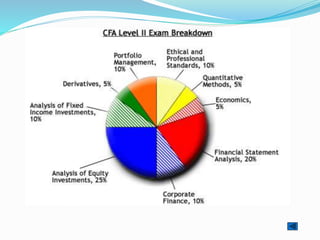
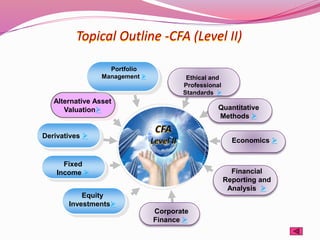
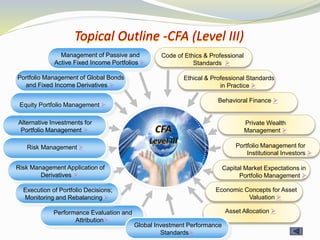
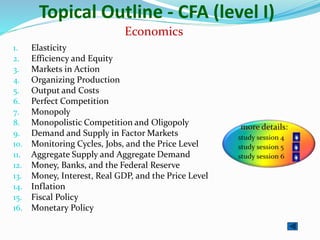
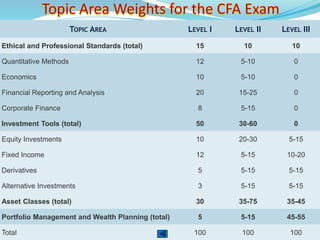
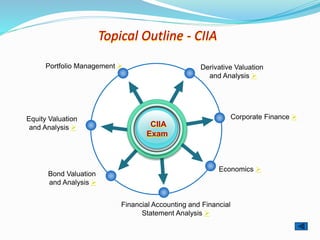
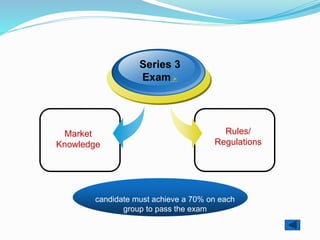
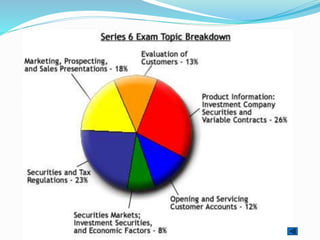
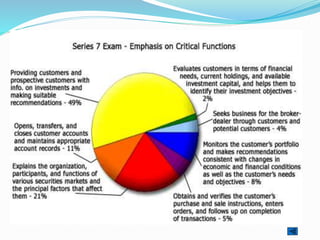
The document provides outlines of the topics covered in the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) program across levels I, II, and III. The CFA program covers a wide range of finance topics including ethics, economics, financial statement analysis, quantitative methods, derivatives, fixed income, equity investments, alternative investments, and portfolio management. Later levels delve deeper into specific subjects like asset valuation, portfolio concepts, and ethical standards in practice.