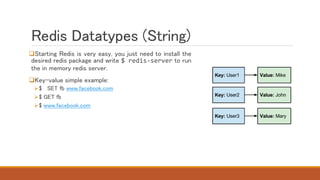
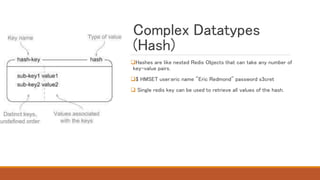
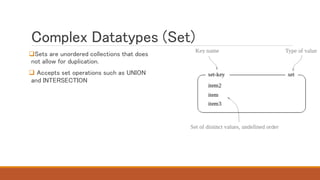
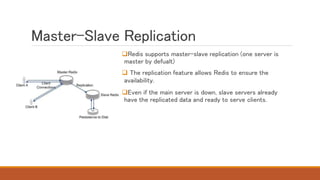
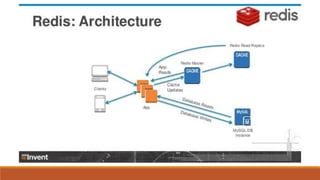
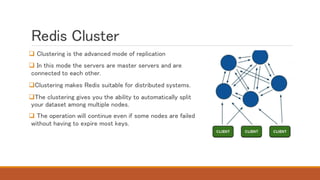
Redis is an in-memory data structure store that can be used as a database, cache, or message broker. It supports various data types like strings, hashes, lists, and sets. Data can be persisted to disk for durability. Redis guarantees consistency through append-only files and availability through master-slave replication and clustering, where data is automatically distributed across multiple nodes.