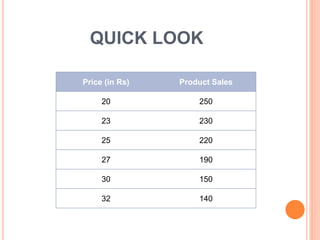
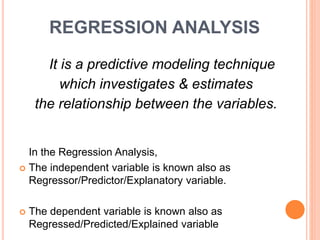
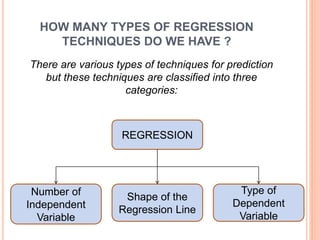
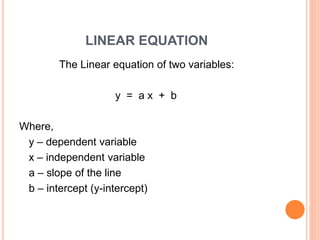
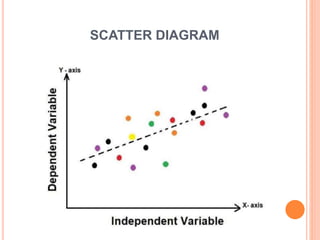
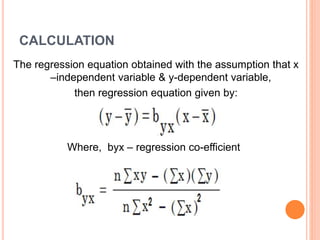
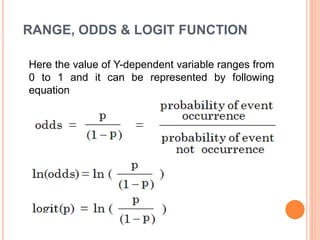
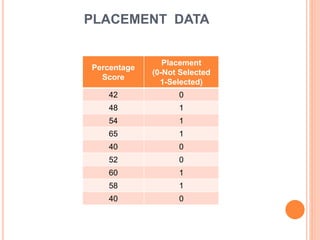
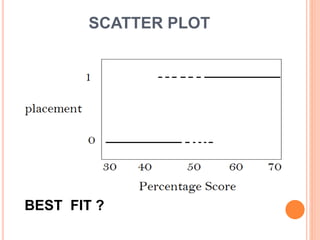
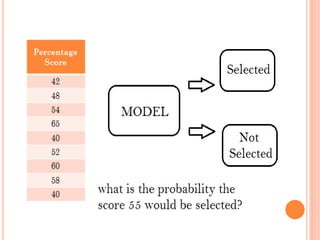
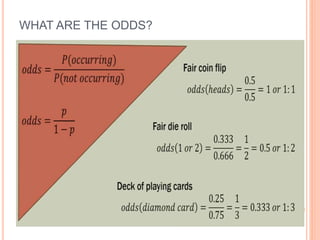
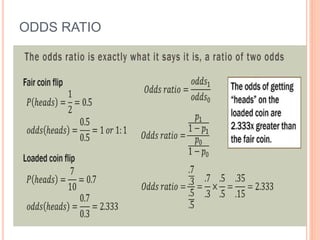
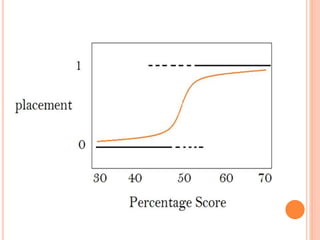
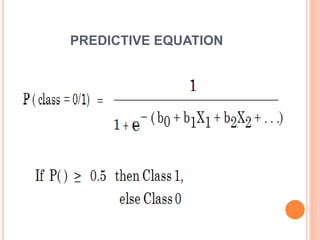
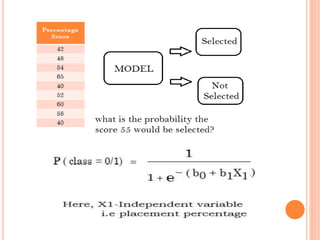
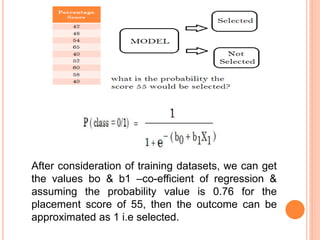
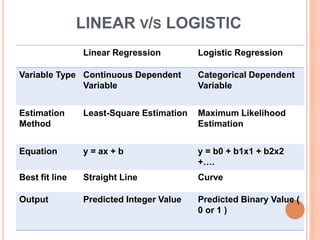
This document discusses regression analysis techniques. It defines regression as the tendency for estimated values to be close to actual values. Regression analysis investigates the relationship between variables, with the independent variable influencing the dependent variable. There are three main types of regression: linear regression which uses a linear equation to model the relationship between one independent and one dependent variable; logistic regression which predicts the probability of a binary outcome using multiple independent variables; and nonlinear regression which models any non-linear relationship between variables. The document provides examples of using linear and logistic regression and discusses their key assumptions and calculations.