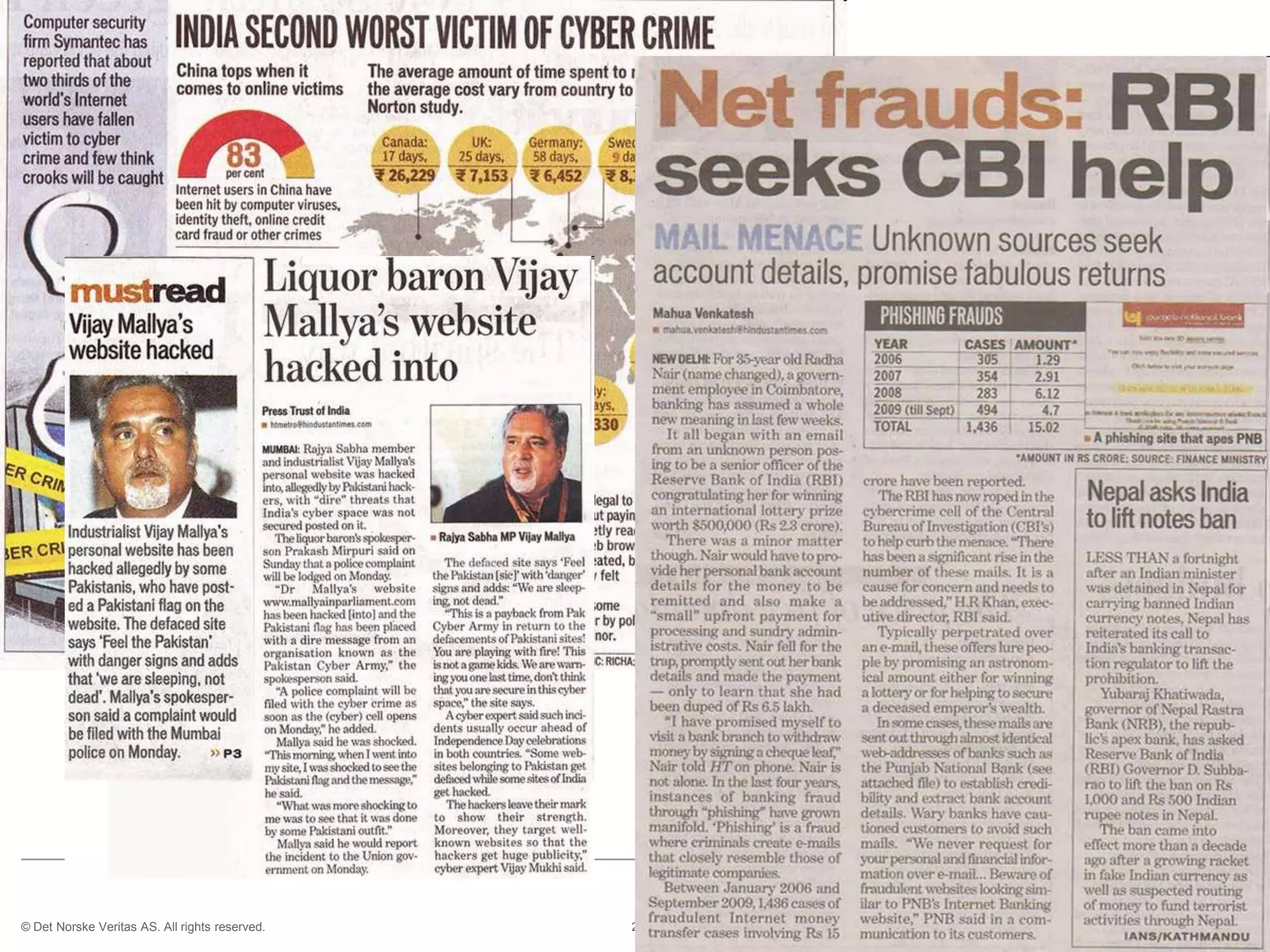
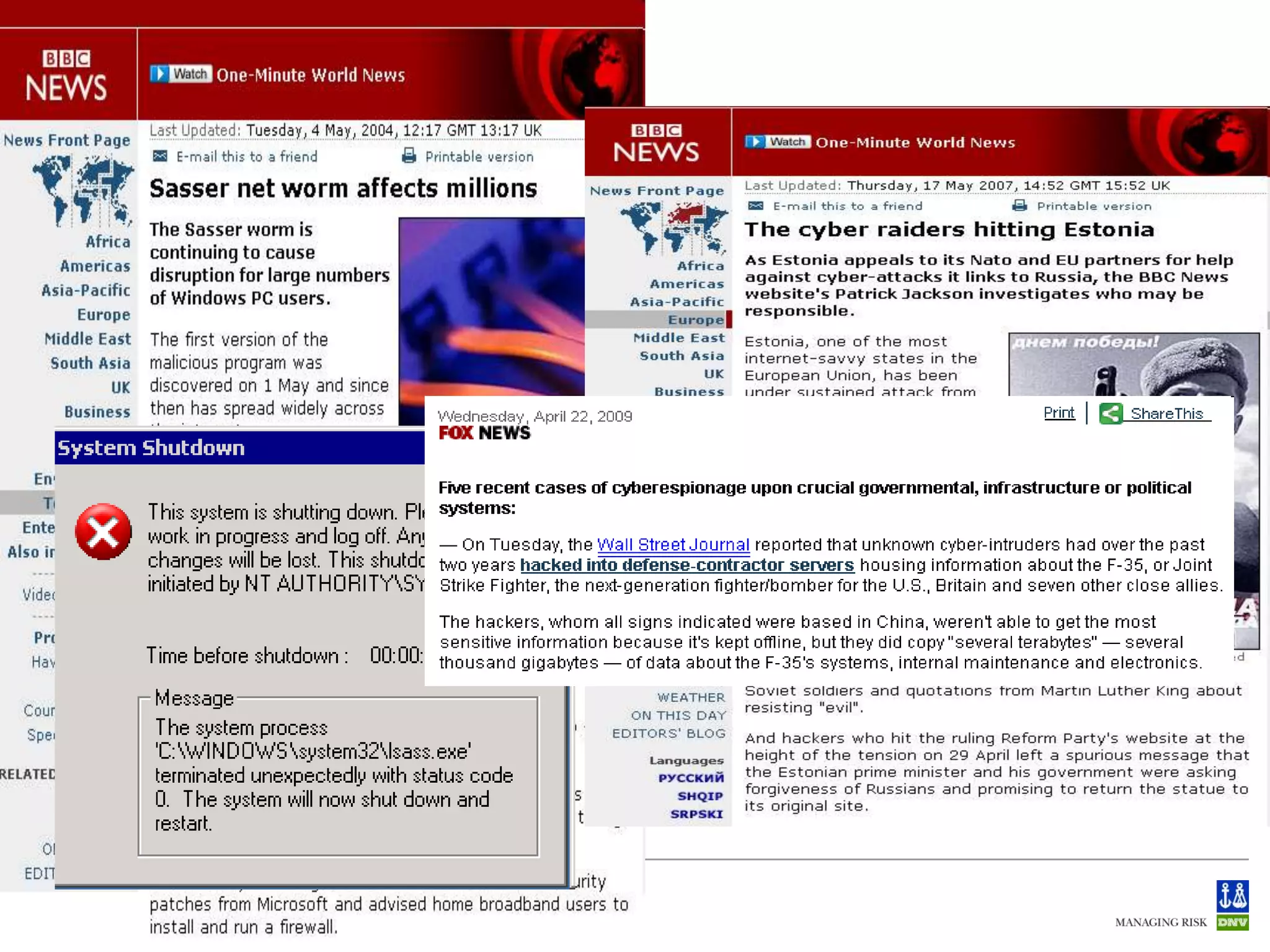
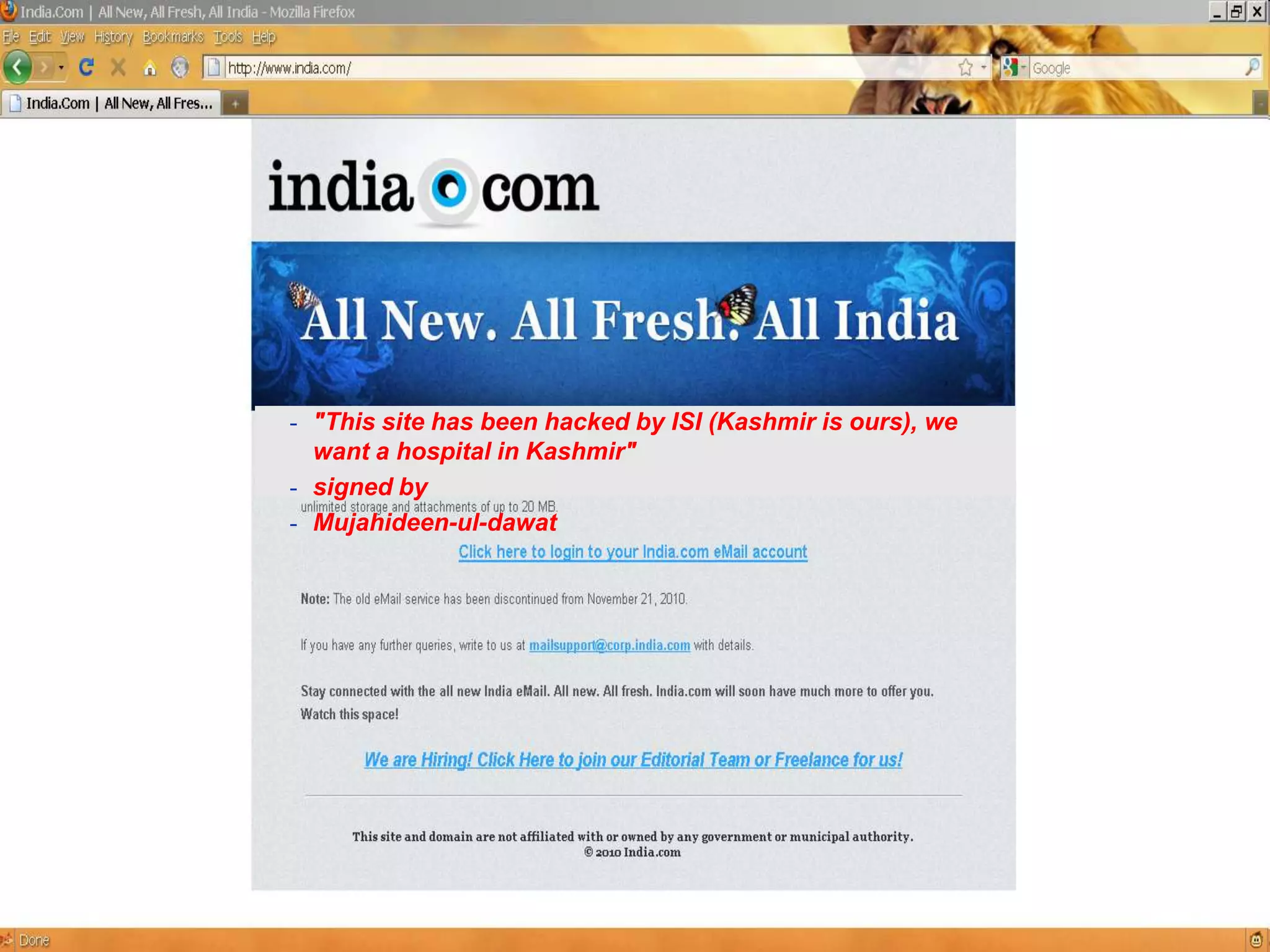
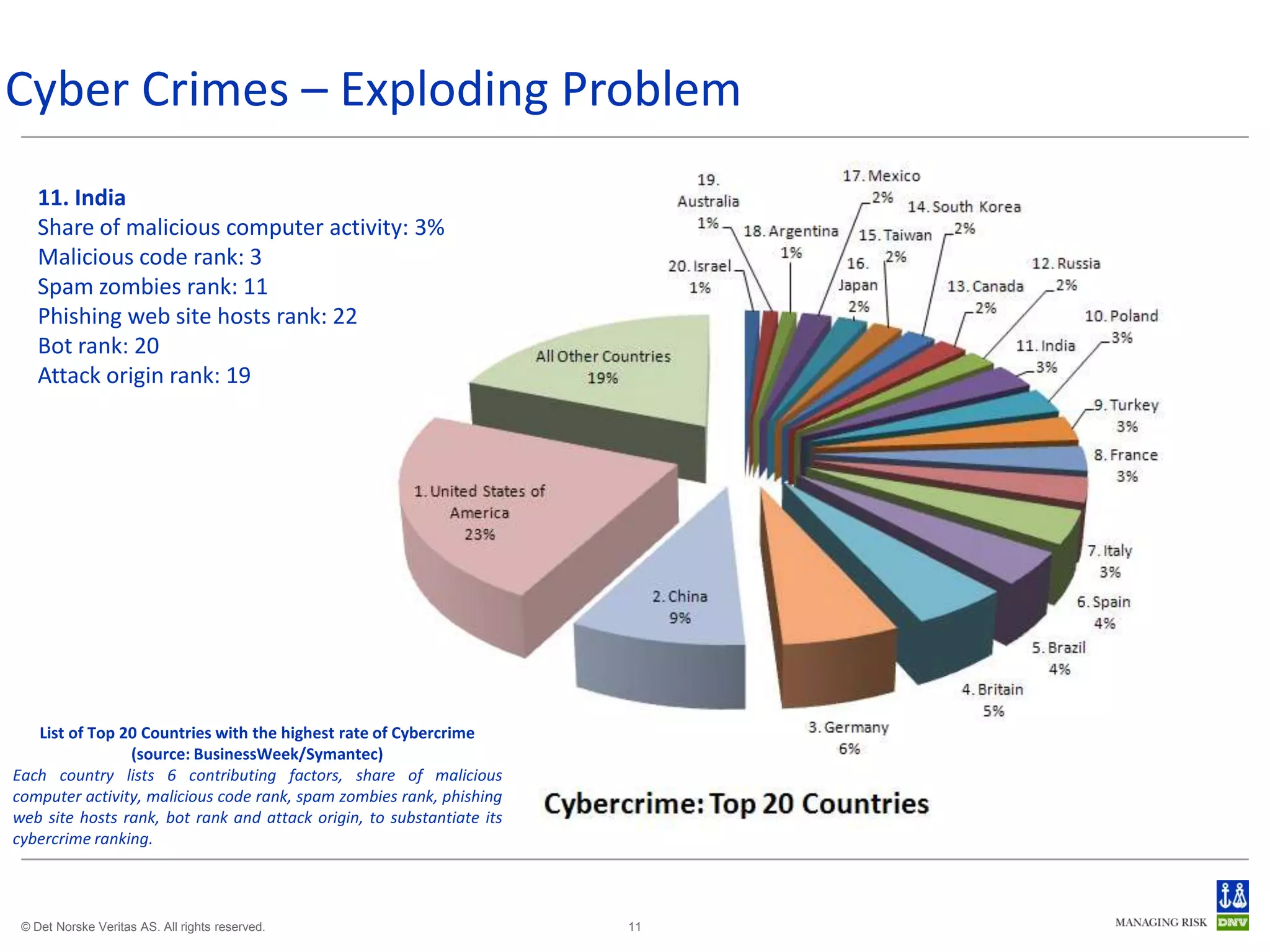
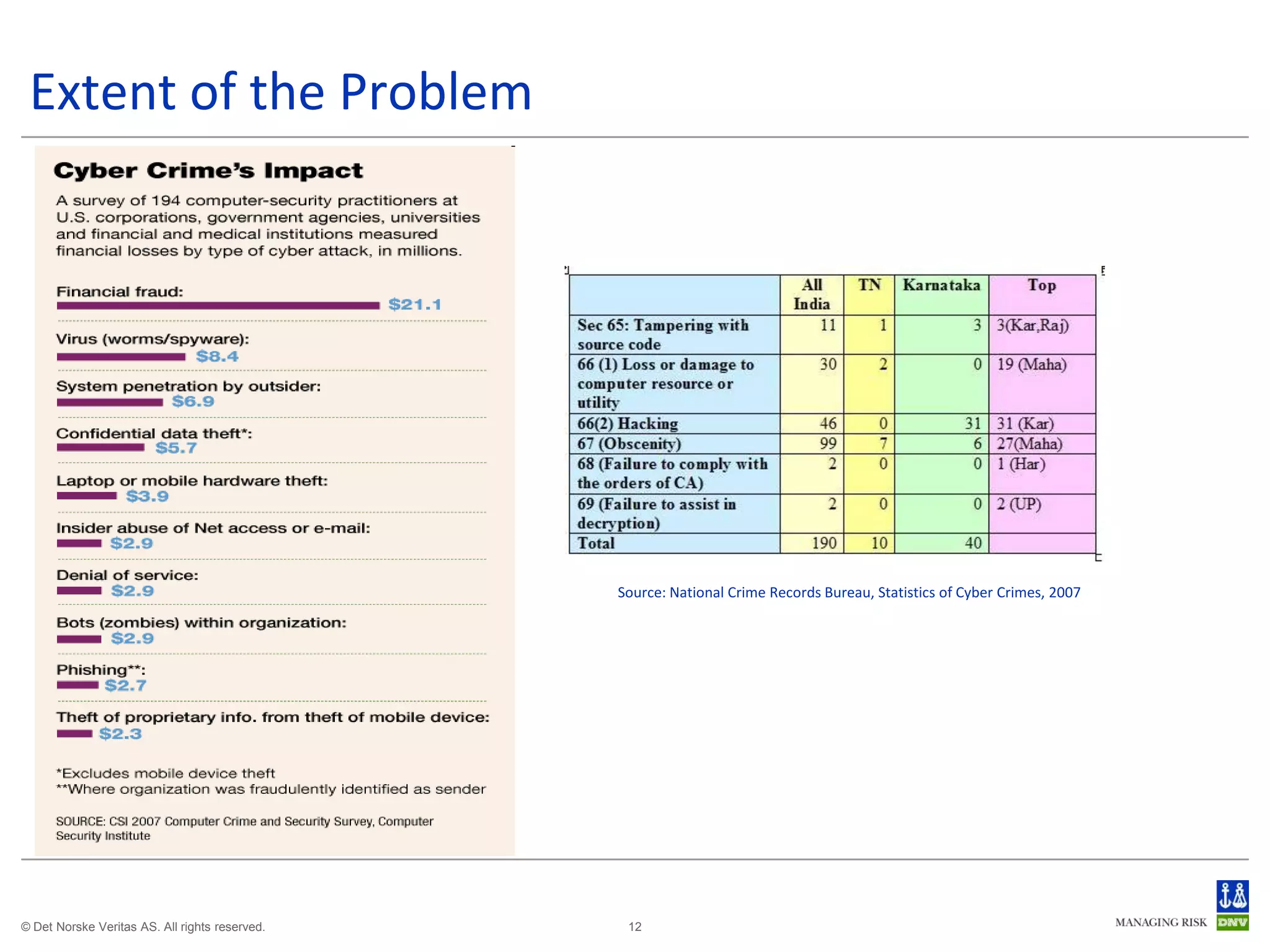
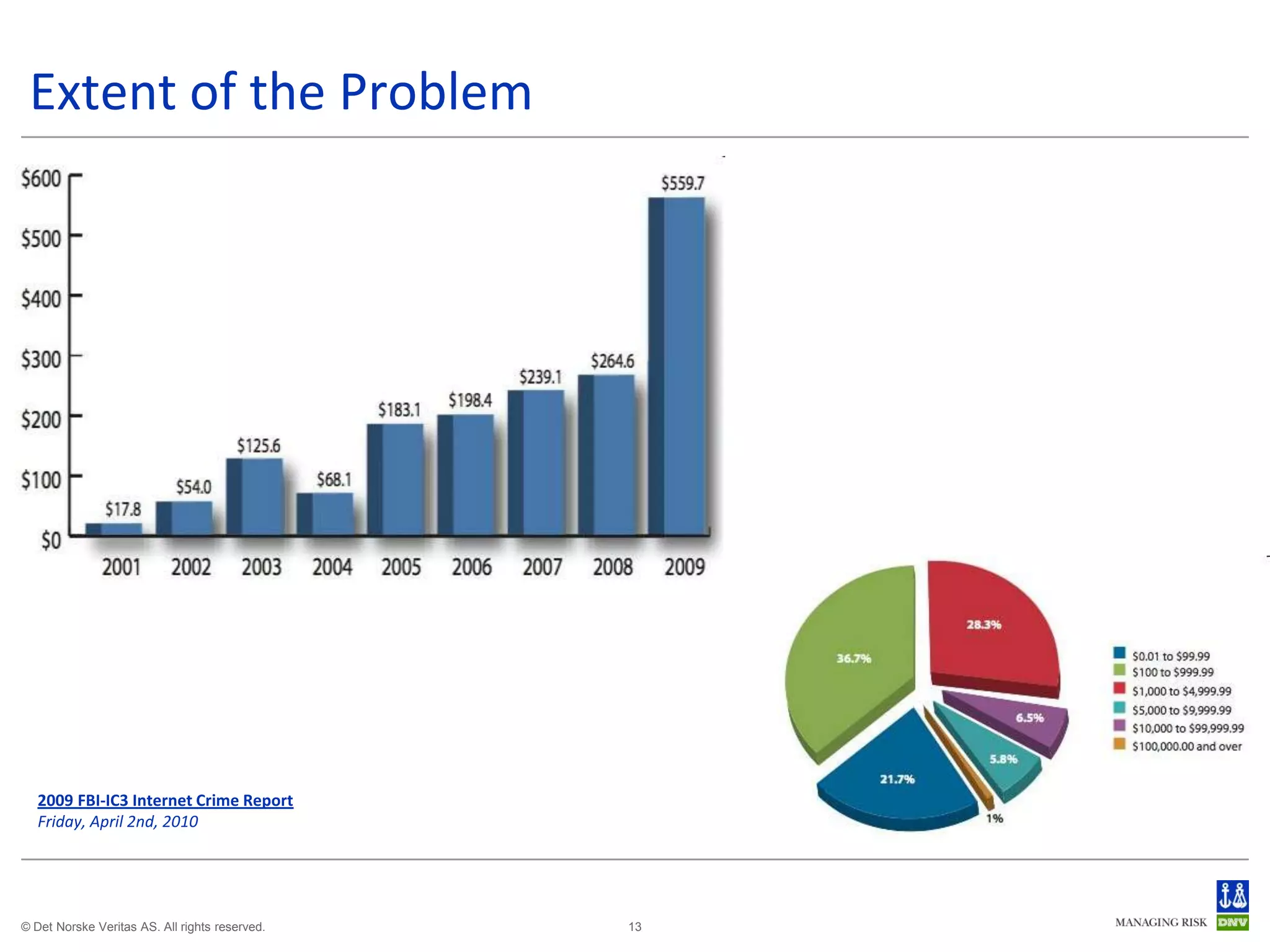
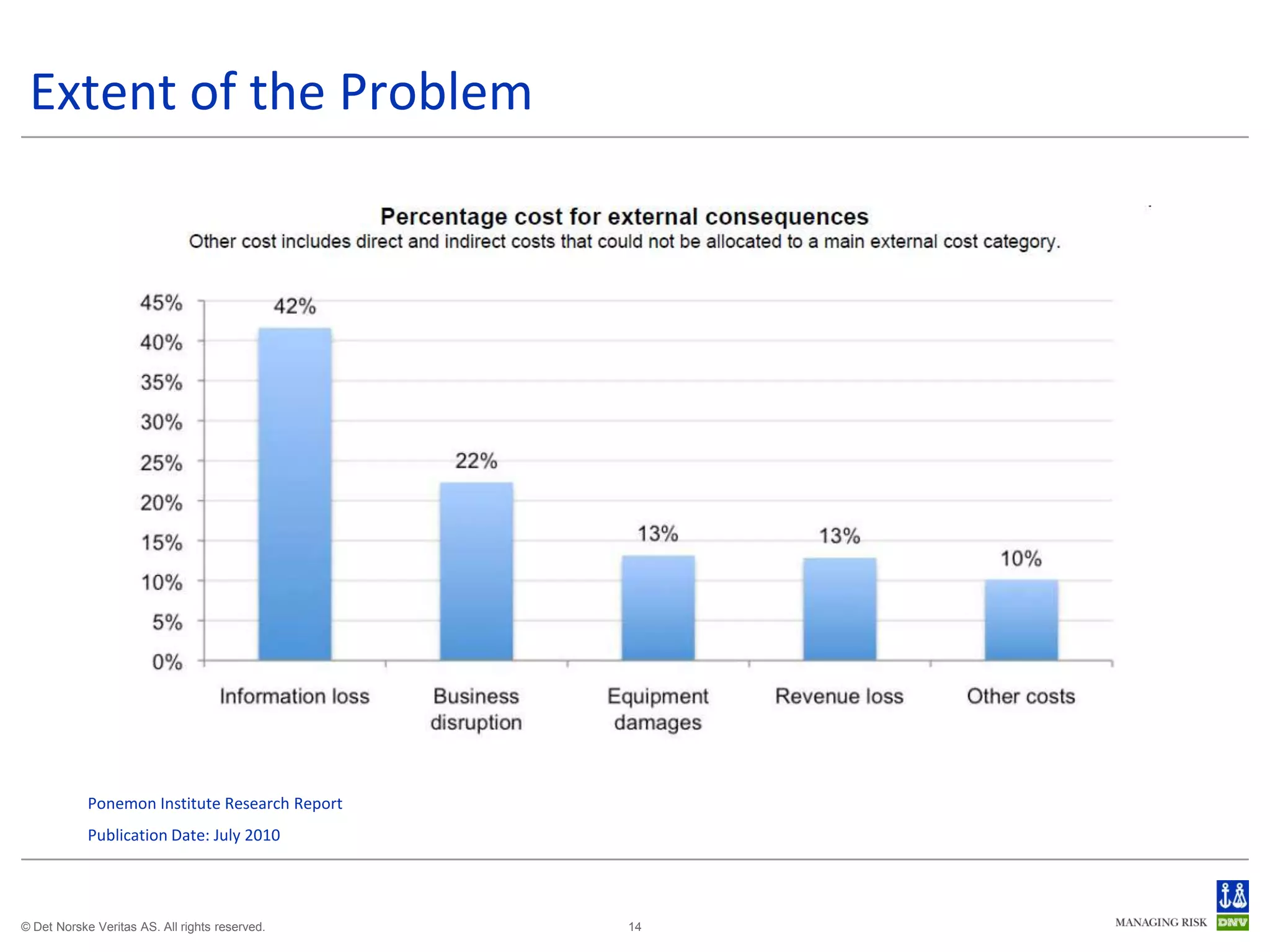
The document discusses cyber crimes and IT risk management. It describes the nature of cyber crimes, highlighting