Recommended
PDF
sap basis certification training
PPTX
Developing Enterprise Applications Using Java Technology
PPTX
PDF
SAP S4 HANA_JAVA Architecture_sys Admin_Day 4.pdf
PPT
Financial Programmer - How to break into investment banks for java developers
PDF
Get Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel free all chapters
PPTX
PPTX
SAP ARCHITECTURE (I).pptx
PDF
Building Soabased Composite Applications Using Netbeans Ide 6 Frank Jennings
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PDF
PDF
Best SAP Basis Training Institute in Hyderabad – Mythri Institute of Technolo...
PPT
ejb.ppt java lecture notes enterprise java
ODP
JBUG.be EJB3 Why use Spring?
PDF
Injecting evil code in your SAP J2EE systems. Security of SAP Software Deploy...
PDF
Free EJB Tutorial | VirtualNuggets
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PPTX
Sap security online training
PDF
PDF
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PDF
Sap basis made_easy321761331053730
DOC
Java online training from hyderabad
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
SAP BASIS from LCC Infotech,Hyderabad
PDF
Enterprise Javabeans 3rd Edition Monsonhaefel R
PDF
Top Five Trends Shaping RCM in 2026 - Revenue Cycle Resources-HUB
PDF
Best 8 Websites to Buy Facebook Accounts Detailed 2026 Guide.pdf
More Related Content
PDF
sap basis certification training
PPTX
Developing Enterprise Applications Using Java Technology
PPTX
PDF
SAP S4 HANA_JAVA Architecture_sys Admin_Day 4.pdf
PPT
Financial Programmer - How to break into investment banks for java developers
PDF
Get Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel free all chapters
PPTX
PPTX
SAP ARCHITECTURE (I).pptx
Similar to SAP_JAVA_Architecture_Advanced_Training.pptx
PDF
Building Soabased Composite Applications Using Netbeans Ide 6 Frank Jennings
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PDF
PDF
Best SAP Basis Training Institute in Hyderabad – Mythri Institute of Technolo...
PPT
ejb.ppt java lecture notes enterprise java
ODP
JBUG.be EJB3 Why use Spring?
PDF
Injecting evil code in your SAP J2EE systems. Security of SAP Software Deploy...
PDF
Free EJB Tutorial | VirtualNuggets
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PPTX
Sap security online training
PDF
PDF
PDF
Enterprise JavaBeans 3rd Edition Richard Monson-Haefel
PDF
Sap basis made_easy321761331053730
DOC
Java online training from hyderabad
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
SAP BASIS from LCC Infotech,Hyderabad
PDF
Enterprise Javabeans 3rd Edition Monsonhaefel R
Recently uploaded
PDF
Top Five Trends Shaping RCM in 2026 - Revenue Cycle Resources-HUB
PDF
Best 8 Websites to Buy Facebook Accounts Detailed 2026 Guide.pdf
PDF
Buy Verified PayPal Accounts – A Complete Guide for Secure and Efficient Onli...
DOCX
8 Best Places to Buy Facebook Accounts at Wholesale Prices.docx
DOCX
Buy Verified Paypal Accounts_ A Safely Complete Guide Usa.docx
PDF
ICv2 White Paper - Navigating the New World of Comics
PDF
EDIH Trakia Ecosystem Transformation to Maturity
PDF
LA Building Inspections & Compliance offers
PDF
Step-by-Step 17 Guide to Purchasing Verified PayPal Account.pdf
PDF
Maksym Vyshnivetskyi: Business Value & Benefits Realization (UA)
PDF
Stablecoins beyond narrow banking - Lombard Notes
PDF
20260203 CDB Investor Deck_Feb26_vF.pdf
PPTX
423784969-Aquaria-Grande-by-Faisal.pptxh
PDF
Buy Telegram Accounts_ A Complete Educational Guide to Understanding Digital ...
PDF
Chris Elwell Woburn - Specializes In Cybersecurity And Audit Preparedness
PPTX
Commercial Sewage Treatment Plant in Vizag | Vijayawada| Hyderabad | Naidupet...
