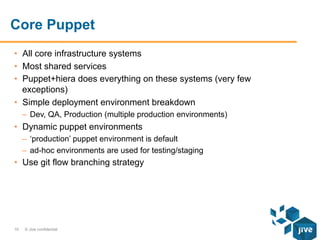
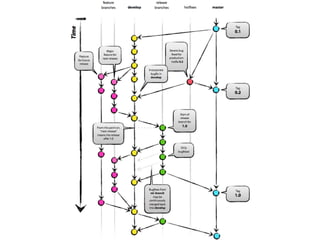
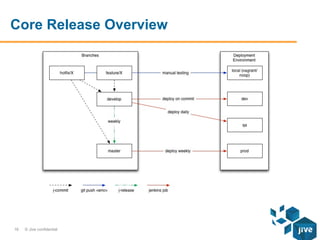
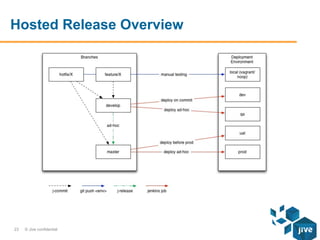
The document describes the release workflows for three different domains of Puppet code at Jive: Core, Hosted, and Continuous Deployment. Core Puppet manages all infrastructure and shared services across about 1000 nodes. It uses a bi-weekly change control process. Hosted Puppet manages customer installations across 14,000 nodes and releases are tied to the application release cycle. Continuous Deployment uses a fully automated deployment pipeline to deploy over 70 services across less than 200 nodes, with puppet code changes triggering test and deployment jobs.