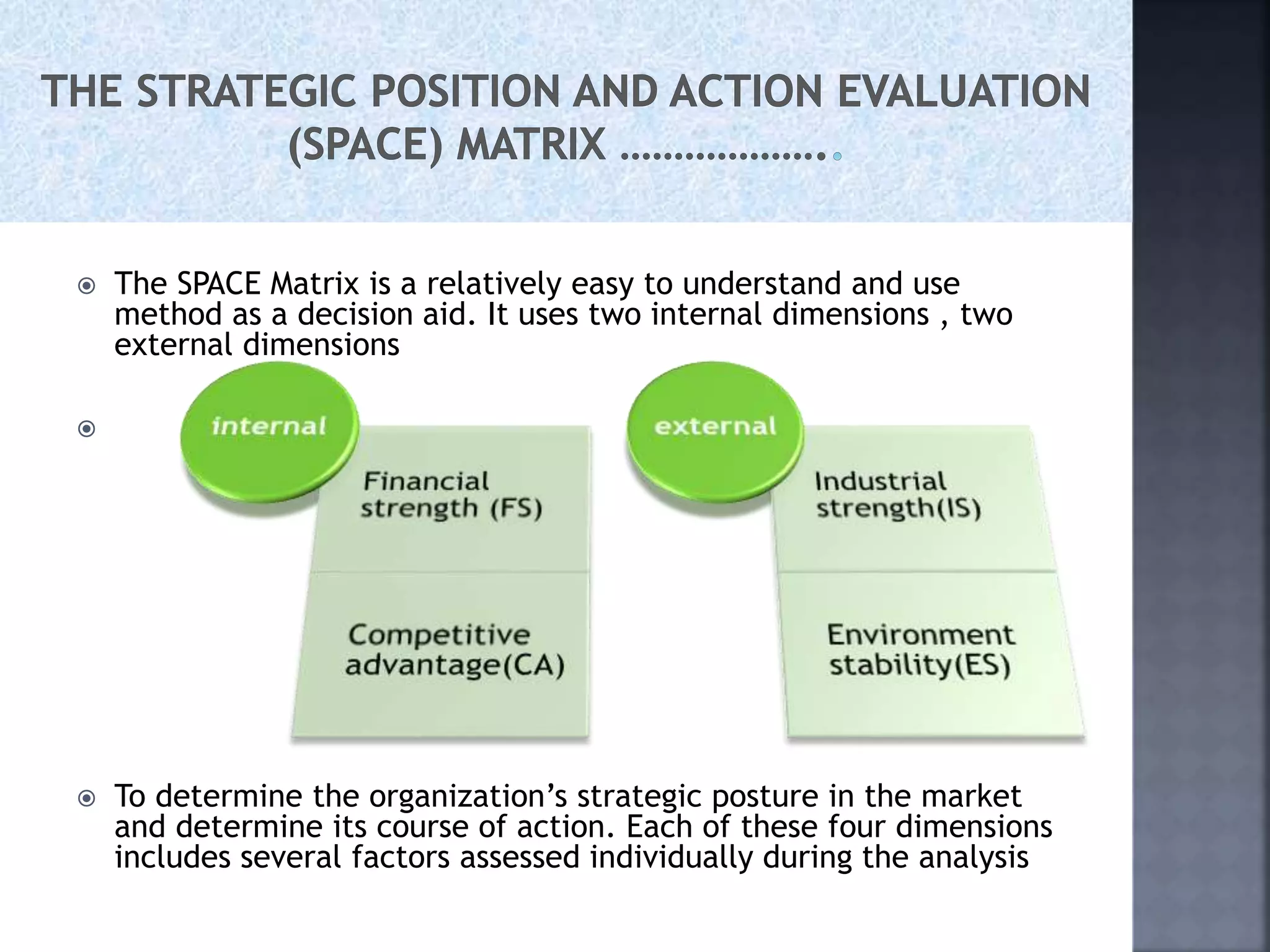
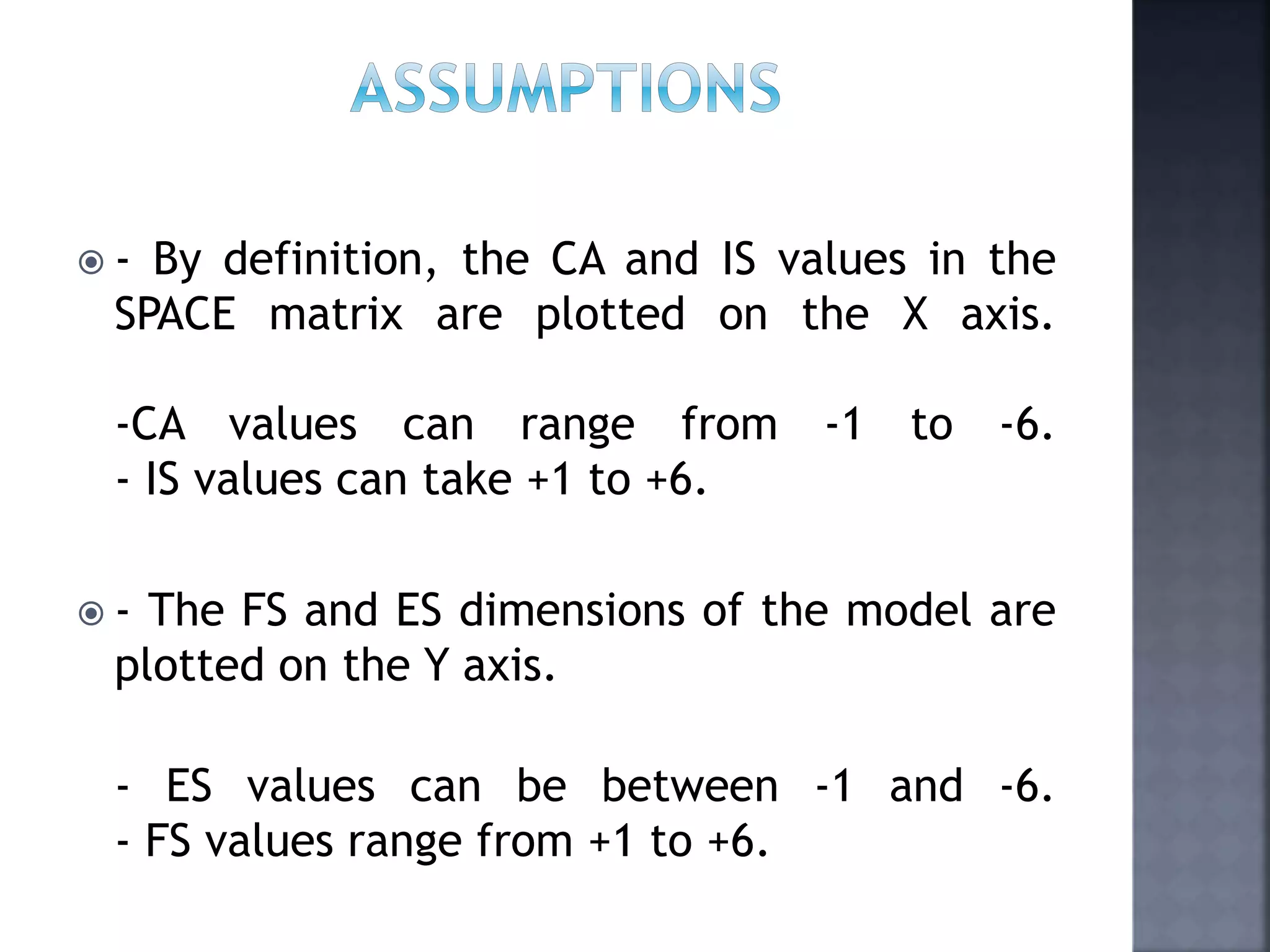
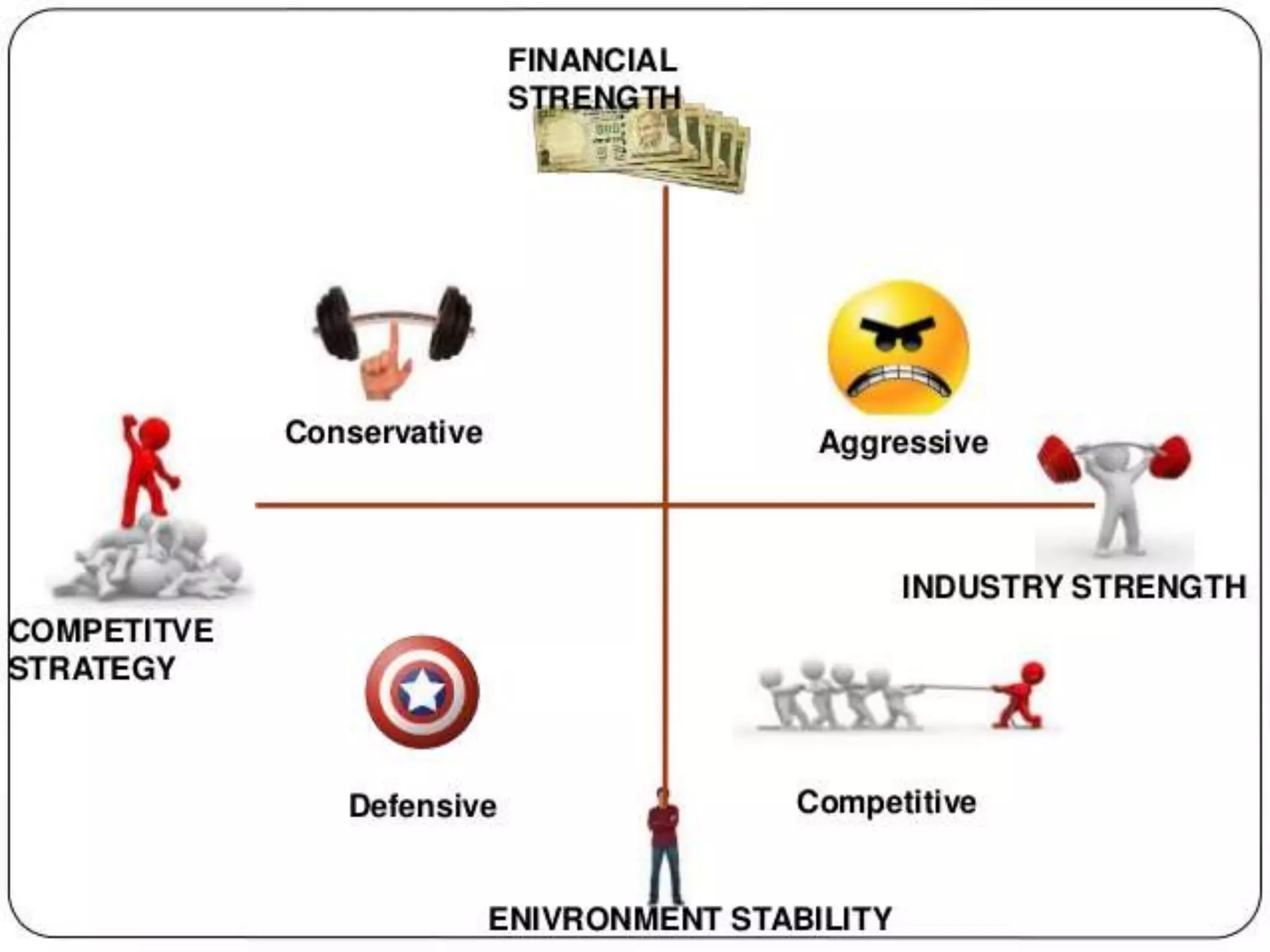
