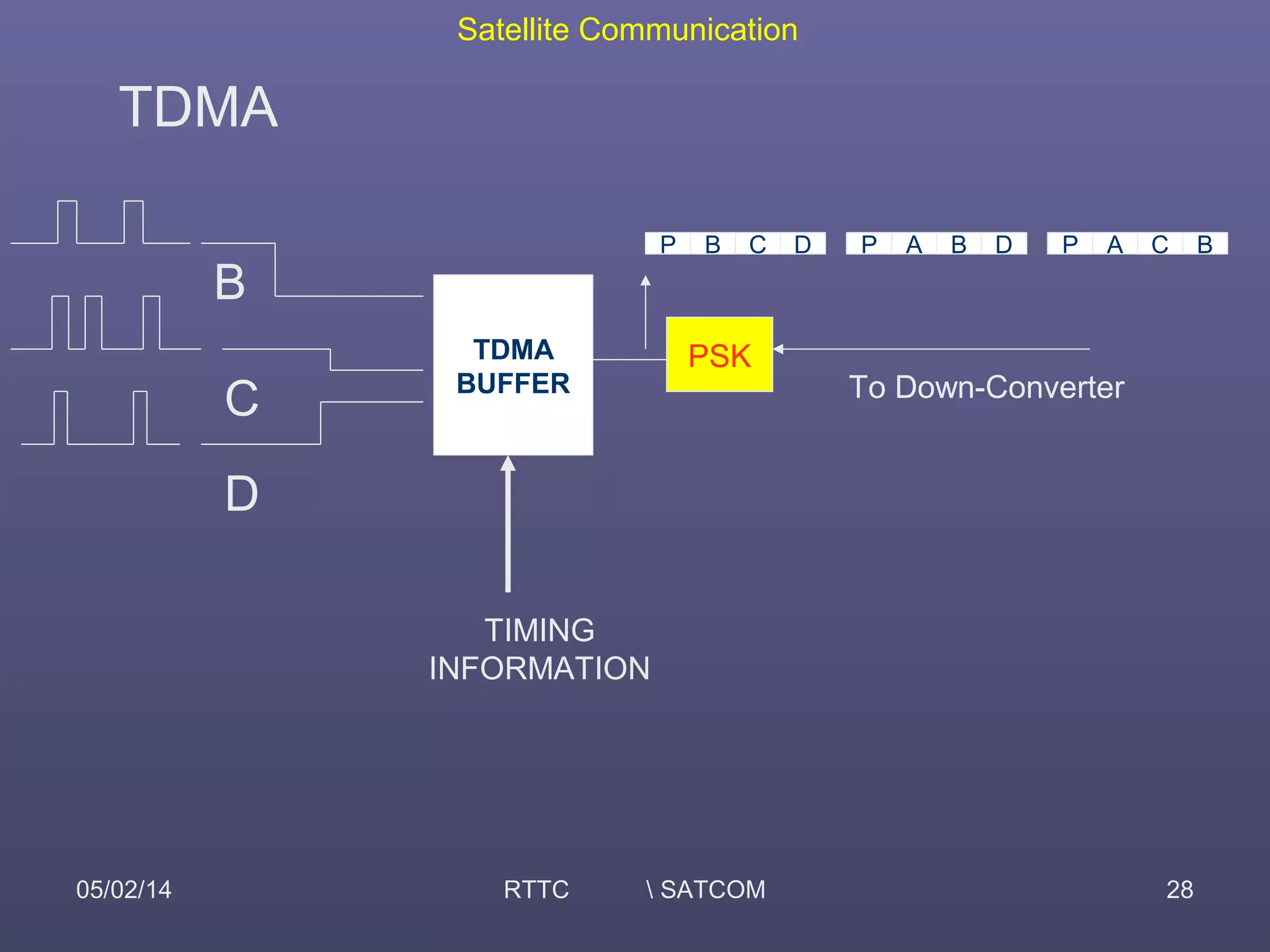
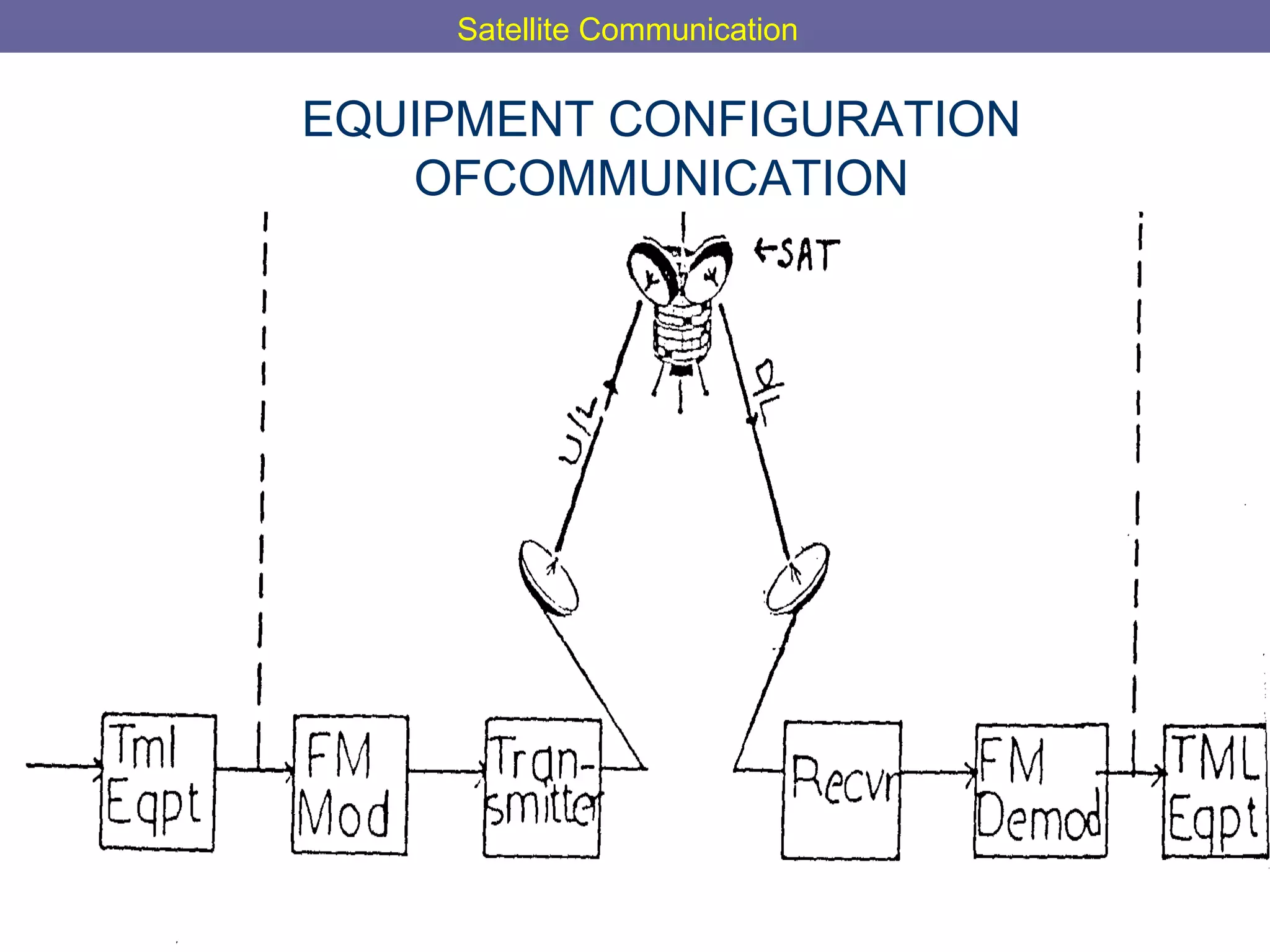
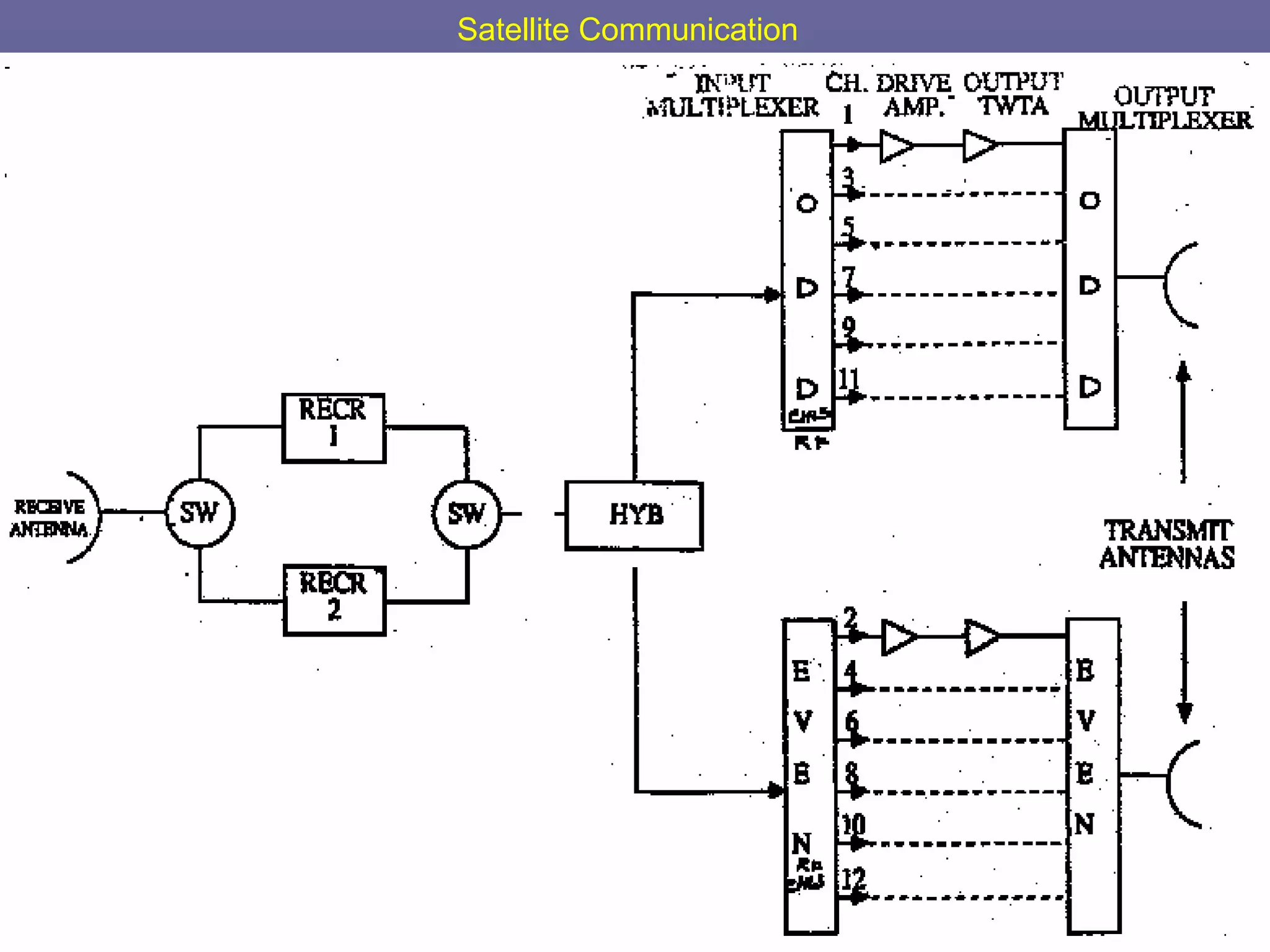
This document provides an overview of satellite communication and satellite systems. It discusses different types of transmission systems including radio, coaxial cable, and optical fiber systems. It describes how radio systems use electromagnetic waves to transmit signals and the portions of the frequency spectrum used. The document outlines the layers of the atmosphere and how the ionosphere and troposphere can propagate radio waves. It also categorizes different types of radio communication including ionosphere communication, line of sight microwave communication, and troposphere scatter communication. The document discusses advantages of satellite communication and components of a satellite communication network including the space and ground segments. It covers topics like satellite orbits, frequency bands used, and multiple access techniques in satellite systems.