PDF
Ultra Map Section II Multifaceted Second Edition.pdf
PDF
LCP-consultation-response-to-TPR-CDC-code-of-practice.pdf
PPTX
s4hana is an evolution not just a migration
PDF
What Is the Fastest Way to Buy Facebook Accounts.pdf
SAP_JAVA_Architecture_Advanced_Training.pptx 1. SAP JAVA Architecture –
Enterprise Training
L3 Support | Technical Deep Dive |
Corporate Training Material
2. Agenda
• SAP Java – Concept and Enterprise Usage
• SAP NetWeaver Java Deep Architecture
• SAP Java Start/Stop Internal Flow
• Java Stack Administration Tools (Deep Dive)
• SAP Java Monitoring & Performance Tuning
• Support Package & Patch Lifecycle
Management
• Best Practices – L3 Support Perspective
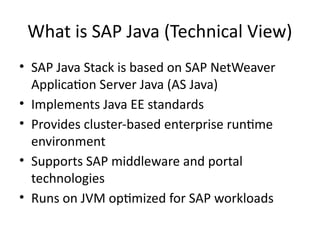
3. What is SAP Java (Technical View)
• SAP Java Stack is based on SAP NetWeaver
Application Server Java (AS Java)
• Implements Java EE standards
• Provides cluster-based enterprise runtime
environment
• Supports SAP middleware and portal
technologies
• Runs on JVM optimized for SAP workloads
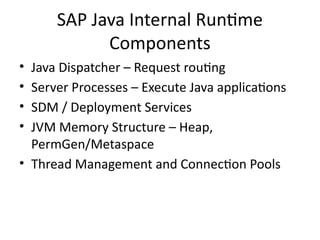
4. SAP Java Internal Runtime
Components
• Java Dispatcher – Request routing
• Server Processes – Execute Java applications
• SDM / Deployment Services
• JVM Memory Structure – Heap,
PermGen/Metaspace
• Thread Management and Connection Pools
5. Enterprise Use Cases of SAP Java
• SAP Enterprise Portal (EP)
• SAP PI/PO Integration Engines
• SAP Solution Manager Java Components
• Identity Management and Access Control
• SAP Cloud Connectors
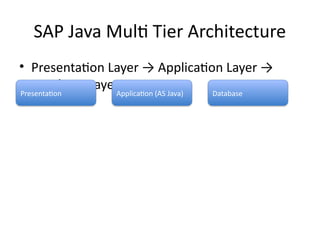
6. SAP Java Multi Tier Architecture
• Presentation Layer → Application Layer →
Database Layer
Presentation Application (AS Java) Database
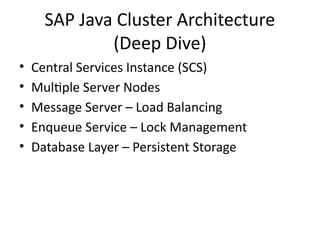
7. SAP Java Cluster Architecture
(Deep Dive)
• Central Services Instance (SCS)
• Multiple Server Nodes
• Message Server – Load Balancing
• Enqueue Service – Lock Management
• Database Layer – Persistent Storage
8. SAP Java Cluster Logical View
• User Requests → Dispatcher → Server Nodes
→ DB
Dispatcher Server Node 1 Server Node 2
9. SAP NetWeaver Java Engine Deep
Architecture
• Java EE Containers (Web, EJB, Services)
• Cluster Manager
• Security Provider Framework
• JMX Monitoring Layer
• Service Registry
10. Java Security Architecture
• UME – User Management Engine
• Authentication – LDAP, AD, SSO
• Authorization – Role Based Access
• Secure Network Communication (SSL)
• Ticket Based Authentication
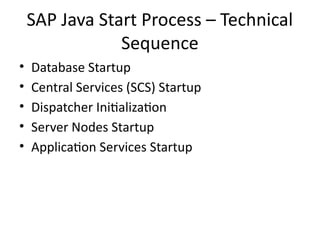
11. SAP Java Start Process – Technical
Sequence
• Database Startup
• Central Services (SCS) Startup
• Dispatcher Initialization
• Server Nodes Startup
• Application Services Startup
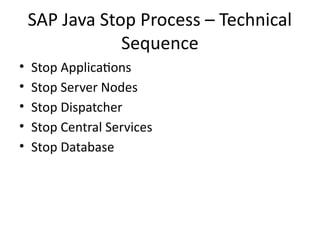
12. SAP Java Stop Process – Technical
Sequence
• Stop Applications
• Stop Server Nodes
• Stop Dispatcher
• Stop Central Services
• Stop Database
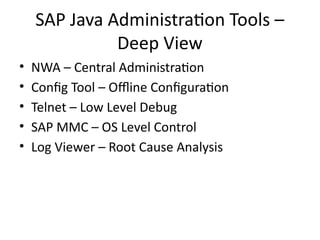