that they can often be committed across jurisdictions without physical presence. It also outlines various types of cyber crimes and security challenges in India given its increasing reliance on technology. The document advocates implementing security systems and processes as well as following information security frameworks and standards to combat cyber crimes and manage IT risks.















![ISO 27000 Series - Published standards
ISO/IEC 27000 — Information security management systems — Overview and vocabulary
ISO/IEC 27001 — Information security management systems — Requirements
ISO/IEC 27002 — Code of practice for information security management
ISO/IEC 27003 — Information security management system implementation guidance
ISO/IEC 27004 — Information security management — Measurement
ISO/IEC 27005 — Information security risk management
ISO/IEC 27006 — Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of information
security management systems
ISO/IEC 27011 — Information security management guidelines for telecommunications
organizations based on ISO/IEC 27002
ISO/IEC 27033-1 - Network security overview and concepts
ISO 27799 - Information security management in health using ISO/IEC 27002 [standard
produced by the Health Infomatics group within ISO, independently of ISO/IEC JTC1/SC27]
© Det Norske Veritas AS. All rights reserved. 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snandakumar-101221054056-phpapp01/75/S-nandakumar-26-2048.jpg)


![Cyber Crimes and Law
Electronic Signature Laws
U.S. - Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act
U.S. - Uniform Electronic Transactions Act - adopted by 46 states
U.S. - Digital Signature And Electronic Authentication Law
U.S. - Government Paperwork Elimination Act (GPEA)
U.S. - The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC)
UK - s.7 Electronic Communications Act 2000
European Union - Electronic Signature Directive (1999/93/EC)
Mexico - E-Commerce Act [2000]
