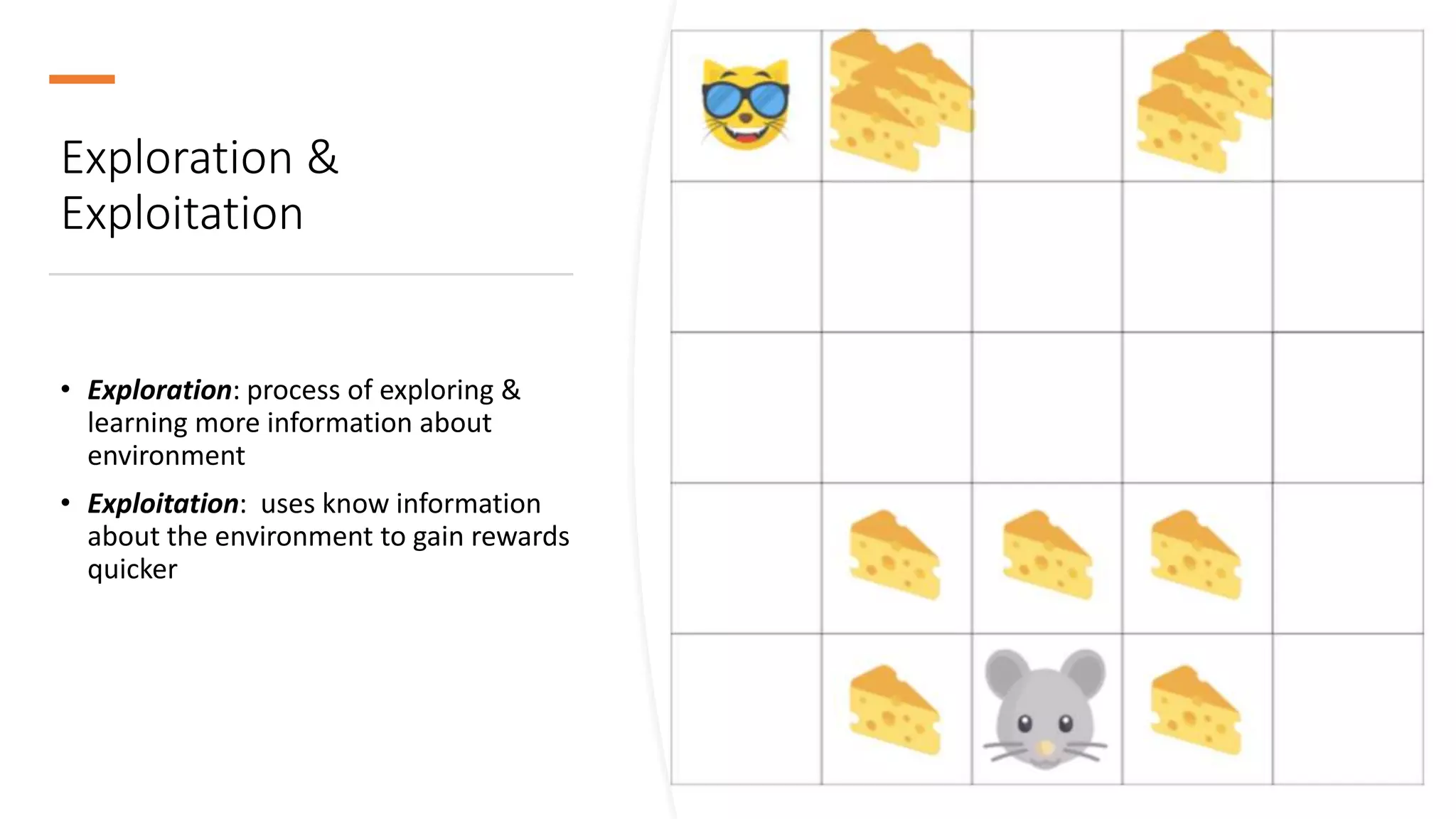
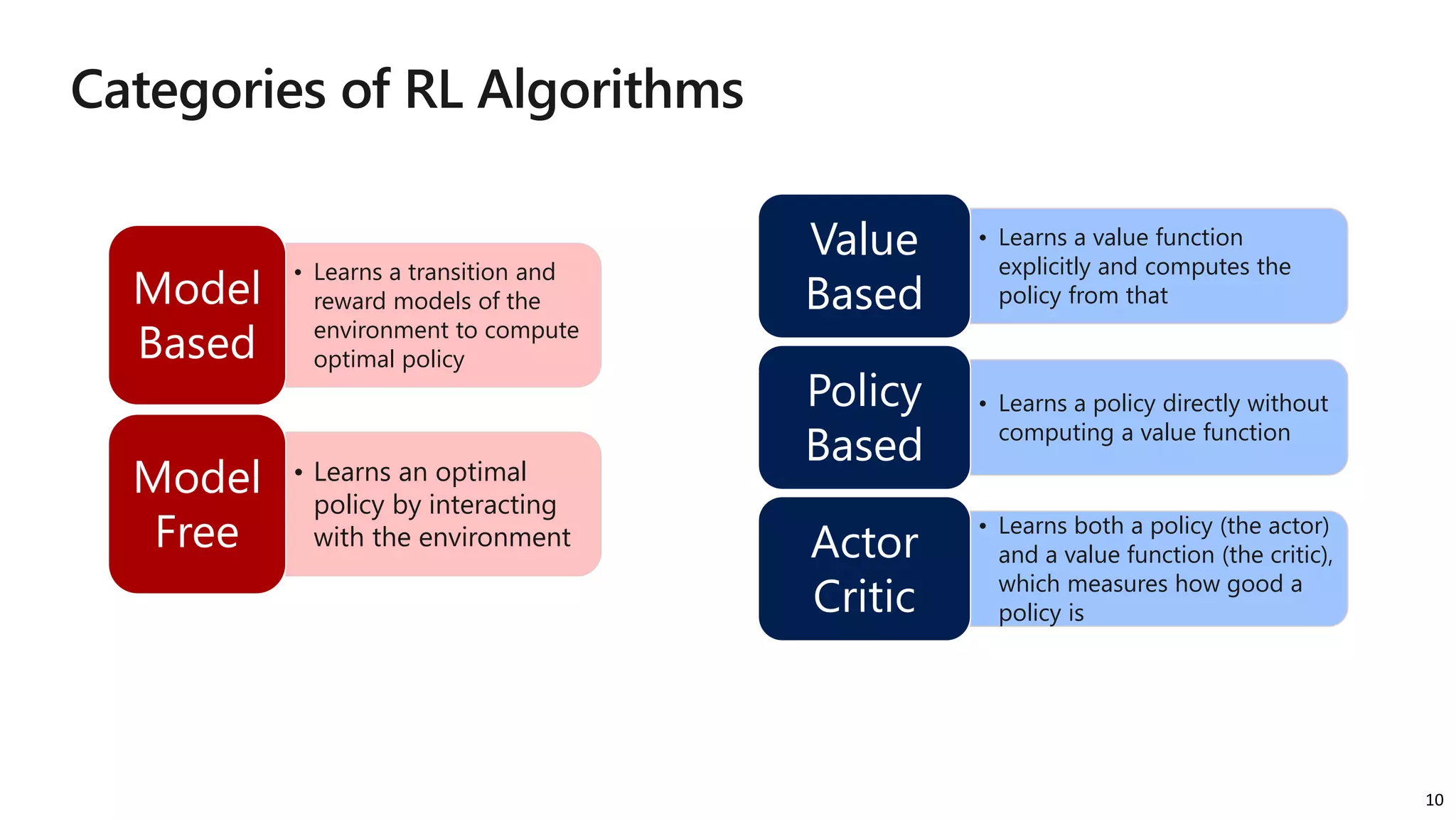
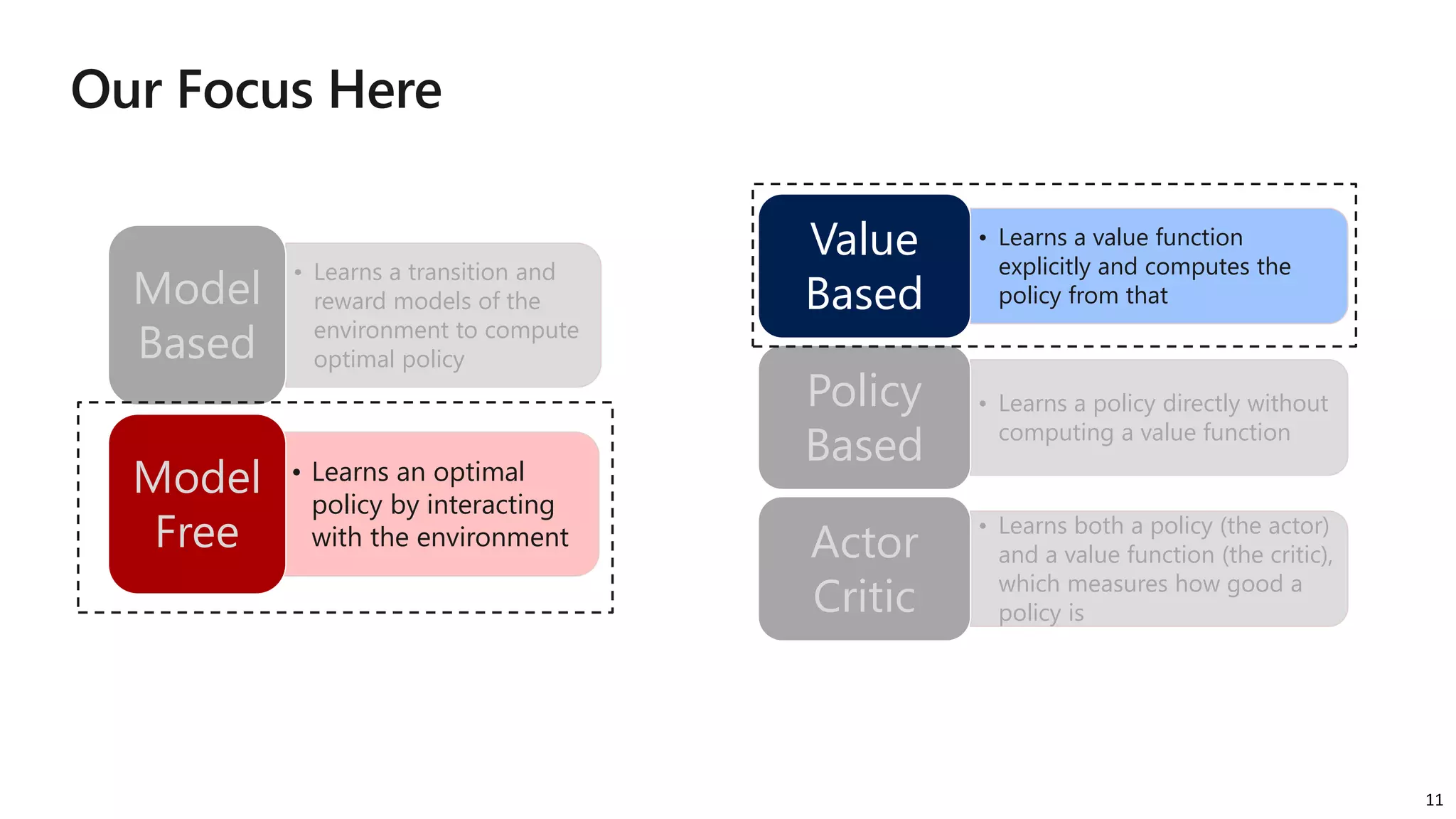
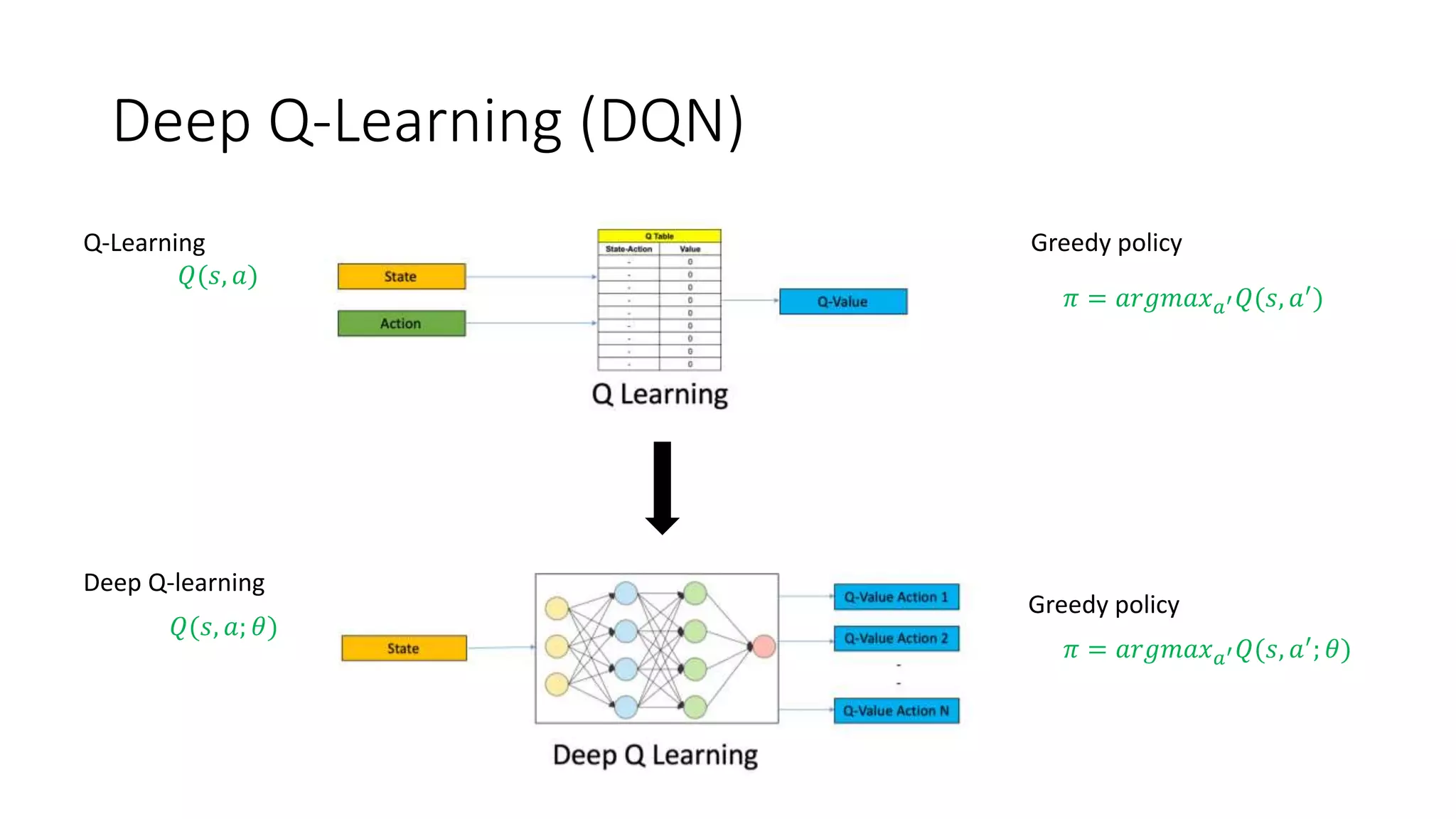
