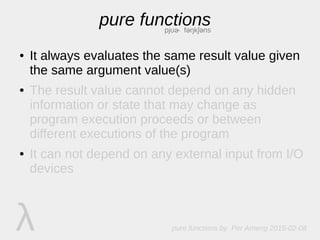
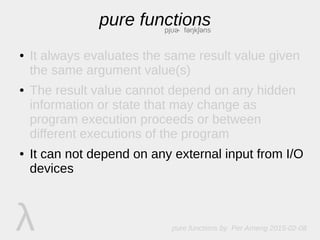
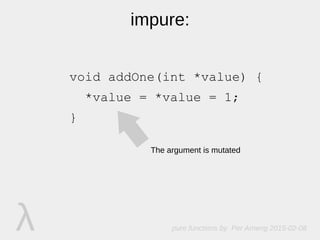
The document discusses pure functions, which always return the same result for the same inputs, do not depend on hidden state or external inputs that could change, and do not mutate their arguments. Pure functions have advantages like being easy to test, reuse, reason about, and use in multithreading. Some examples of pure and impure functions are provided.