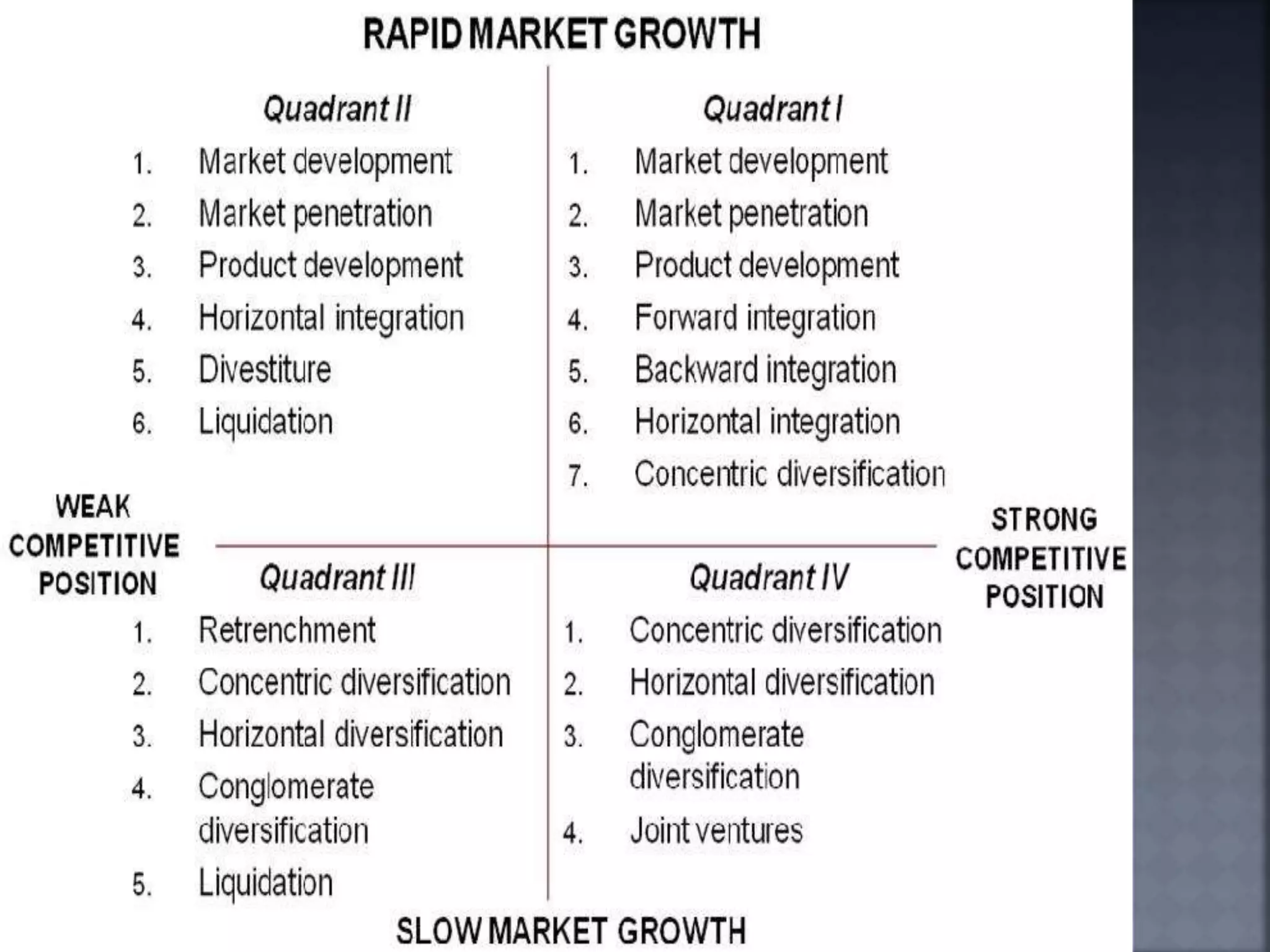
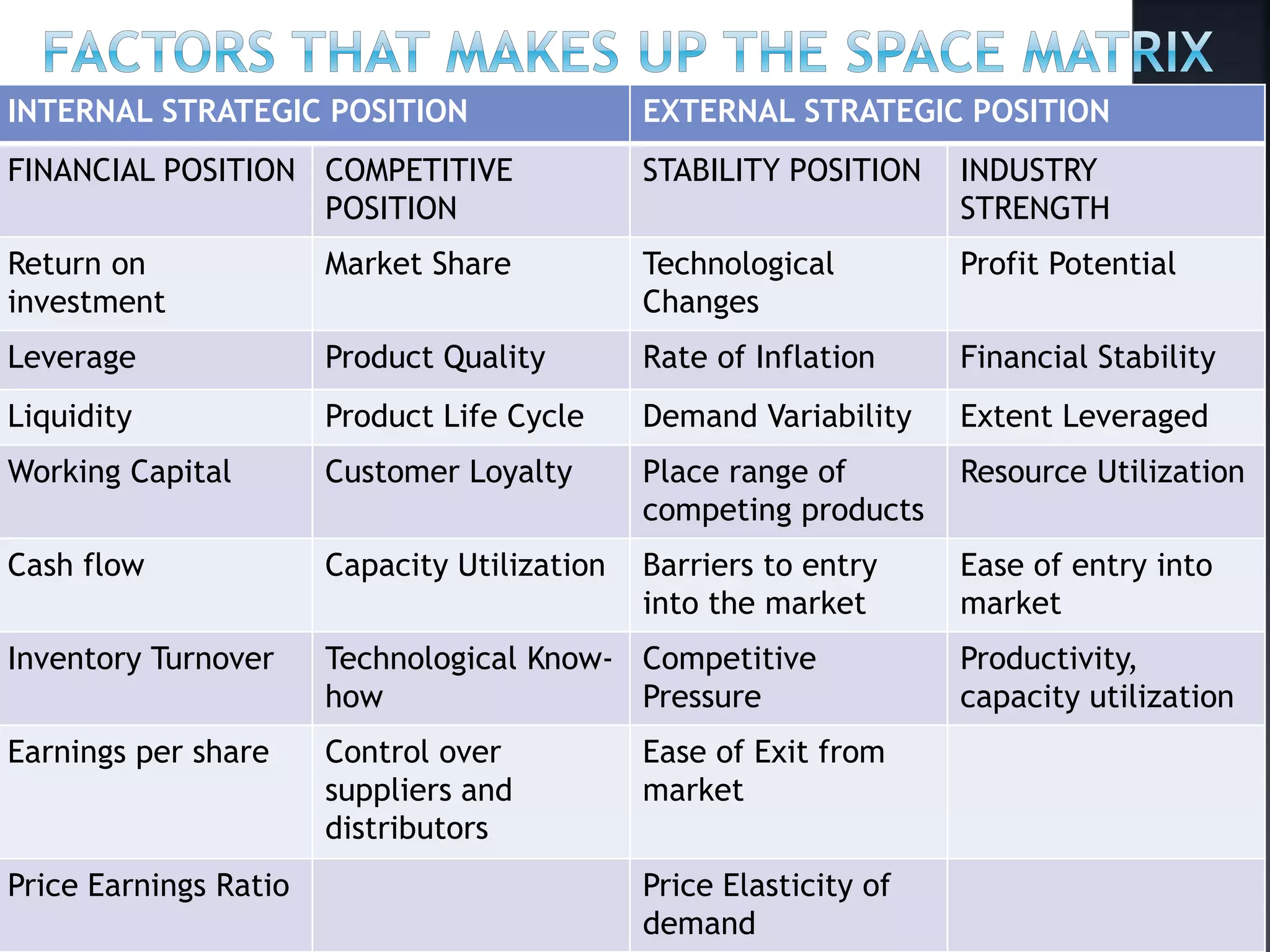
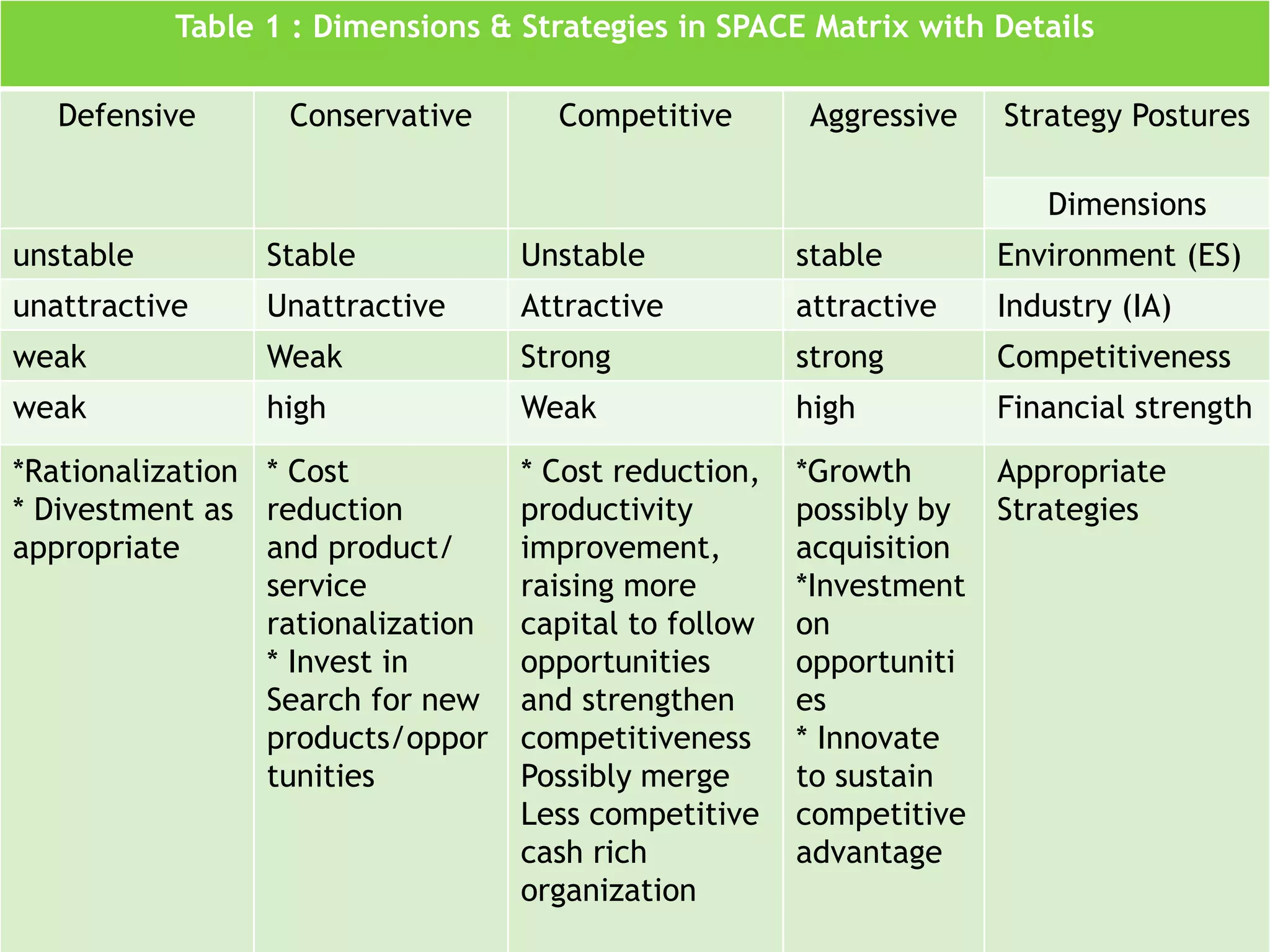
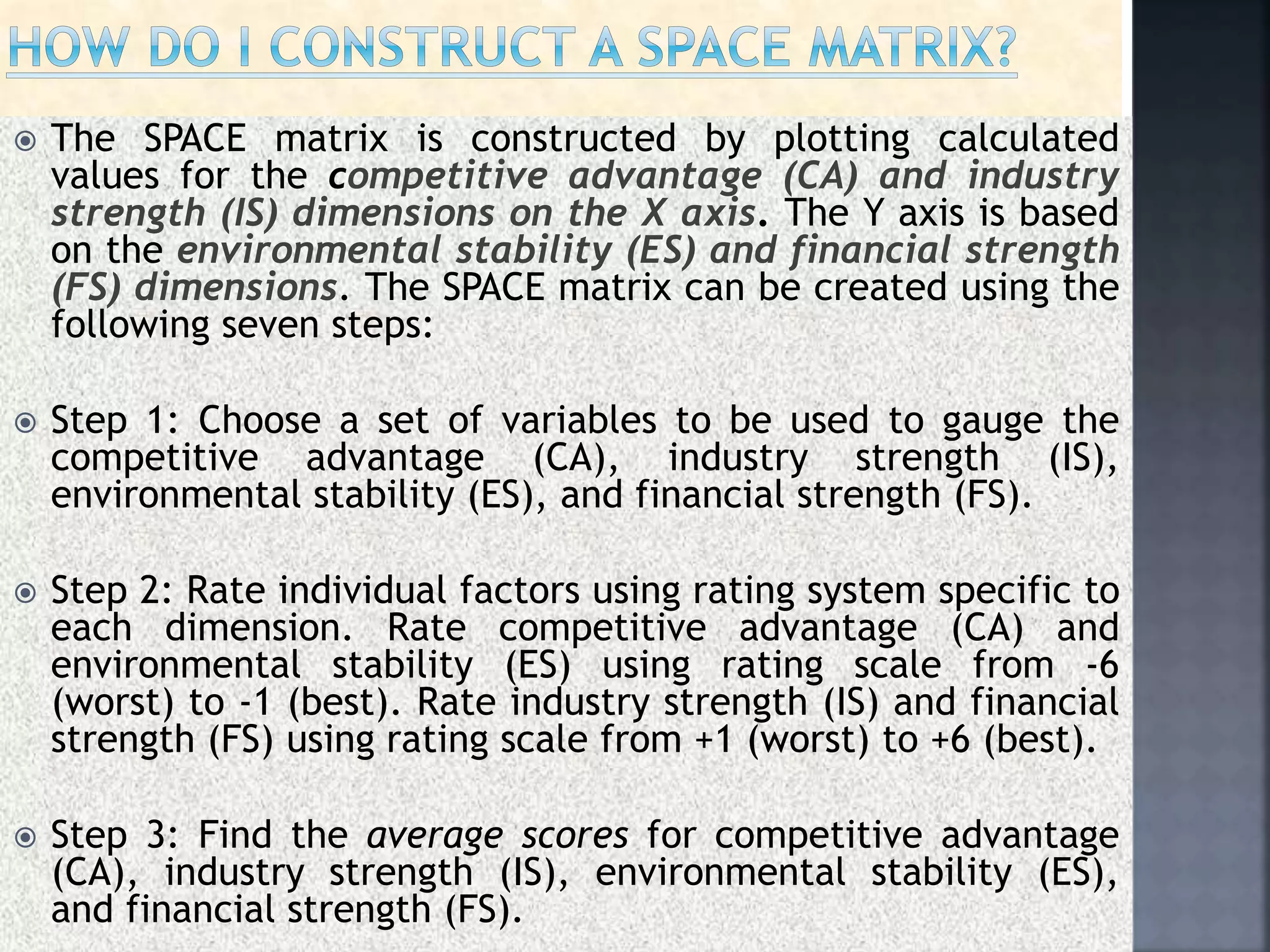
