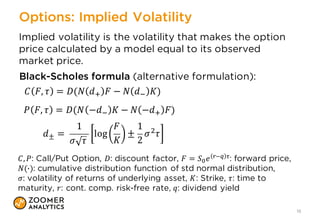
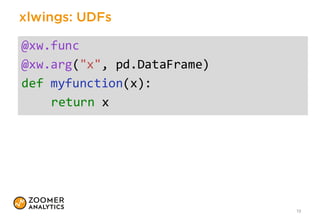
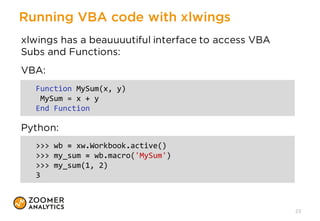
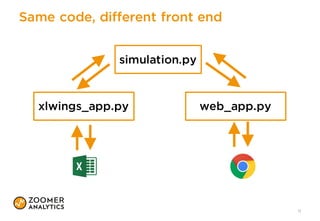
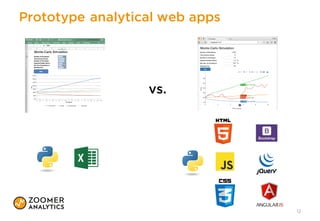
The document outlines a presentation on implementing classic financial models using Python and Excel, emphasizing practical applications like portfolio optimization, Monte Carlo simulations, and option pricing. It introduces tools like xlwings, QuantLib, and Jupyter Notebook, and discusses the integration of Python with Excel for enhanced financial analysis and automation. The talk also highlights the importance of unit testing for ensuring reliability in spreadsheet models.







![10
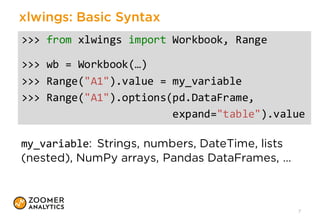
Random walk
𝑑𝑆# =
𝜇 𝑆# 𝑑𝑡
+
𝜎 𝑆# 𝑑𝑊#
In the Black-Scholes model, asset prices 𝑆# are assumed to follow a
geometric Brownian motion (GBM), as defined by this stochastic
differential equation (SDE):
𝜇: drift, 𝜎: volatility, 𝑊#: brownian motion
Discrete time version:
𝑆# = 𝑆#+,# exp 𝜇 −
𝜎1
2
Δ𝑡
+
𝜎 𝜀# Δ𝑡
S[0, :] = starting_price
for t in range(n_timesteps):
rand_nums = np.random.randn(n_simulations)
S[t + 1, :] = S[t, :] * np.exp((mu -‐ 0.5 * vol ** 2) * dt +
vol * rand_nums * np.sqrt(dt))
Python: (for full context look at the repo as mentioned on slide 13)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thalesianszrh-160609145731/85/Python-Finance-Excel-The-Thalesians-10-320.jpg)



![QuantLib
16
• Open-source framework for quant finance. Released in
2000 and written in C++ with bindings for many languages.
• ”Offers […] features such as market conventions, yield curve
models, solvers, PDEs, Monte Carlo (low-discrepancy
included), exotic options, VAR, and so on.” (quantlib.org)
• Installation
- Windows: Download the Python wheel from
http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#quantlib
and pip-install it
- Linux: apt-‐get install quantlib-‐python quantlib-‐swig
- Mac: Err…Right now, no binaries (wheels or conda
package) and building it is not exactly fun](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thalesianszrh-160609145731/85/Python-Finance-Excel-The-Thalesians-16-320.jpg)