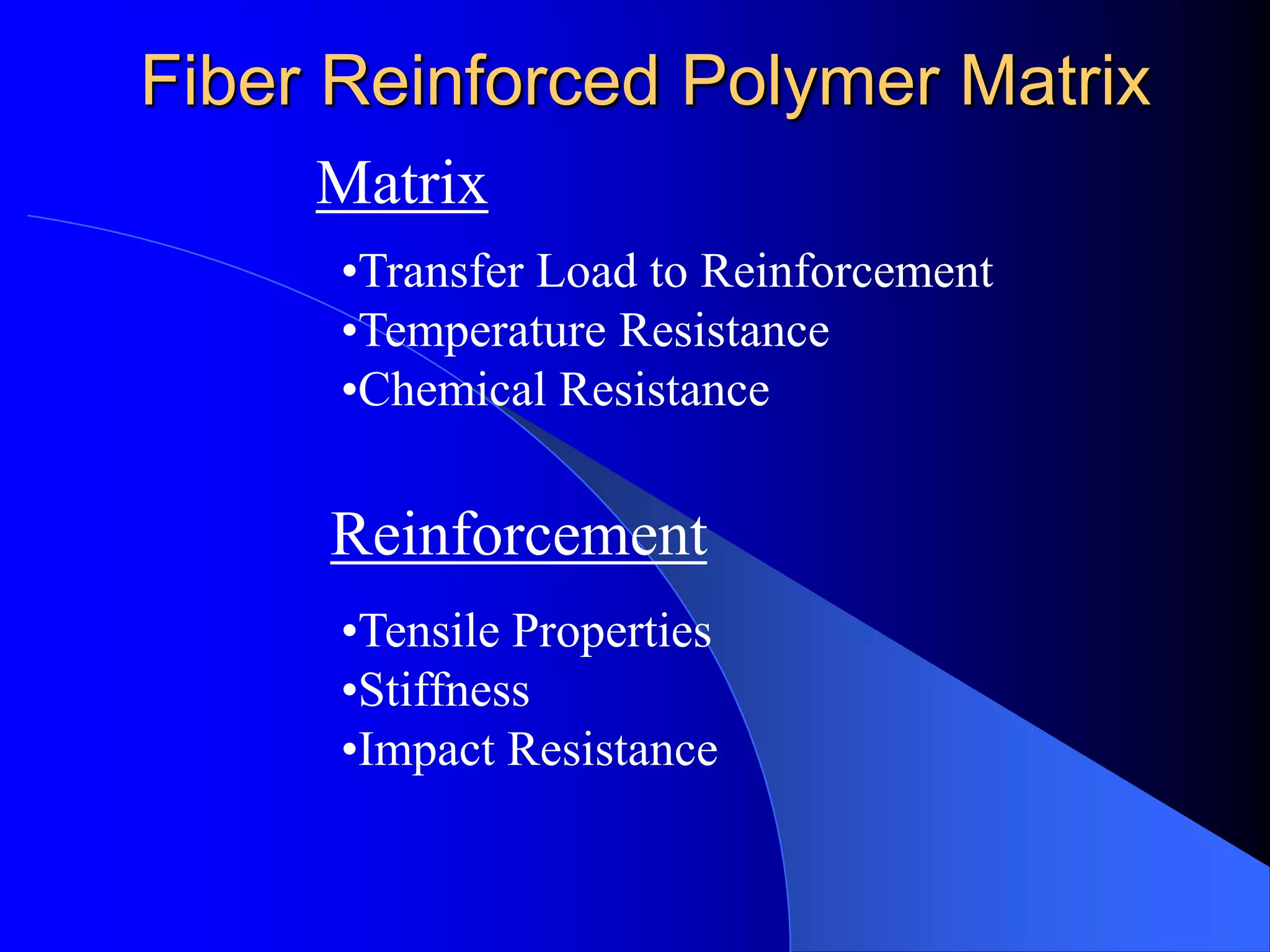
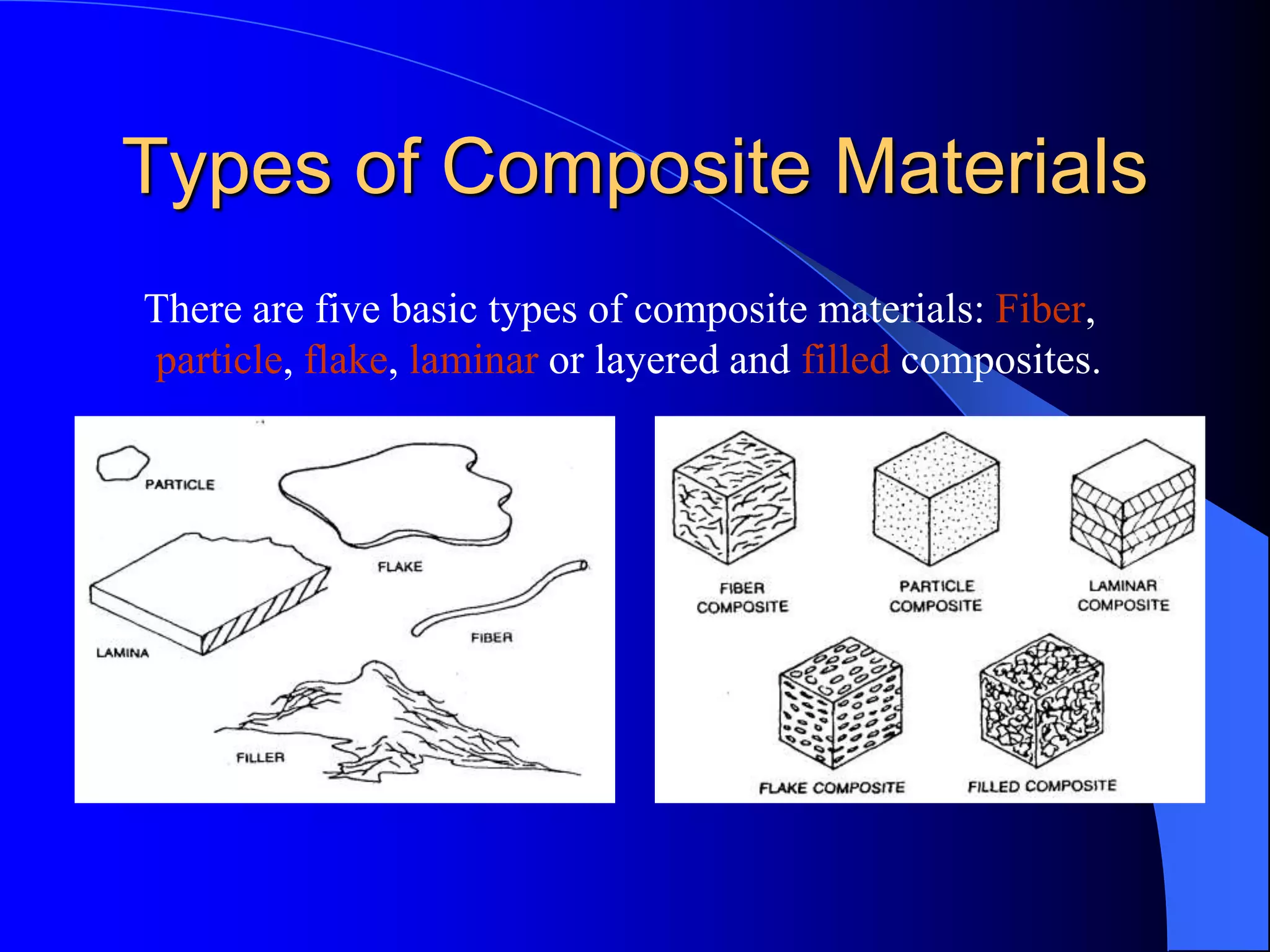
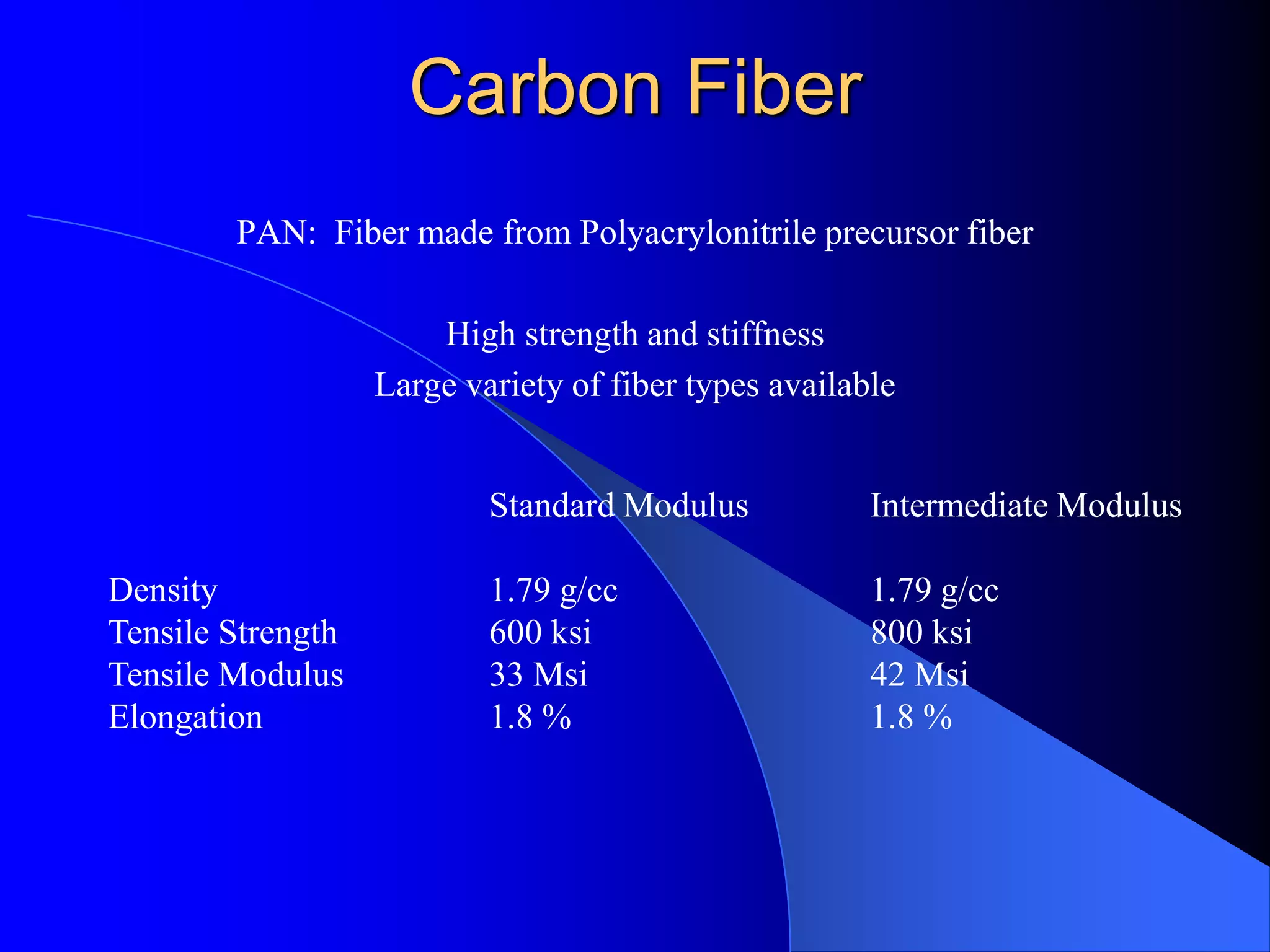
This document provides an introduction to composite materials. It defines composites as materials made of two or more inherently different materials that when combined produce properties exceeding the individual components. The matrix holds the reinforcement and transfers load, while the reinforcement provides properties like strength and stiffness. Common matrix materials include epoxies, metals, and ceramics. Fiber reinforcements include glass, carbon, and aramid fibers. The document discusses different types of composites and their applications, advantages like high strength and design flexibility, and disadvantages like anisotropic properties and difficulties in inspection.