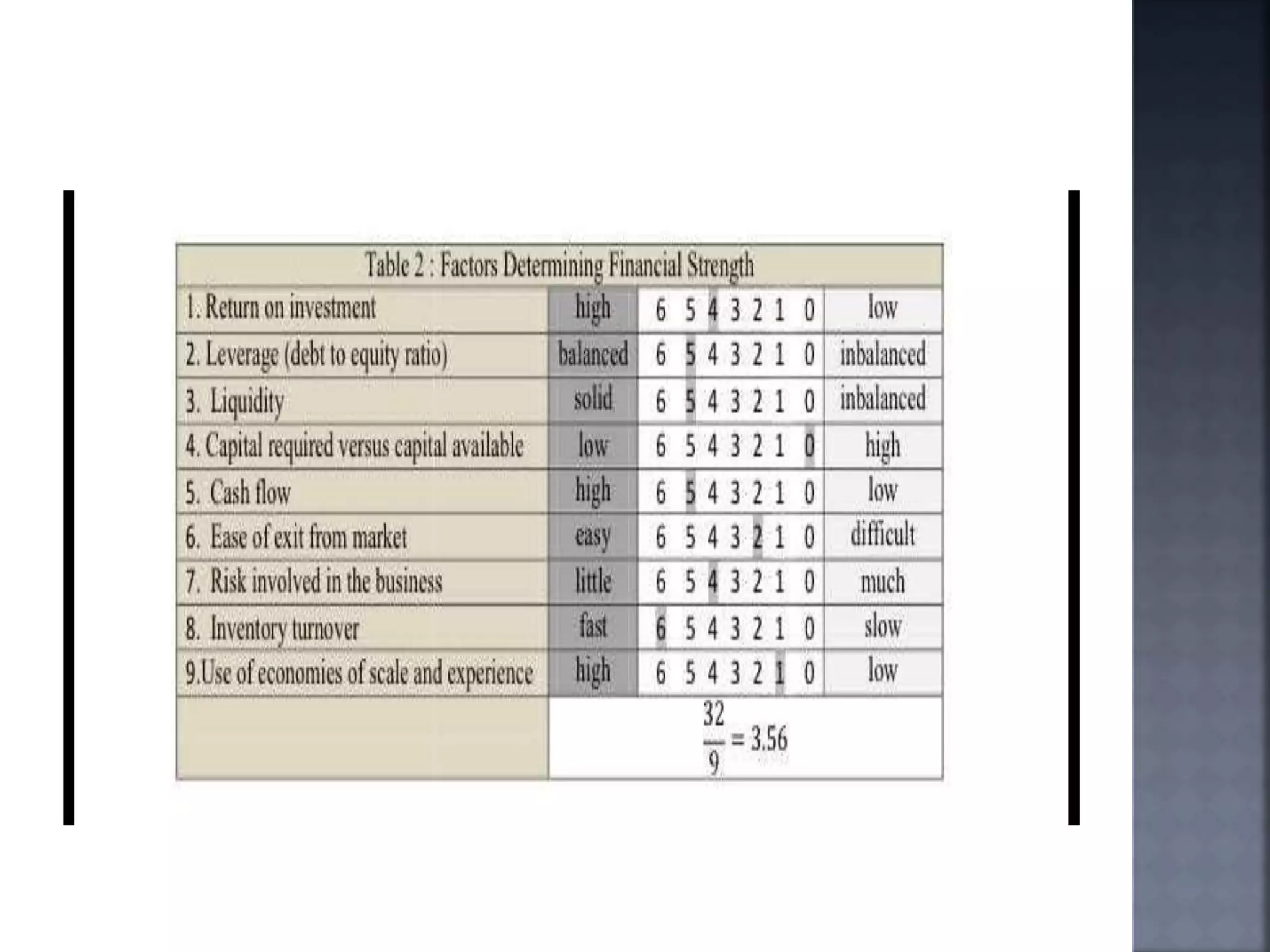
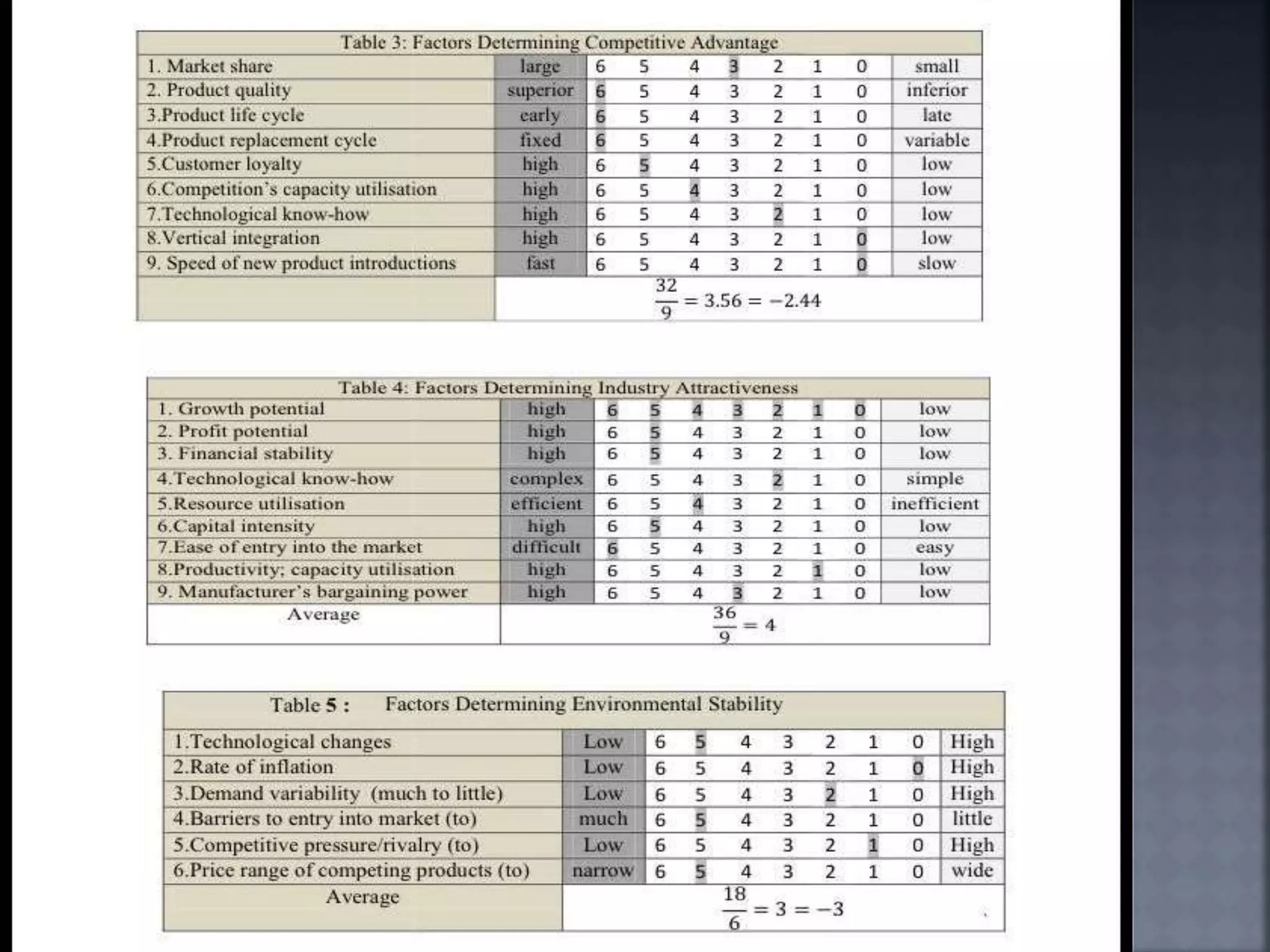
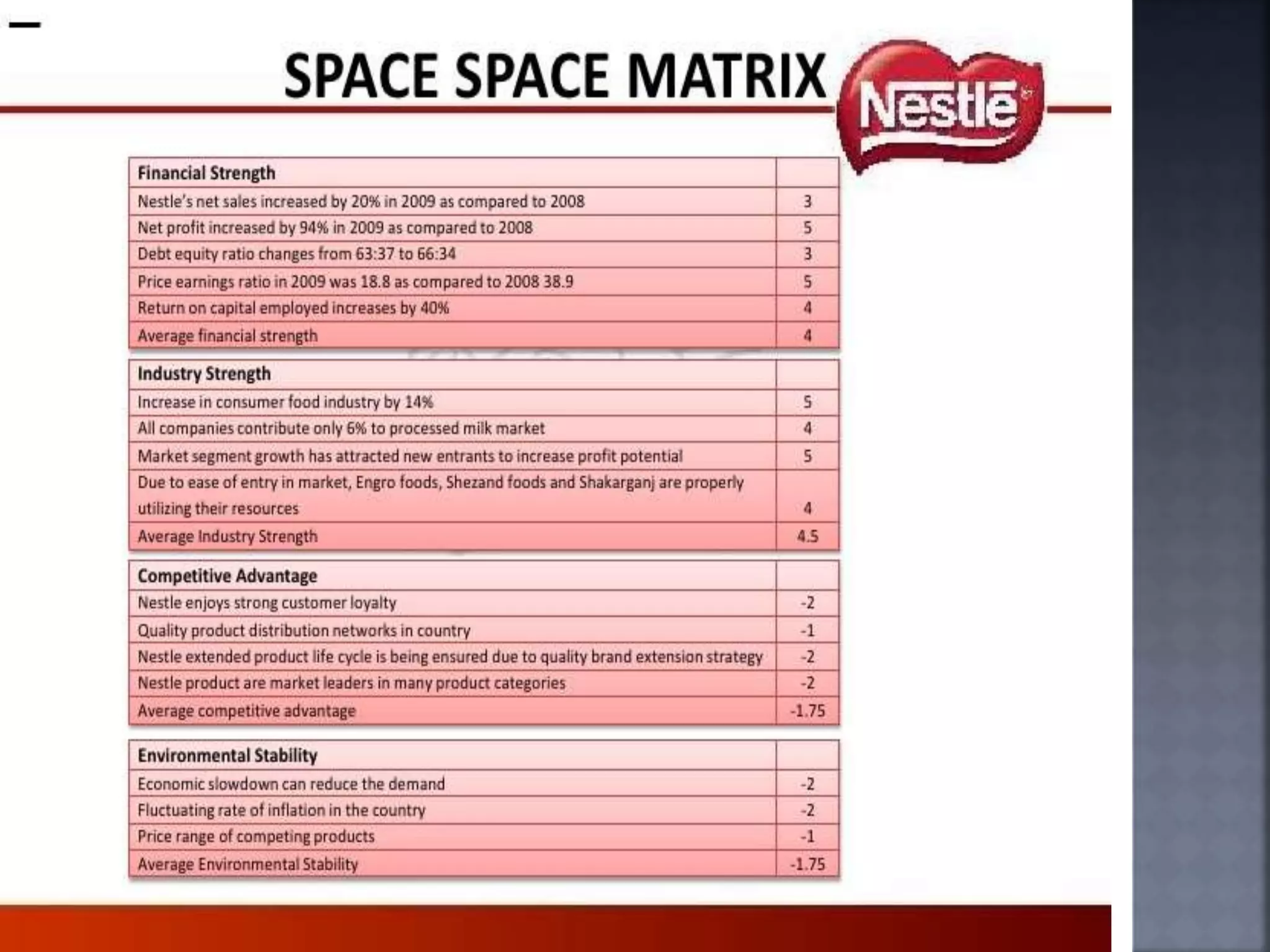
