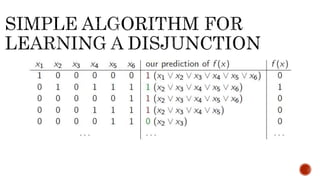
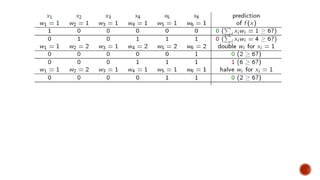
The document discusses random forest, an ensemble classifier that uses multiple decision tree models. It describes how random forest works by growing trees using randomly selected subsets of features and samples, then combining the results. The key advantages are better accuracy compared to a single decision tree, and no need for parameter tuning. Random forest can be used for classification and regression tasks.