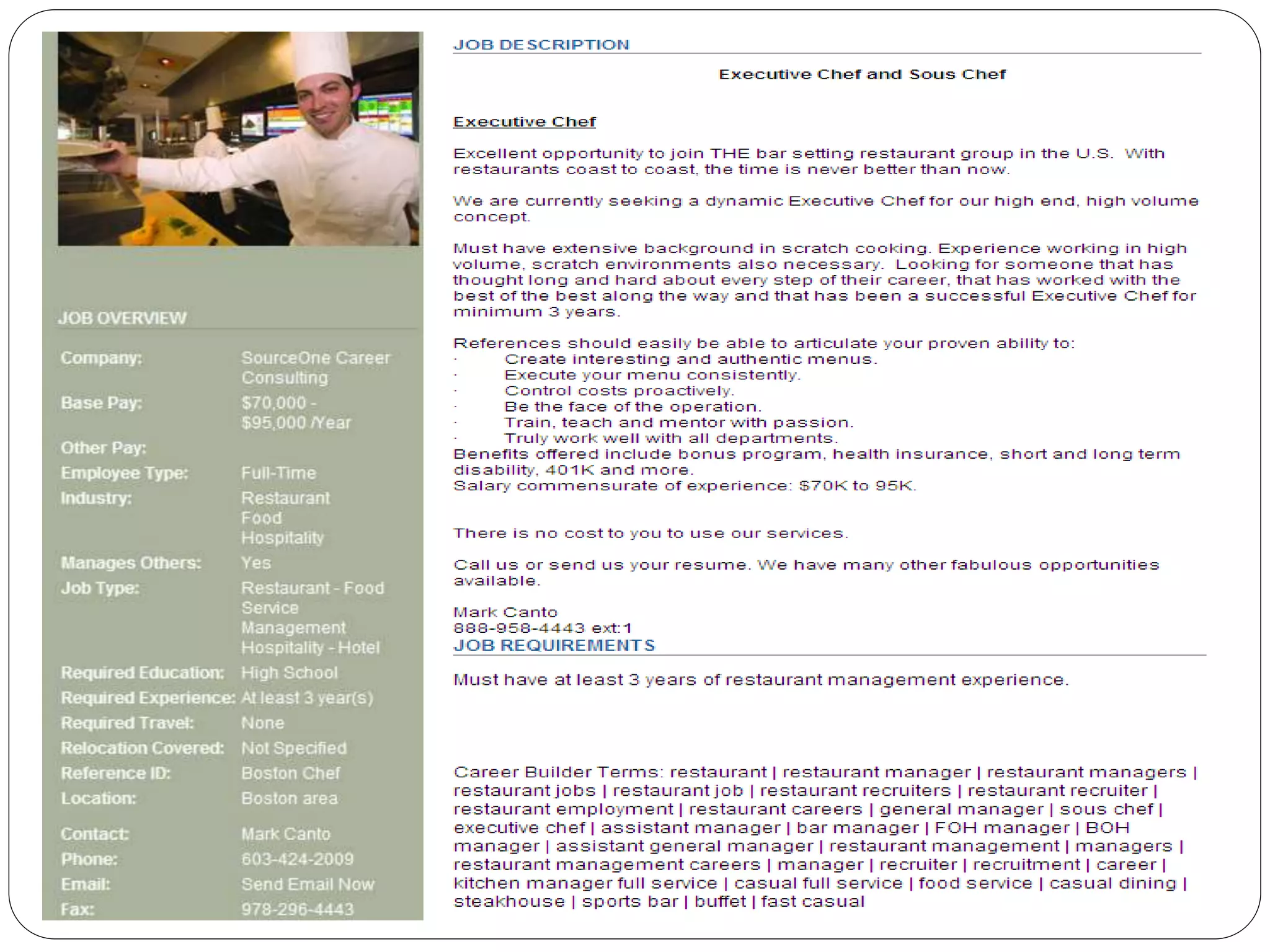
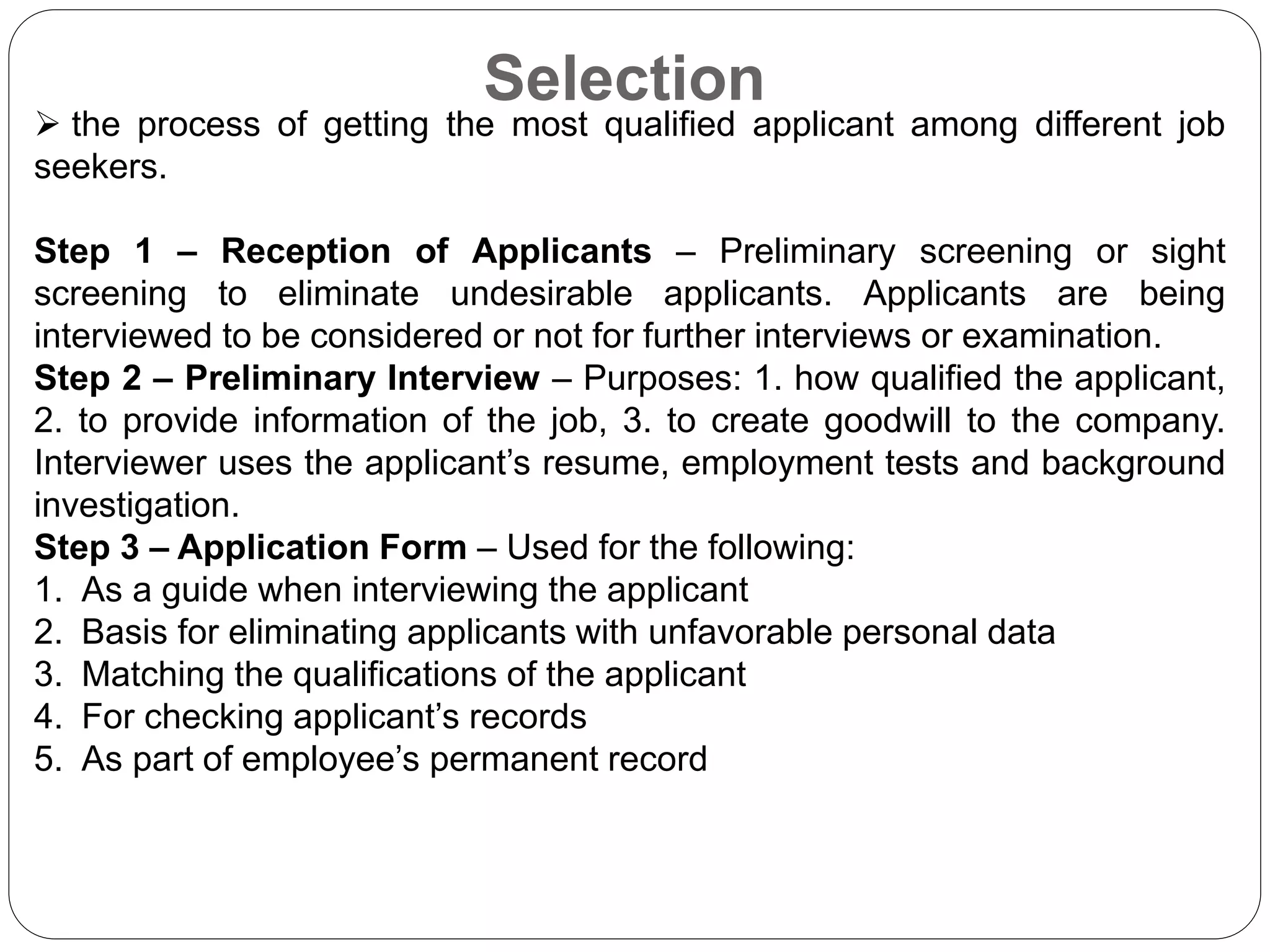
This chapter discusses the staffing process which includes recruiting, selecting, and training employees. It defines staffing as putting the right employees in the right jobs through evaluation and development. The key aspects of staffing covered are the recruitment process, selection steps, types of training, identifying training needs, human asset accounting, and movements of personnel such as transfers, promotions, and separations. Staffing is important for organizational effectiveness and efficiency.