13. SAP Java Administration Tools –
Deep View
• NWA – Central Administration
• Config Tool – Offline Configuration
• Telnet – Low Level Debug
• SAP MMC – OS Level Control
• Log Viewer – Root Cause Analysis
14. NWA Technical Areas
• System Monitoring
• Configuration Management
• Performance Monitoring
• Log and Trace Monitoring
• User Administration
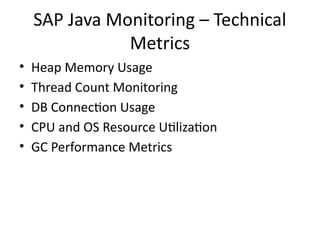
15. SAP Java Monitoring – Technical
Metrics
• Heap Memory Usage
• Thread Count Monitoring
• DB Connection Usage
• CPU and OS Resource Utilization
• GC Performance Metrics
16. Java Performance Tuning Areas
• JVM Parameter Optimization
• GC Tuning
• Thread Pool Optimization
• Connection Pool Optimization
• Service Restart Strategy
17. Java Support Package Lifecycle
• Patch Planning
• SUM Tool Execution
• Downtime Planning
• Validation Testing
• Post Patch Monitoring
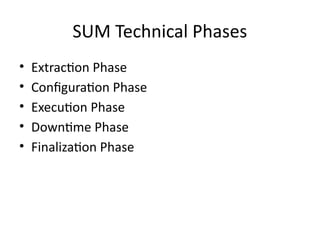
18. SUM Technical Phases
• Extraction Phase
• Configuration Phase
• Execution Phase
• Downtime Phase
• Finalization Phase
19. Common Production Issues (L3
Level)
• OutOfMemory Errors
• Thread Deadlocks
• DB Connection Exhaustion
• Deployment Failures
• Cluster Node Failures
20. SAP Java Logs – Important
Locations
• DefaultTrace Logs
• System Logs
• Server Node Logs
• GC Logs
• Security Logs
21. SAP Java Best Practices (Enterprise)
• Proactive Monitoring
• Patch Compliance
• Capacity Planning
• Regular Log Review
• Backup Validation
22. Training Summary
• SAP Java is Enterprise Grade Runtime Platform
• Architecture Understanding is Critical
• Monitoring Prevents Major Incidents
• Patch Management Ensures Stability
• Tools Knowledge Defines Support Efficiency
Editor's Notes #2 This training is designed for L3 support engineers and senior SAP Basis professionals. #3 Focus on AS Java runtime, cluster nodes, and enterprise workload handling. #4 Important for troubleshooting performance and memory issues in production. #5 Interview focus: Why Java stack used instead of ABAP stack. #6 Explain request flow from browser to database via Java server nodes. #7 Cluster architecture ensures high availability and scalability. #8 Explain load balancing and failover scenarios. #9 Important topic for architecture interviews. #10 Security architecture is critical in production landscape. #11 Explain dependency chain – Common interview question. #12 Used during patching and maintenance windows. #13 Know which tool to use in which scenario. #14 NWA is primary daily working tool for L2/L3 support. #15 Memory leaks and thread locks are common production issues. #16 Used for performance incident resolution. #17 Patch failures require log analysis and rollback planning. #18 Very common L3 troubleshooting topic. #19 Be ready with troubleshooting approach in interviews. #20 Log reading is core L3 skill. #21 Corporate environments require compliance and audit readiness. #22 Summarize key training outcomes.