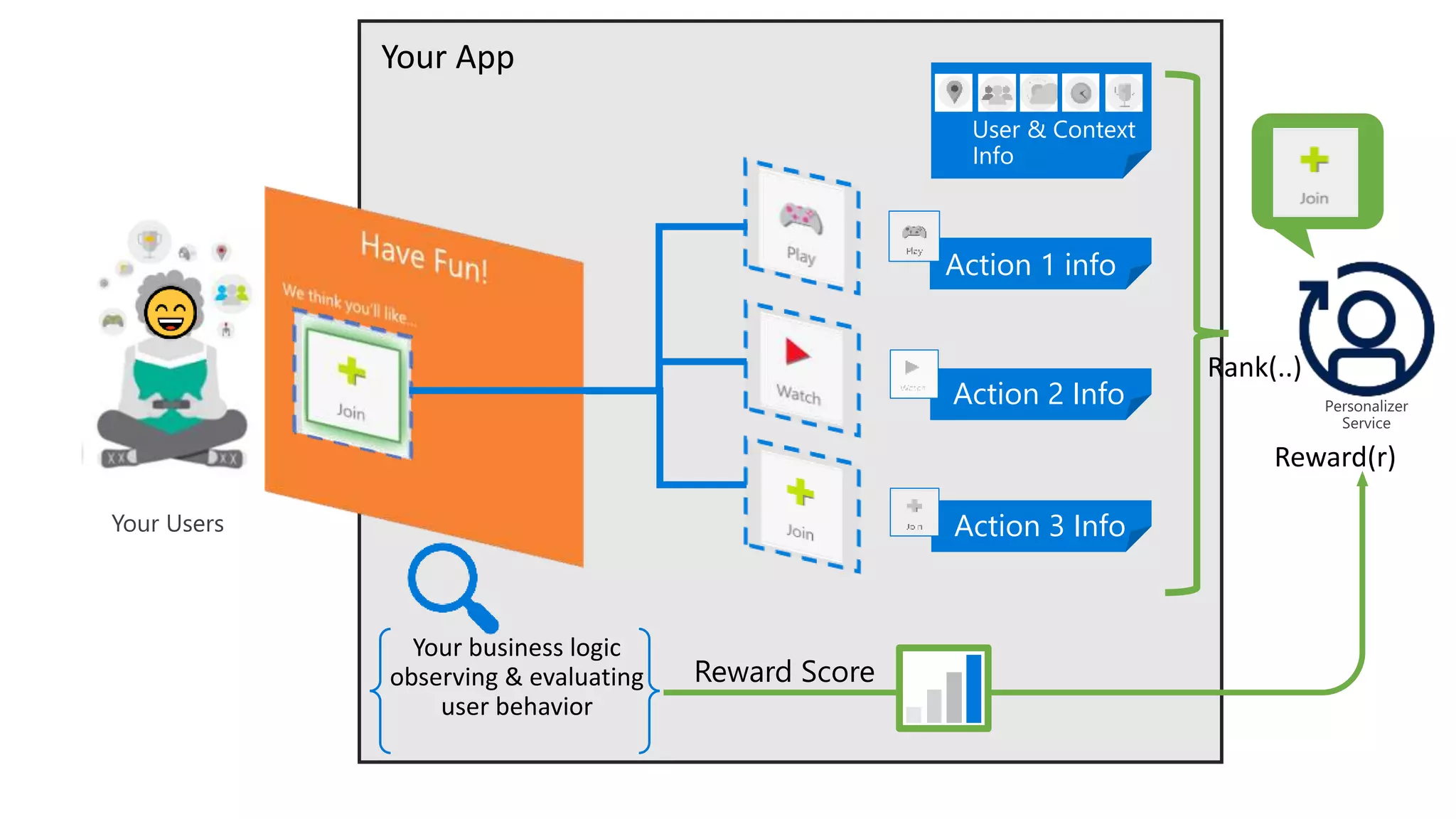
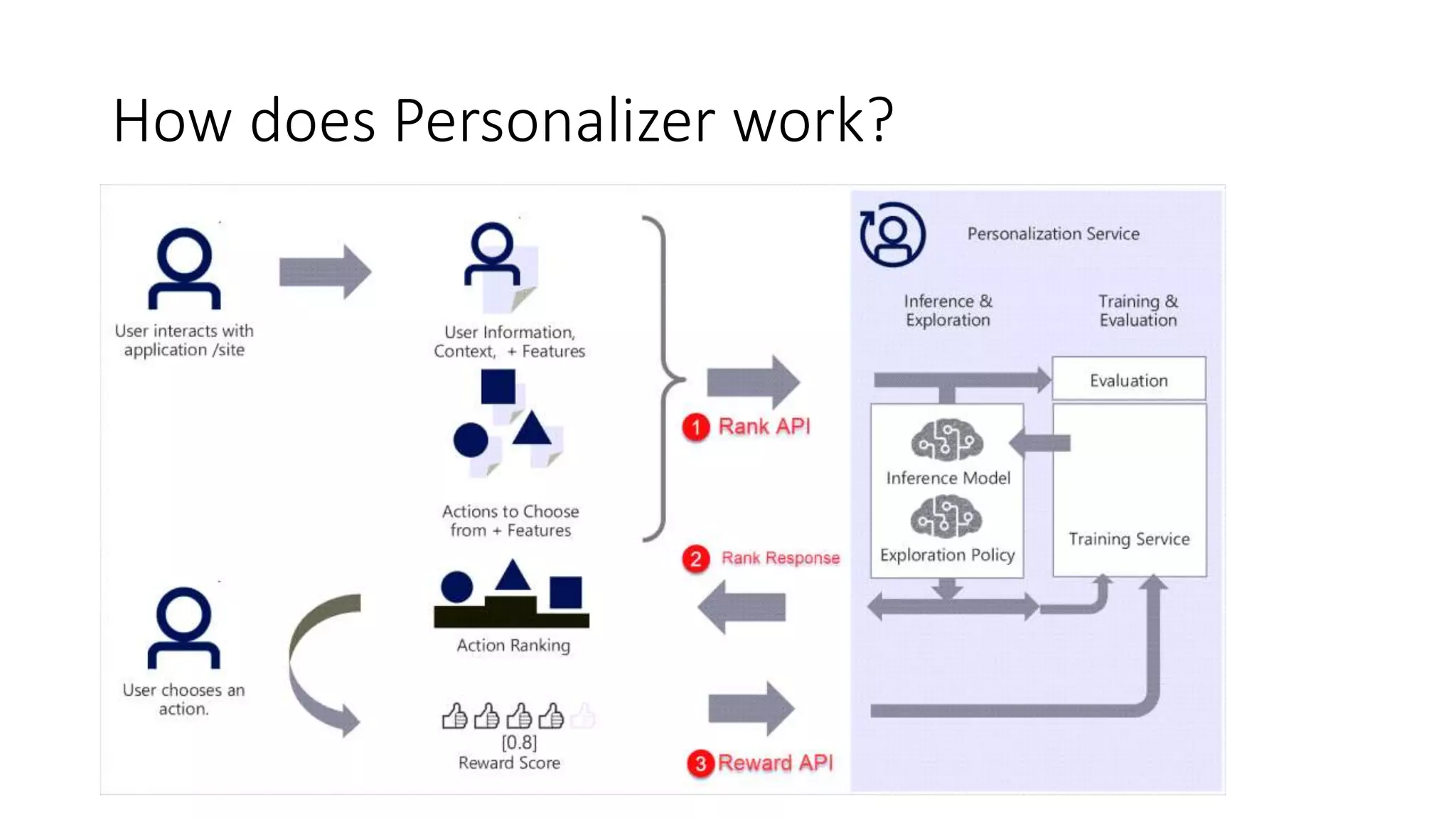
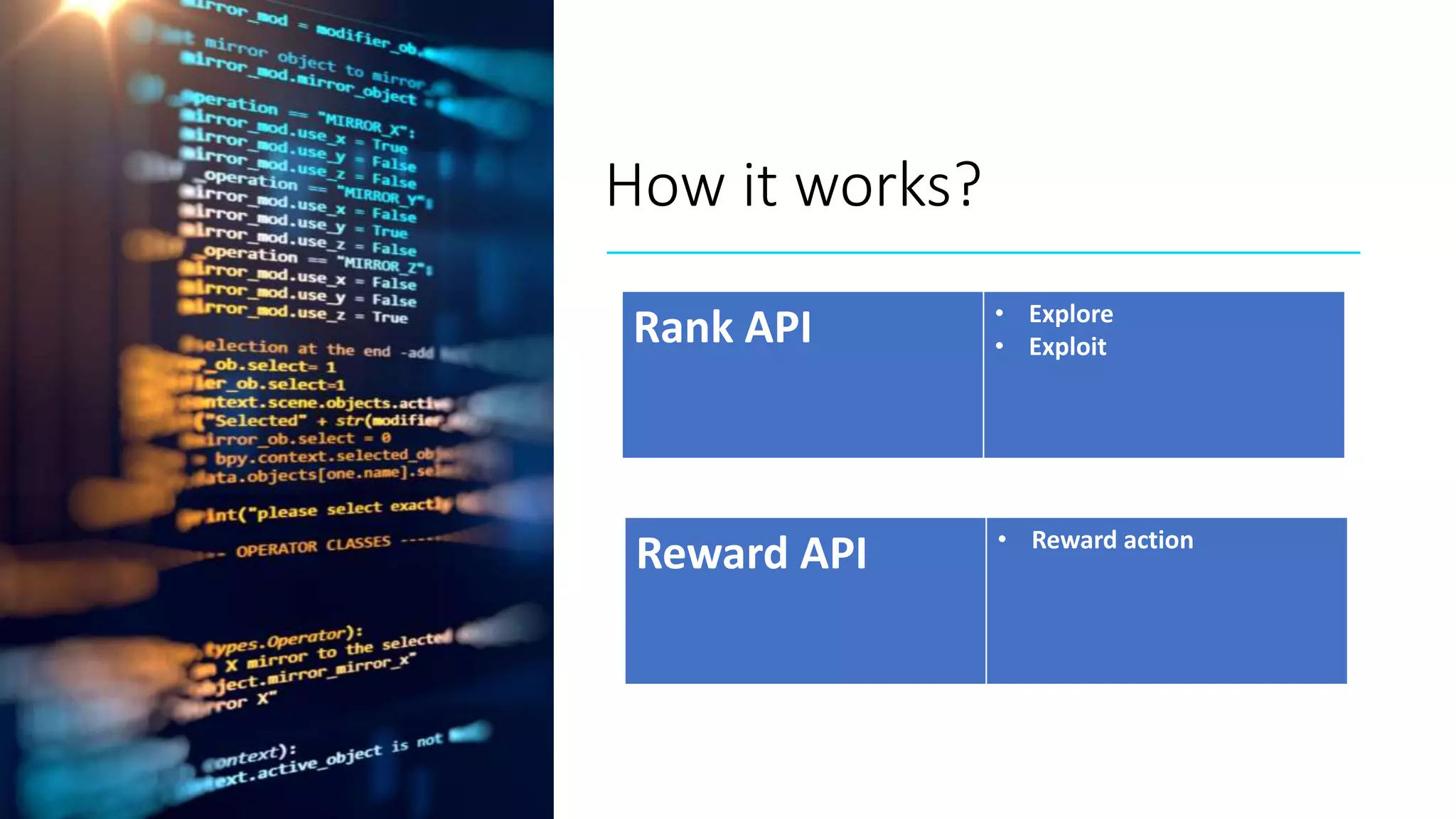
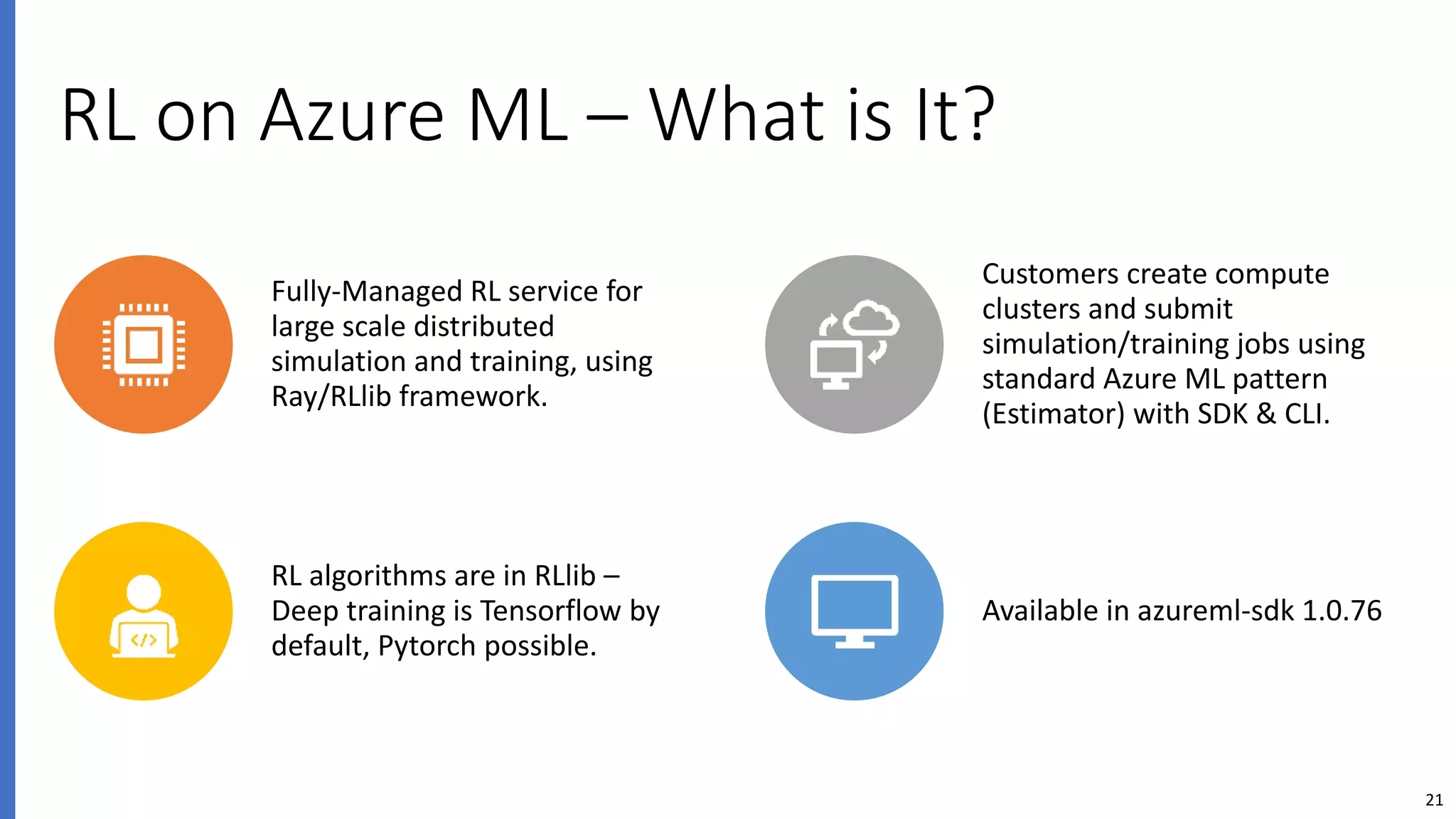
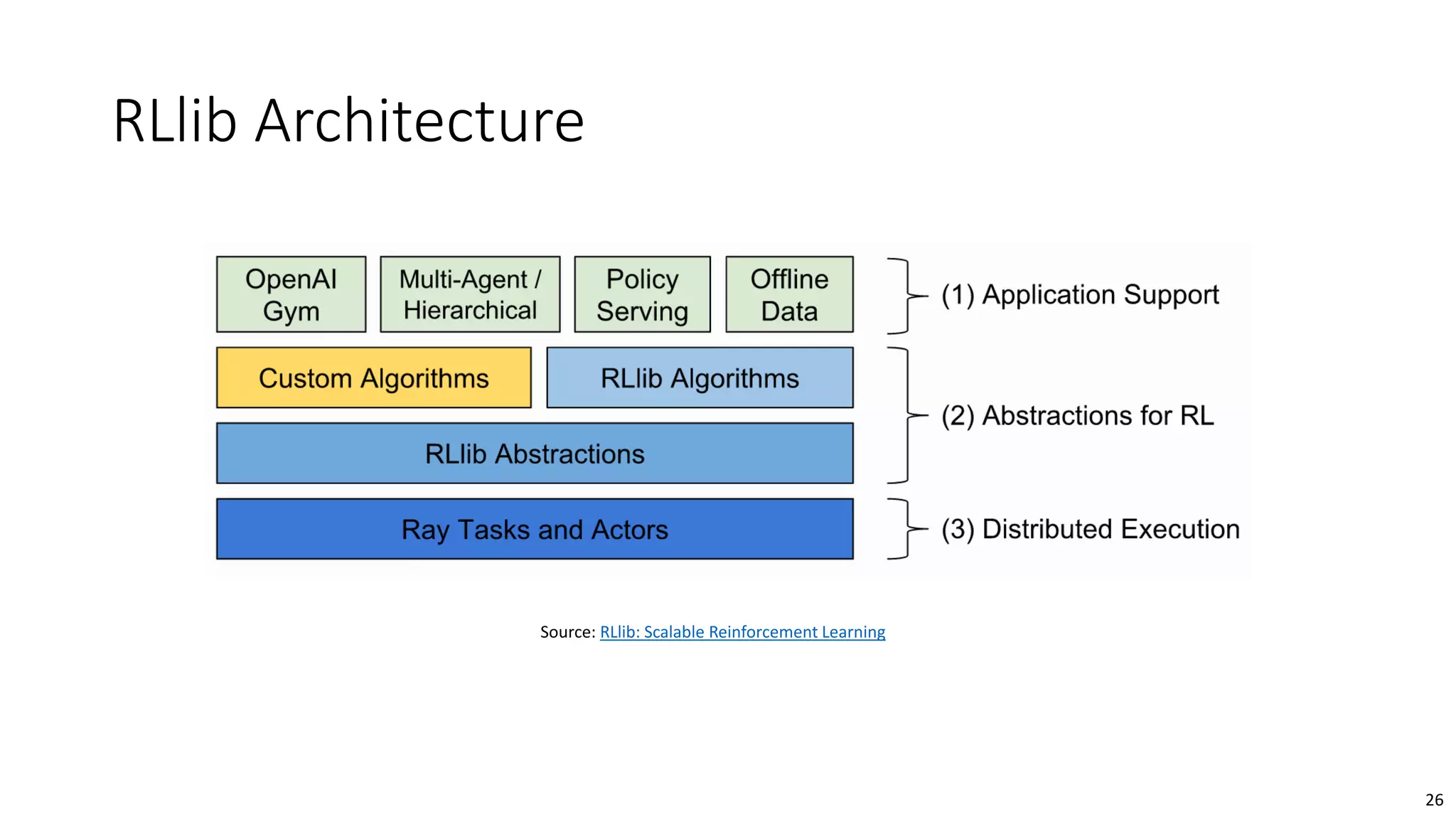
