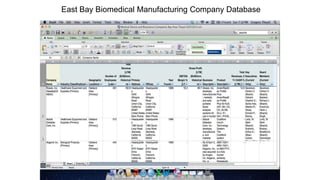
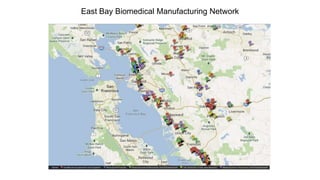
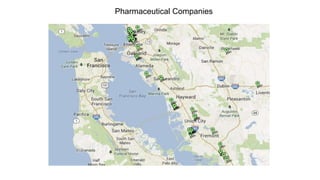
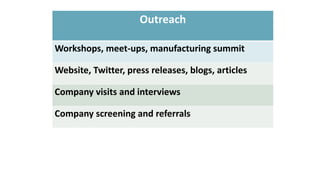
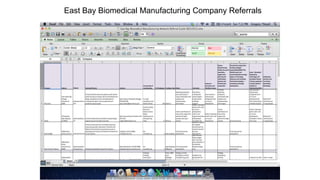
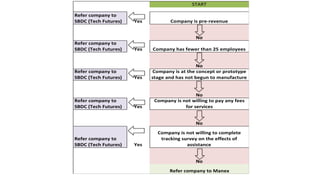
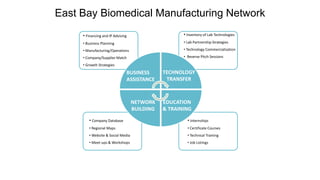
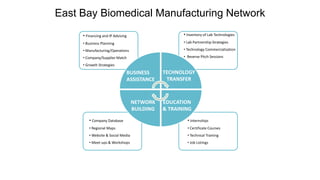
Some information may exist from past surveys, but comprehensive and up-to-date information on all of these topics is unlikely to exist without conducting a new survey. Existing secondary data sources like economic reports may provide some high-level insights but are not tailored to the specific needs of this cluster initiative. A new primary data collection effort is needed.