Costa Rica - Digital Signature Law 8454 (2005)
Australia - Electronic Transactions Act 1999 (Cth) (also note that there is State and Territory mirror legislation)
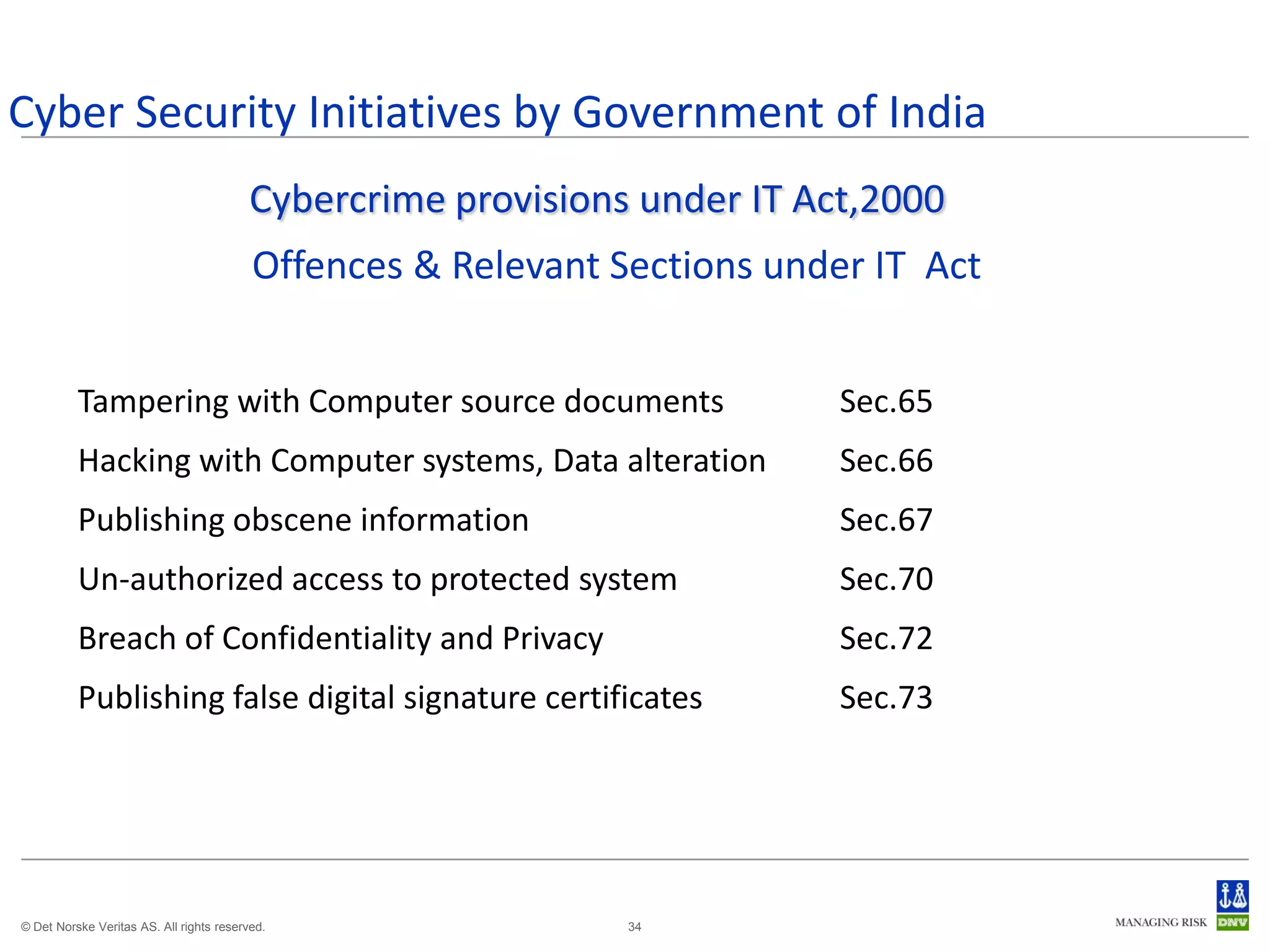
Information Technology Act 2000 of India
Information Technology Laws
Computer Misuse Act 1990
Florida Electronic Security Act
Illinois Electronic Commerce Security Act
Texas Penal Code - Computer Crimes Statute
Maine Criminal Code - Computer Crimes
Singapore Electronic Transactions Act
Malaysia Computer Crimes Act
Malaysia Digital Signature Act
UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Commerce
Information Technology Act 2000 of India
© Det Norske Veritas AS. All rights reserved. 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/snandakumar-101221054056-phpapp01/75/S-nandakumar-33-2048.jpg)