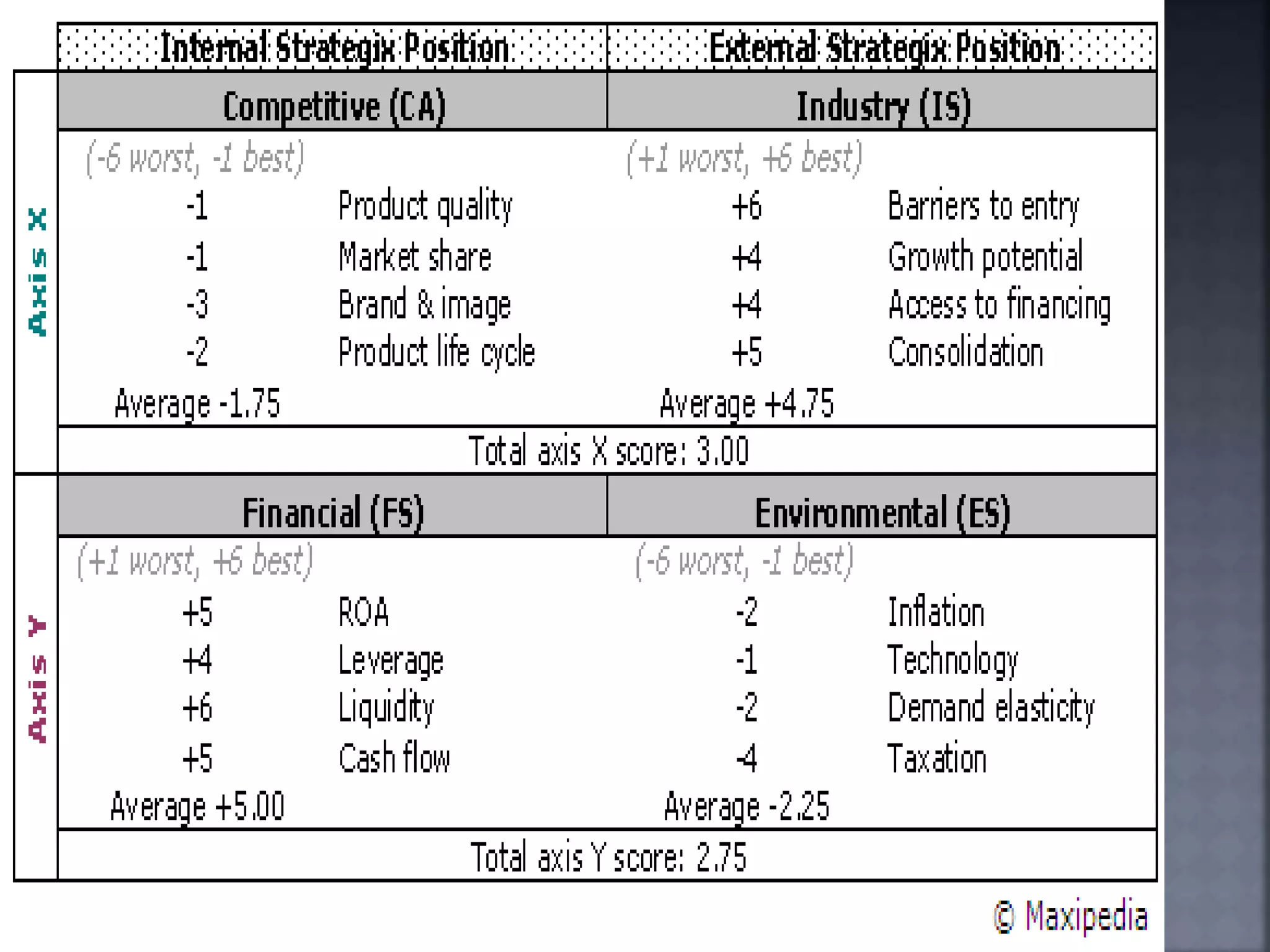
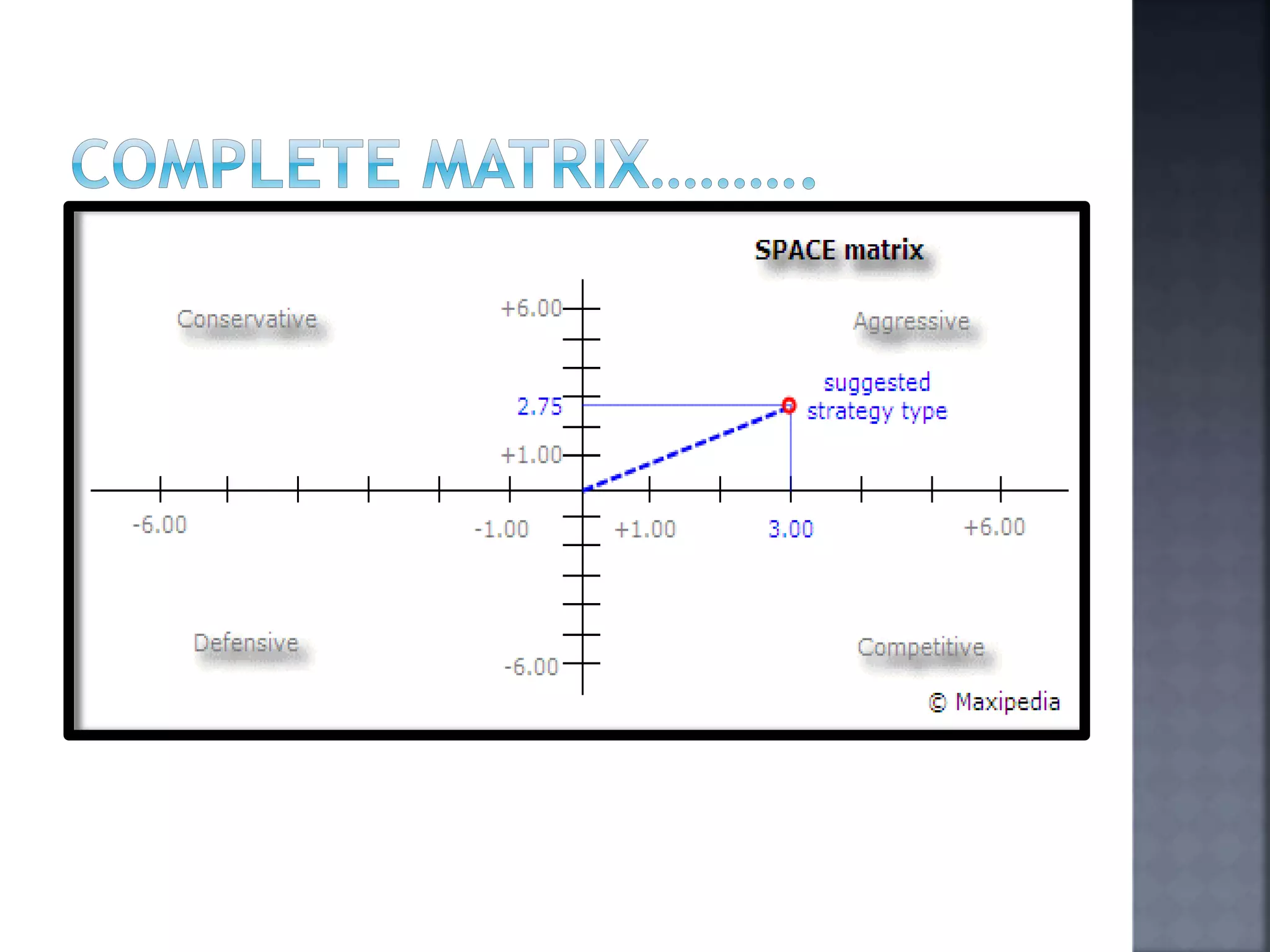
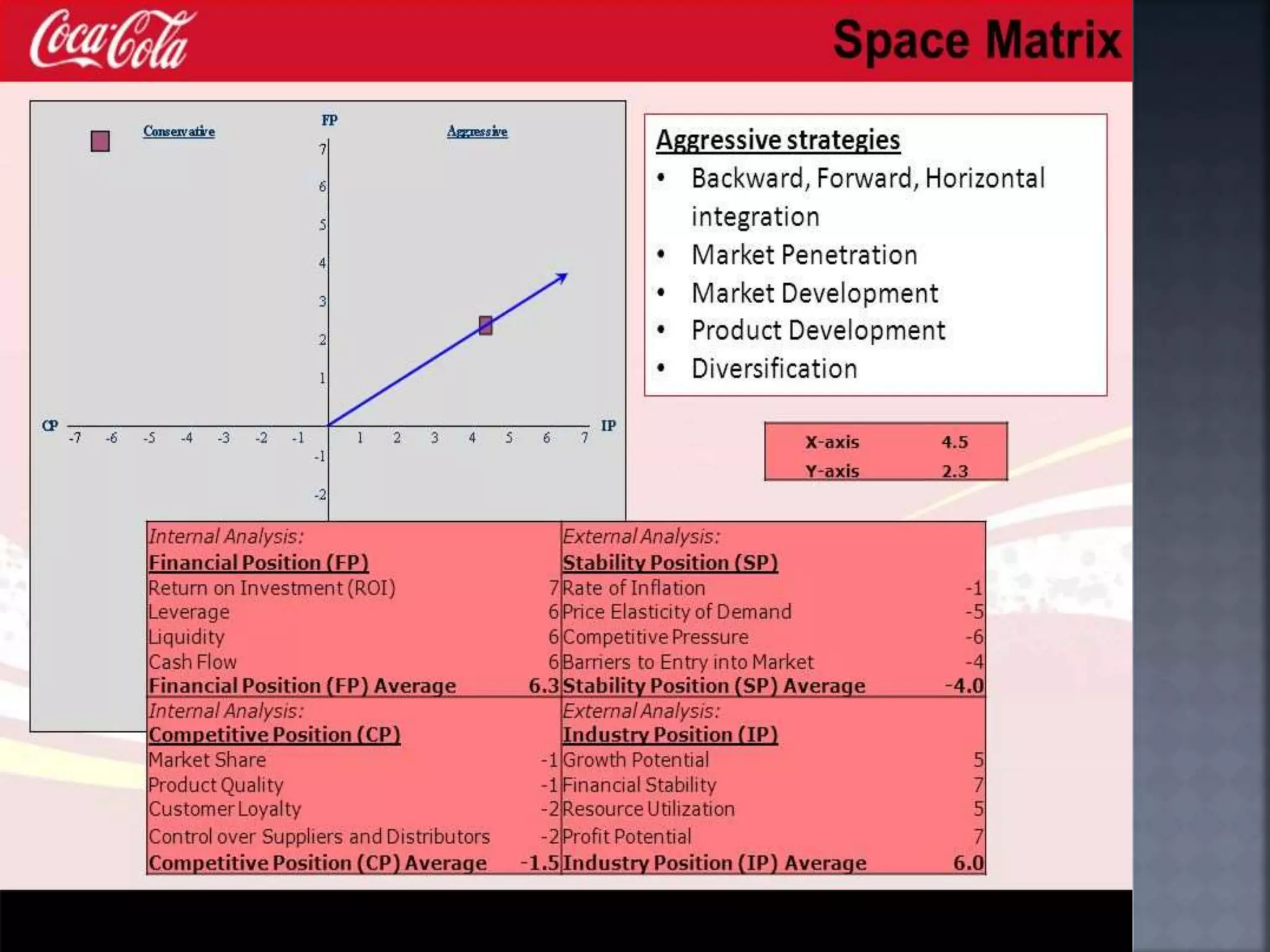
The document discusses the Strategic Position and Action Evaluation (SPACE) matrix, which is a tool used to evaluate strategic plans and determine a company's strategic posture in the market. It involves assessing factors related to an organization's competitive advantage, industry strength, environmental stability, and financial strength to plot the company's position on the SPACE matrix. The position will indicate which of four strategic postures - defensive, conservative, competitive, or aggressive - the company should pursue.