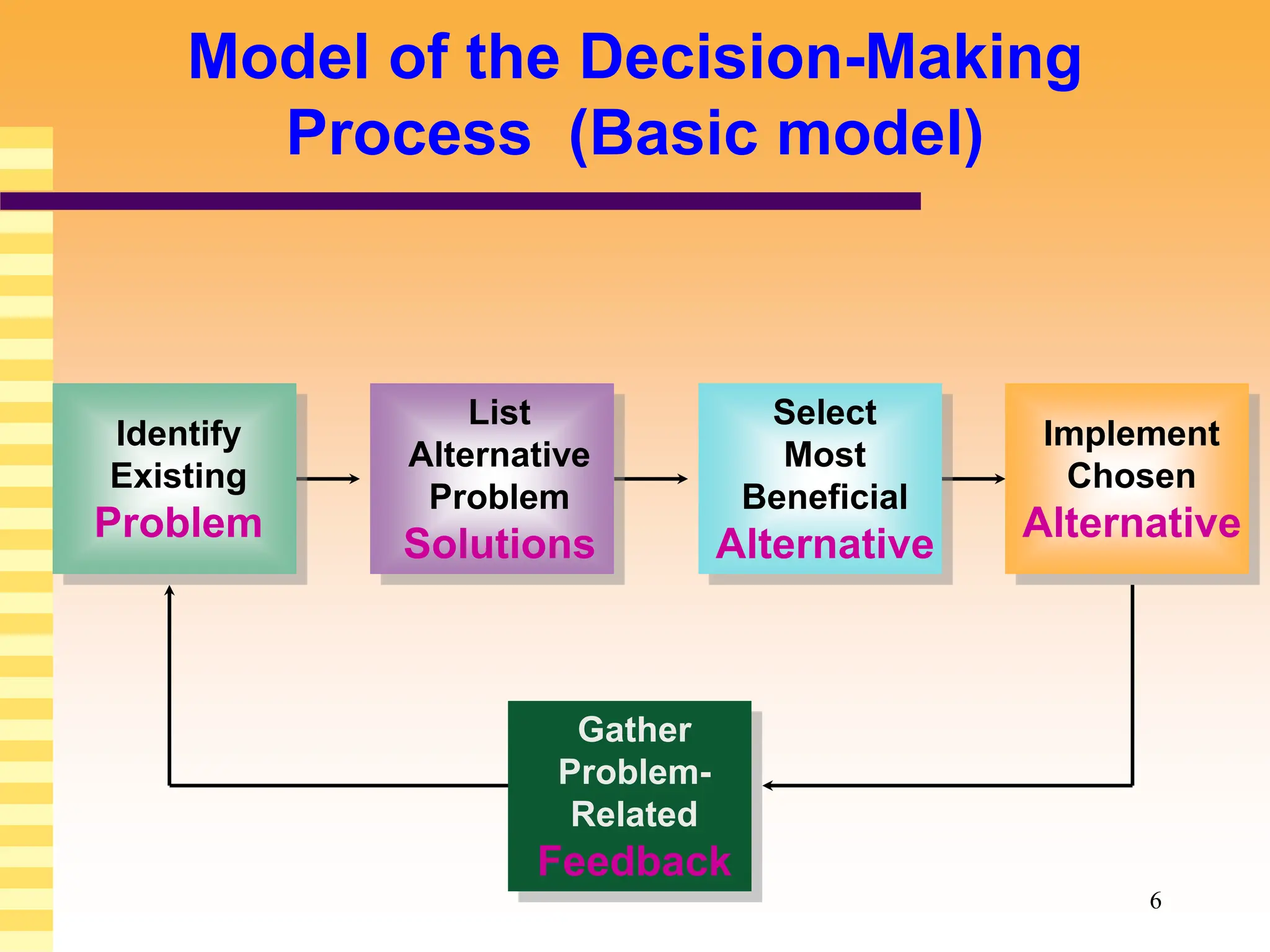
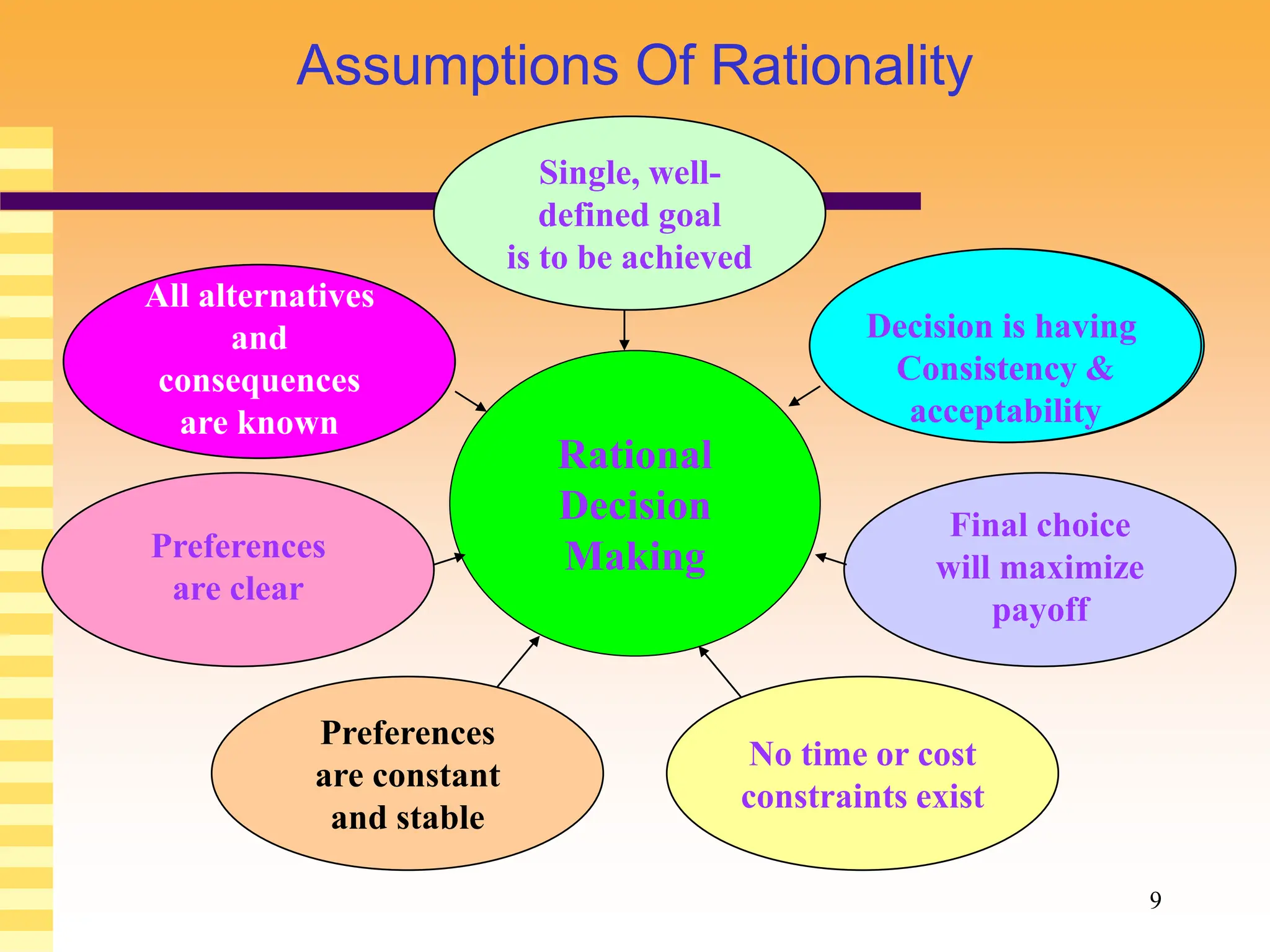
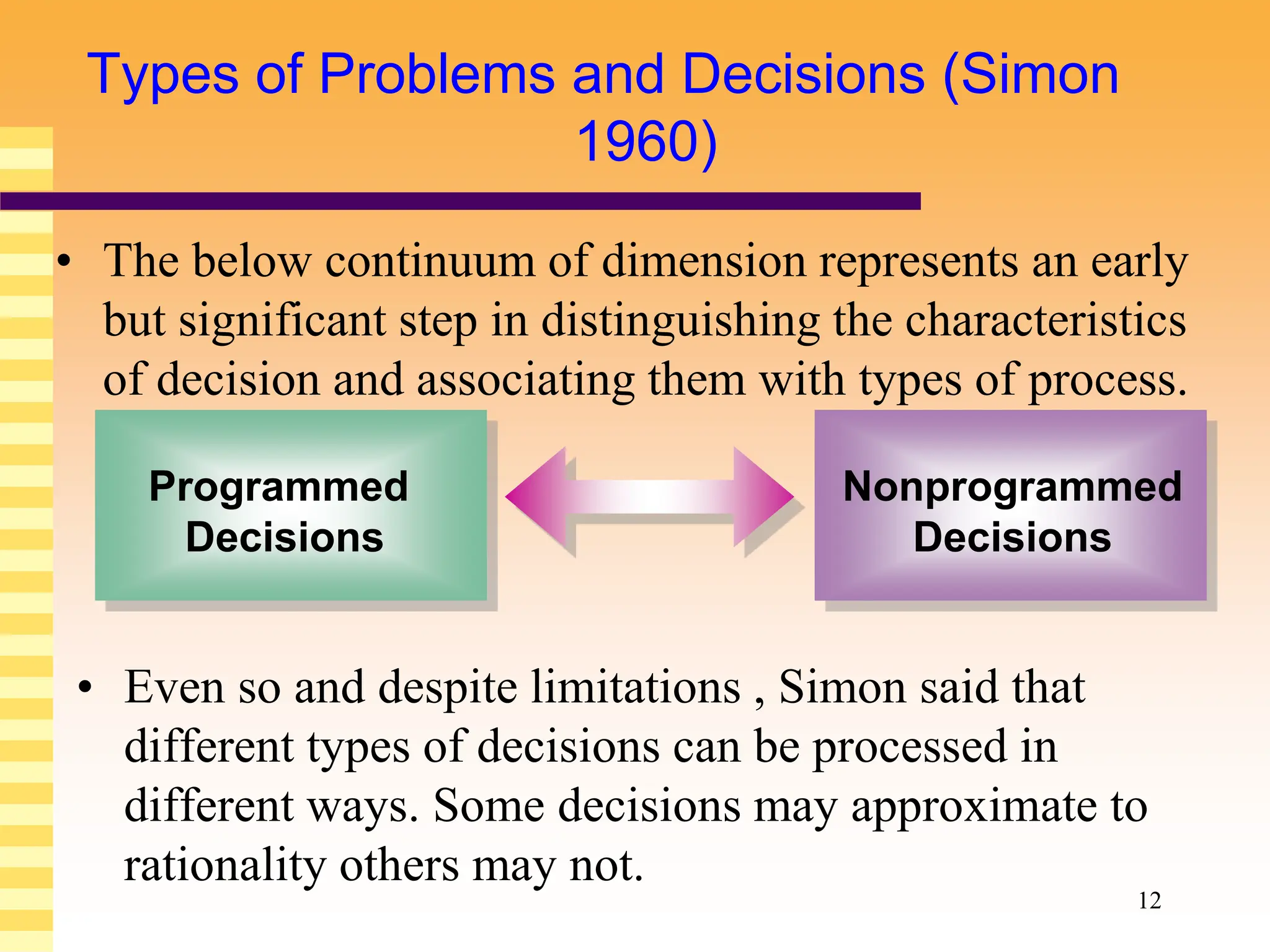
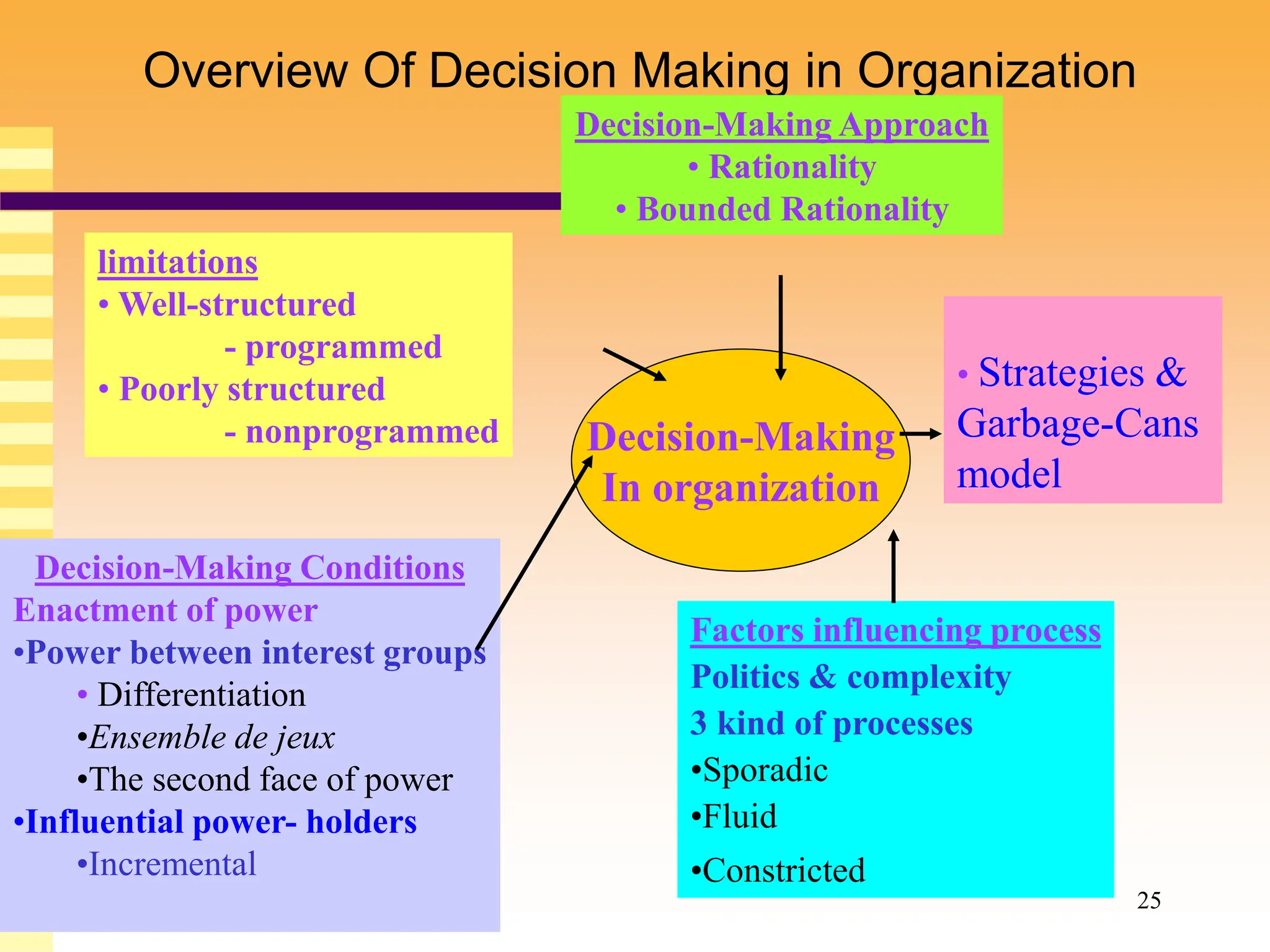
The document discusses various models and theories of decision making in organizations. It describes rational decision making models which assume managers make optimal objective choices, but notes these models ignore limitations like bounded rationality. Decision processes can vary from sporadic to fluid depending on factors like politics and complexity. Alternative models like garbage can theory view decision making as more chaotic, with problems, solutions, participants and choices colliding randomly. Overall, the document examines both rational and more behavioral perspectives on organizational decision making.