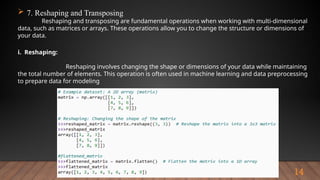
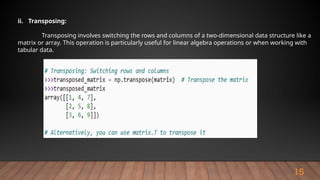
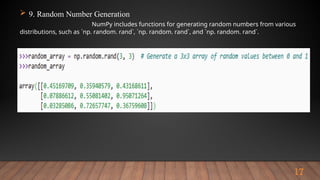
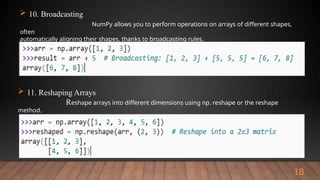
The document outlines the importance and various functionalities of Python libraries for data analysis, particularly focusing on libraries like NumPy and Pandas. It explains how these libraries facilitate numerical computing, data manipulation, and preprocessing. Key concepts include creating and managing arrays with NumPy, and leveraging Pandas for structured data handling and analysis.















![Pandas - Data Analysis - Indexing and Selecting Data
Examples - Indexing and Selecting Data
Viewing Data
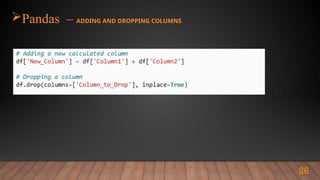
Name_Column = df[`Name`
Subset = df[[‘Name’, ‘Age’]]
Young_People = df[df[“age”] <30]
Hint : For further reference
https://pandas.pydata.org/Pandas_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-241029081501-8139ff9c/85/To-understand-the-importance-of-Python-libraries-in-data-analysis-23-320.jpg)