Recommended
PPTX
Python_Programming_Presentation PRESENTATION
PPTX
Python Basic knowledge ppt for beginners
PPTX
Python_Introduction_Presentation.pptxhHaajhs
PPTX
Python_Introduction_Presentation.pptx gss sus
PPTX
Introduction to Python Programming for Beginner.pptx
PPTX
Introduction_to_Python_Presentation.pptx
PPTX
Introduction_to_Python_Presentation.pptx
PPTX
A Brief Introduction to Python - English
PPTX
Introduction of Python History and Features of Python, Installing Python and ...
PPTX
Introduction Of Python History And Features Of Python, Installing Python And ...
PPTX
Introduction Of Python History And Features Of Python..pptx
PPTX
Introduction-to-Python-Programming-Language (1).pptx
PPTX
introduction to python for programming using python
PPTX
Python presentation for engineering .pptx
PPTX
Python Basics for python understanding.pptx
PPTX
paython the Programming language .pptx
PDF
PPTX
Introduction to python for dummies
PPTX
trabalho ingles instrumental prof Anderson.pptx
PPTX
introduction to python in computer graphics.pptx
PDF
Python Presentation.pdf introduction of python programing
PDF
Overview and Introduction to Python-Programming
PDF
Brief Introduction to Python Programming
PDF
PPTX
Python_Programming_Filled_PPT.pptx PYTHON
PDF
Python Basics – Learn Coding from Scratch
PDF
Copy of Introduction to Python.
PDF
Introduction To Python For Beginners
PPTX
Mohan - "A man of silence and authority"
PPTX
Reimagining Academic Library Services through Artificial Intelligence: A Case...
More Related Content
PPTX
Python_Programming_Presentation PRESENTATION
PPTX
Python Basic knowledge ppt for beginners
PPTX
Python_Introduction_Presentation.pptxhHaajhs
PPTX
Python_Introduction_Presentation.pptx gss sus
PPTX
Introduction to Python Programming for Beginner.pptx
PPTX
Introduction_to_Python_Presentation.pptx
PPTX
Introduction_to_Python_Presentation.pptx
PPTX
A Brief Introduction to Python - English
Similar to Python_Full_Explanation_PPT.pptx Ginn Ruby
PPTX
Introduction of Python History and Features of Python, Installing Python and ...
PPTX
Introduction Of Python History And Features Of Python, Installing Python And ...
PPTX
Introduction Of Python History And Features Of Python..pptx
PPTX
Introduction-to-Python-Programming-Language (1).pptx
PPTX
introduction to python for programming using python
PPTX
Python presentation for engineering .pptx
PPTX
Python Basics for python understanding.pptx
PPTX
paython the Programming language .pptx
PDF
PPTX
Introduction to python for dummies
PPTX
trabalho ingles instrumental prof Anderson.pptx
PPTX
introduction to python in computer graphics.pptx
PDF
Python Presentation.pdf introduction of python programing
PDF
Overview and Introduction to Python-Programming
PDF
Brief Introduction to Python Programming
PDF
PPTX
Python_Programming_Filled_PPT.pptx PYTHON
PDF
Python Basics – Learn Coding from Scratch
PDF
Copy of Introduction to Python.
PDF
Introduction To Python For Beginners
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Mohan - "A man of silence and authority"
PPTX
Reimagining Academic Library Services through Artificial Intelligence: A Case...
PPTX
That long silence - Novel by Shashi Deshapande
PDF
TỔNG HỢP 156 ĐỀ CHÍNH THỨC KỲ THI CHỌN HỌC SINH GIỎI TIẾNG ANH LỚP 12 CÁC TỈN...
PDF
Q4_LE_English 5_Lesson 1_Week 1.pdf learning instruction
PPTX
West Hatch High School - GCSE Spanish Presentation
PPTX
Appreciations - Jan 26 01.pptxkkkmmkmkmkmkm
PDF
Schrodinger's Capital Finals (SciBiz Quiz).pdf
PPTX
Metabolism ( BIOCHEMISTRY & CLINICAL PATHOLOGY )
PPTX
'Colonial Mentality and Social Identity in Karma by Khushwant Singh'
PDF
Information about Presentation strategies
PPTX
How Physician Assistants in the USA Earn CME Credits Online.pptx
PDF
Information about the author Shashi Deshpande
PDF
West Hatch High School - GCSE Media Specification
PPTX
COMMUNICATION ITS PROCESS ELEMENTS & BARRIER .pptx
PPTX
Drugs modulating serotonergic system.pptx
PPTX
How to Create & Configure Rewards in Odoo 18 Referrals
PPTX
Toba Tek Singh - Visualising Partition through Manto's Lens
PPTX
Definition of communication skills and it's process.
PPTX
" Jaya : Silence as Resistance " - That long silence
Python_Full_Explanation_PPT.pptx Ginn Ruby 1. Introduction to Python
• Python is a high-level, interpreted language.
• Created by Guido van Rossum in 1991.
• Known for simplicity and readability.
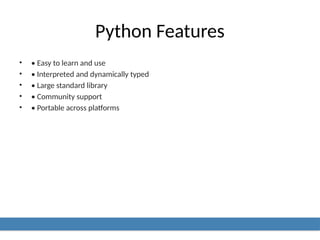
2. Python Features
• • Easy to learn and use
• • Interpreted and dynamically typed
• • Large standard library
• • Community support
• • Portable across platforms
3. Python Use Cases
• • Web Development
• • Data Science
• • Automation and Scripting
• • Artificial Intelligence
• • Game Development
4. Python Installation
• 1. Visit https://www.python.org
• 2. Download installer for your OS
• 3. Install using default settings
• 4. Verify: python --version
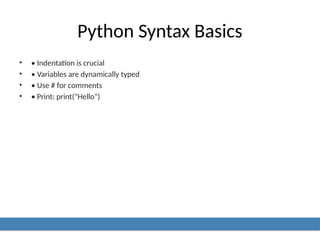
5. Python Syntax Basics
• • Indentation is crucial
• • Variables are dynamically typed
• • Use # for comments
• • Print: print("Hello")
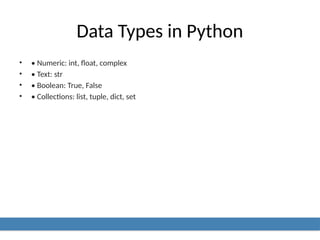
6. Data Types in Python
• • Numeric: int, float, complex
• • Text: str
• • Boolean: True, False
• • Collections: list, tuple, dict, set
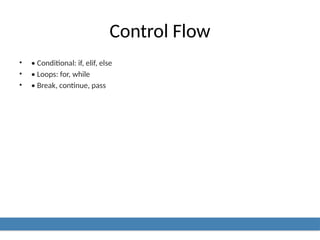
7. Control Flow
• • Conditional: if, elif, else
• • Loops: for, while
• • Break, continue, pass
8. Functions in Python
• • Defined using def keyword
• • Can return values
• • Support default and keyword arguments
9. Modules and Libraries
• • Use import to include modules
• • Built-in: math, random
• • External: numpy, pandas, matplotlib
10.