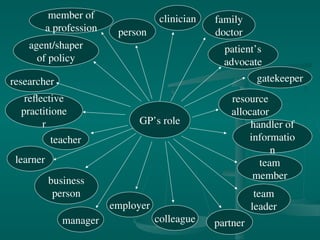
The document outlines the professional roles and responsibilities of General Practitioners (GPs), emphasizing their obligations to patients, colleagues, and the healthcare system. It discusses key ethical principles such as beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, and respect for autonomy, along with moral theories guiding their practice. Additionally, it highlights specific duties outlined by the General Medical Council (GMC) that GPs must adhere to in order to maintain professionalism and patient trust.