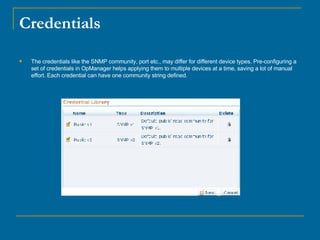
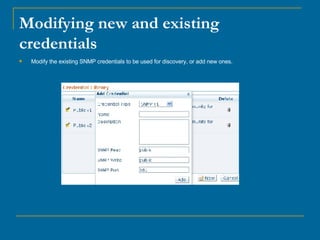
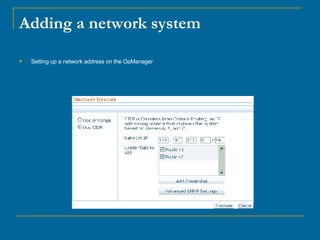
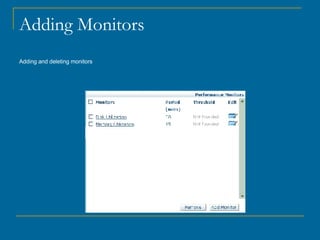
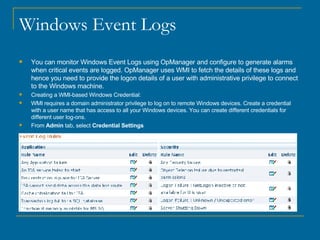
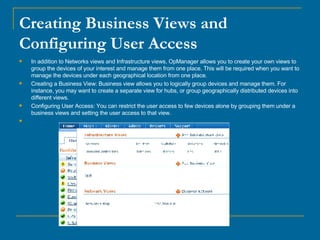
OpManager can automatically discover and monitor devices on a network. It uses SNMP and ICMP to discover devices and classify them. It can monitor non-SNMP devices like Linux servers by using credentials to log in via Telnet or SSH and retrieve CPU and memory utilization. OpManager allows adding monitors, modifying credentials, and creating business views to logically group devices for centralized management.