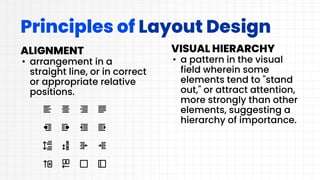
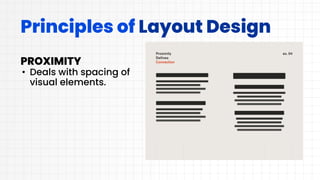
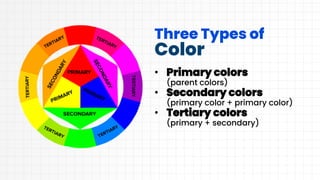
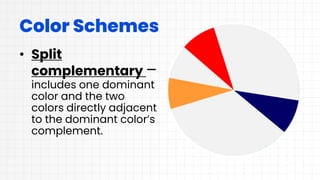
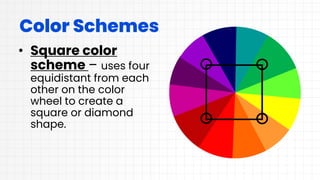
This document discusses layout design and color theory. It covers the principles of layout design including alignment, visual hierarchy, contrast, balance, proximity, and the elements of layout design such as color, line, value, space, and texture. It then discusses color theory including primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. It explains hue, tint, tone, and shade. It also covers different color schemes like monochromatic, analogous, split complementary, triadic, square, and rectangle. It provides tips for choosing a color scheme such as prioritizing user experience, setting a mood, considering context, using the 60-30-10 rule, and drafting multiple designs.