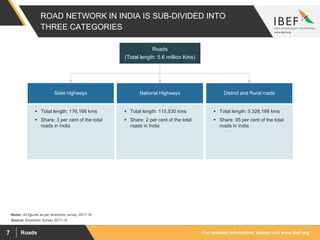
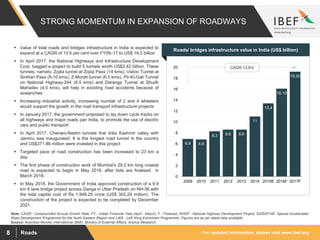
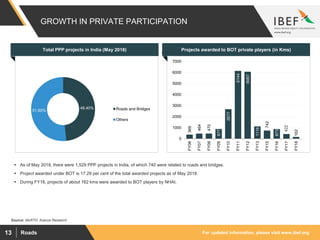
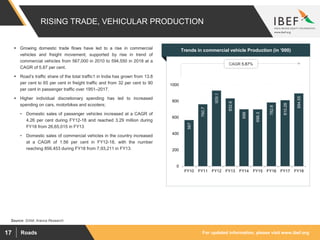
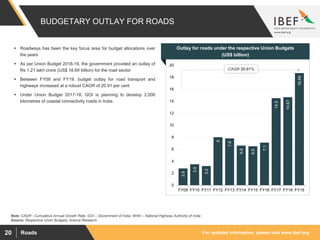
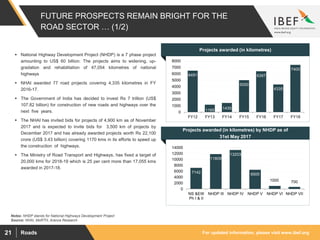
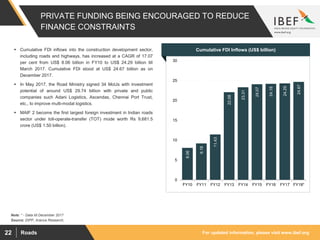
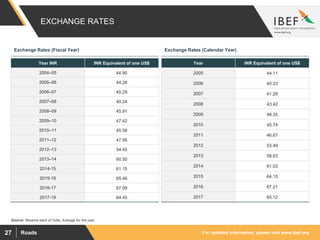
The document discusses India's road network and the road infrastructure sector. It notes that India has one of the largest road networks in the world spanning over 5.6 million km. There has been rising budget allocation and private sector investment in road development projects. The government aims to increase the length of national highways from 122,432 km currently to 200,000 km and accelerate the pace of highway construction. Various initiatives are being taken to boost road infrastructure development in the northeastern region and areas affected by left wing extremism.