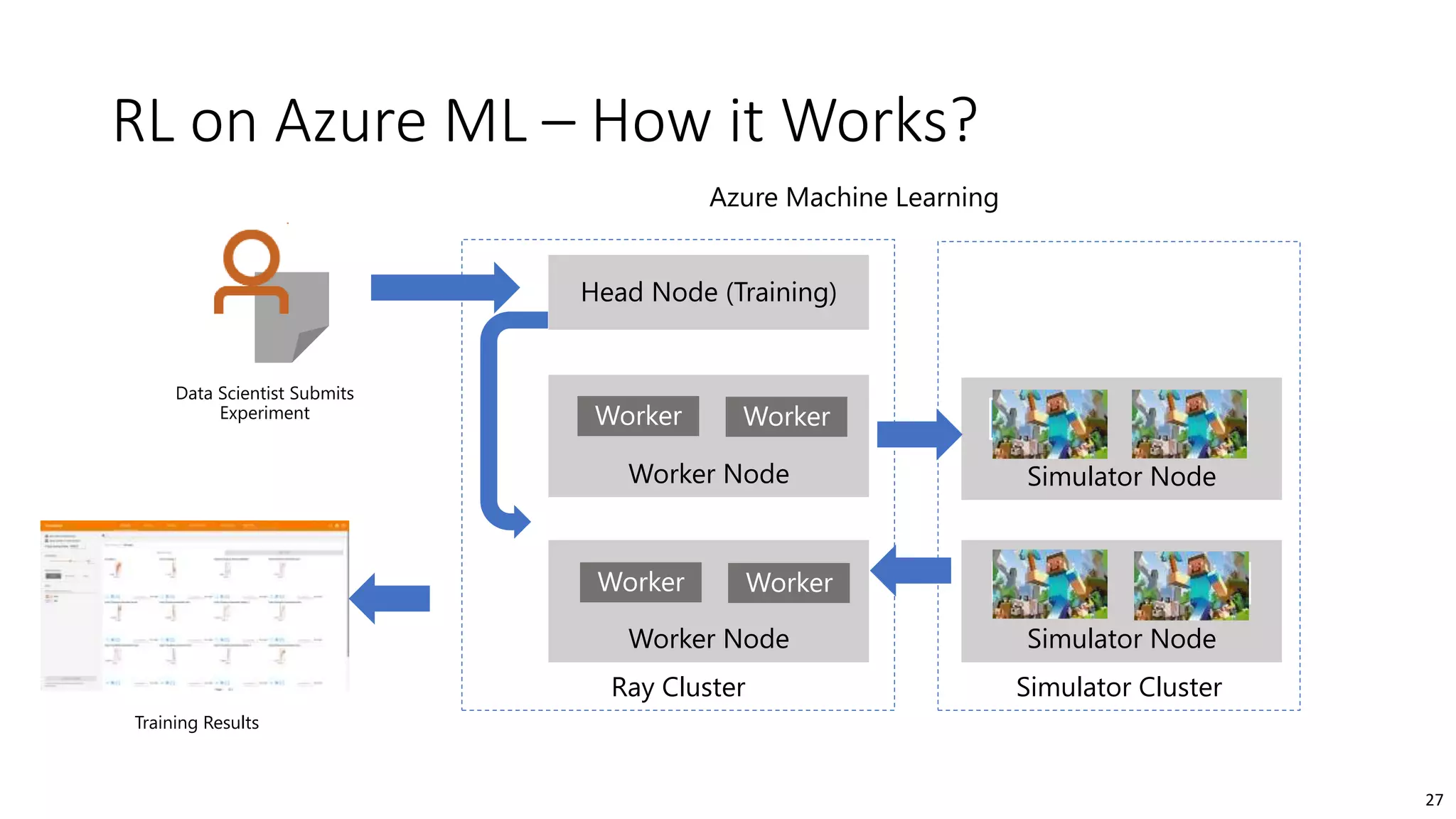
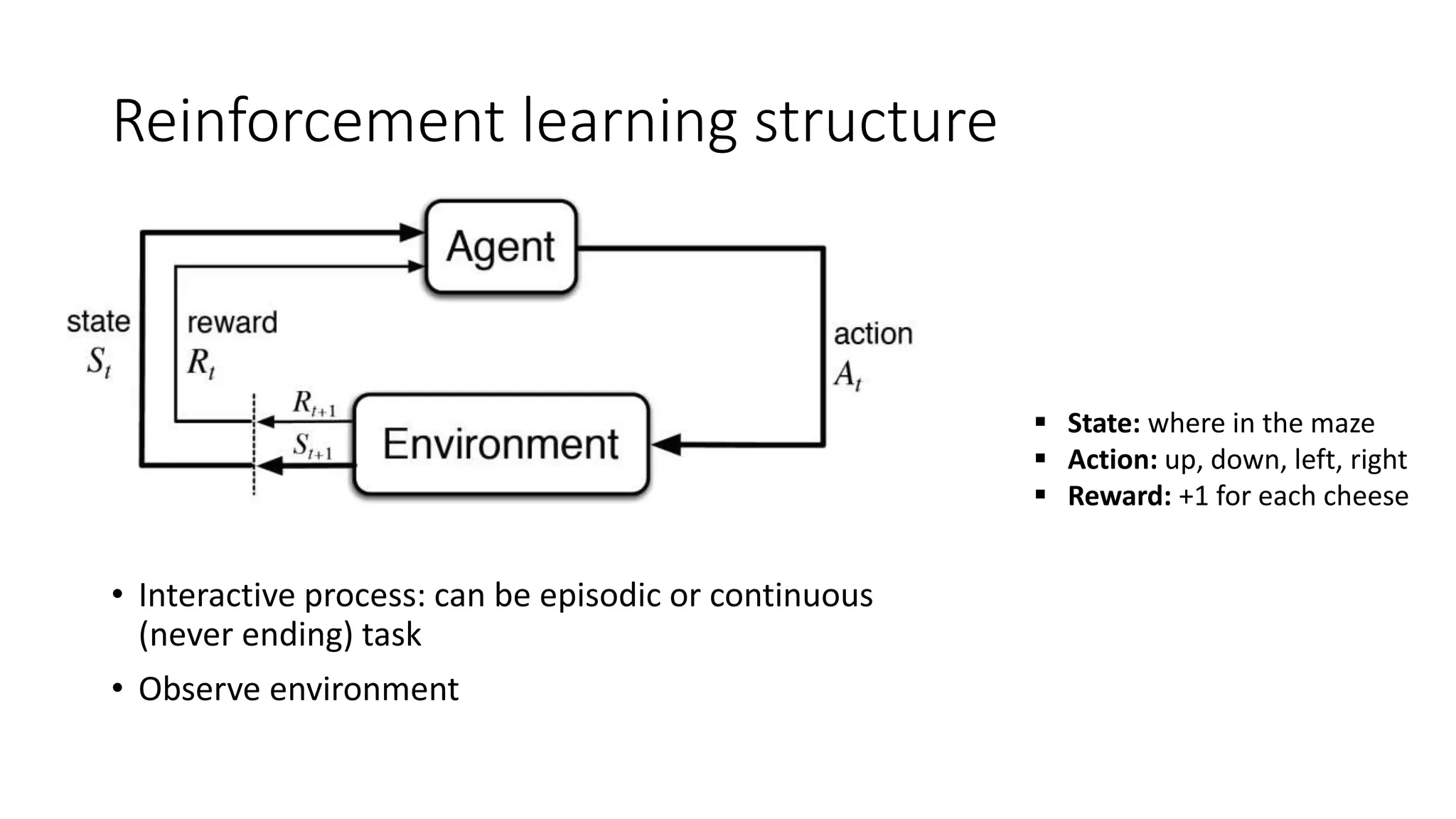
The document provides an overview of reinforcement learning (RL) concepts, challenges, and algorithms, including Q-learning methods and exploration strategies. It also discusses Azure Personalizer, a service utilizing RL for personalized user experiences, and introduces the Ray/RLlib framework for large-scale RL simulations on Azure ML. The document concludes with examples of RL use cases and demonstrations of RL in action.





![7
Q-Learning Algorithm
Start with 𝑄∗ 𝑠, 𝑎 = 0 for all 𝑠, 𝑎
Get initial state 𝑠
Repeat until convergence of 𝑄∗:
Select action 𝑎 and get immediate reward 𝑟 and next state 𝑠′
Update Q-value and current state:
𝑄∗
𝑠, 𝑎 ← 𝑅∗
𝑠, 𝑎 + 𝐺𝑎𝑚𝑚𝑎 ∗ 𝑀𝑎𝑥[𝑄 𝑛𝑒𝑥𝑡 𝑠, 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑎 ]
Type equation here.
Note: Gamma is a discount value that ranges between 0 and 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reinforcementlearning-azureml-200831210506/75/Making-smart-decisions-in-real-time-with-Reinforcement-Learning-7-2048.jpg)