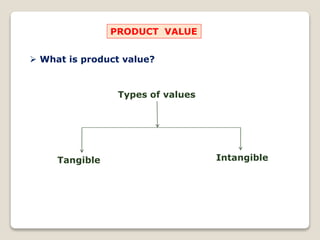
The document discusses product categories, product planning, product value, and achieving product preference through superior products. It identifies 5 product categories and lists tangible and intangible values that products can provide. It then discusses how to categorize superior products through technical innovation, superior performance, new benefits, and other factors. Finally, it provides ways to look for product improvements such as increasing speed, efficiency, convenience, longevity, aesthetics, value, and extending usage.