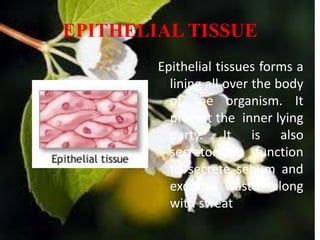
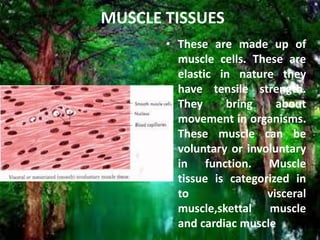
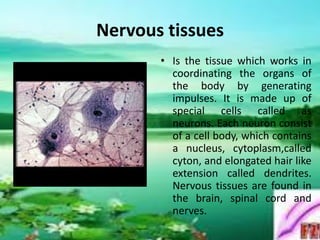
There are four main types of animal tissues: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Each tissue has a distinct structure and function. Epithelial tissue forms linings and covers surfaces, and can be secretory. Connective tissues include structures like blood, bone, and cartilage that support and bind other tissues. Muscle tissues contain muscle cells and provide movement. Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and coordinates the body's organs through signal transmission. Together these four tissue types form the basic building blocks that compose animal organs through various combinations tailored to function.