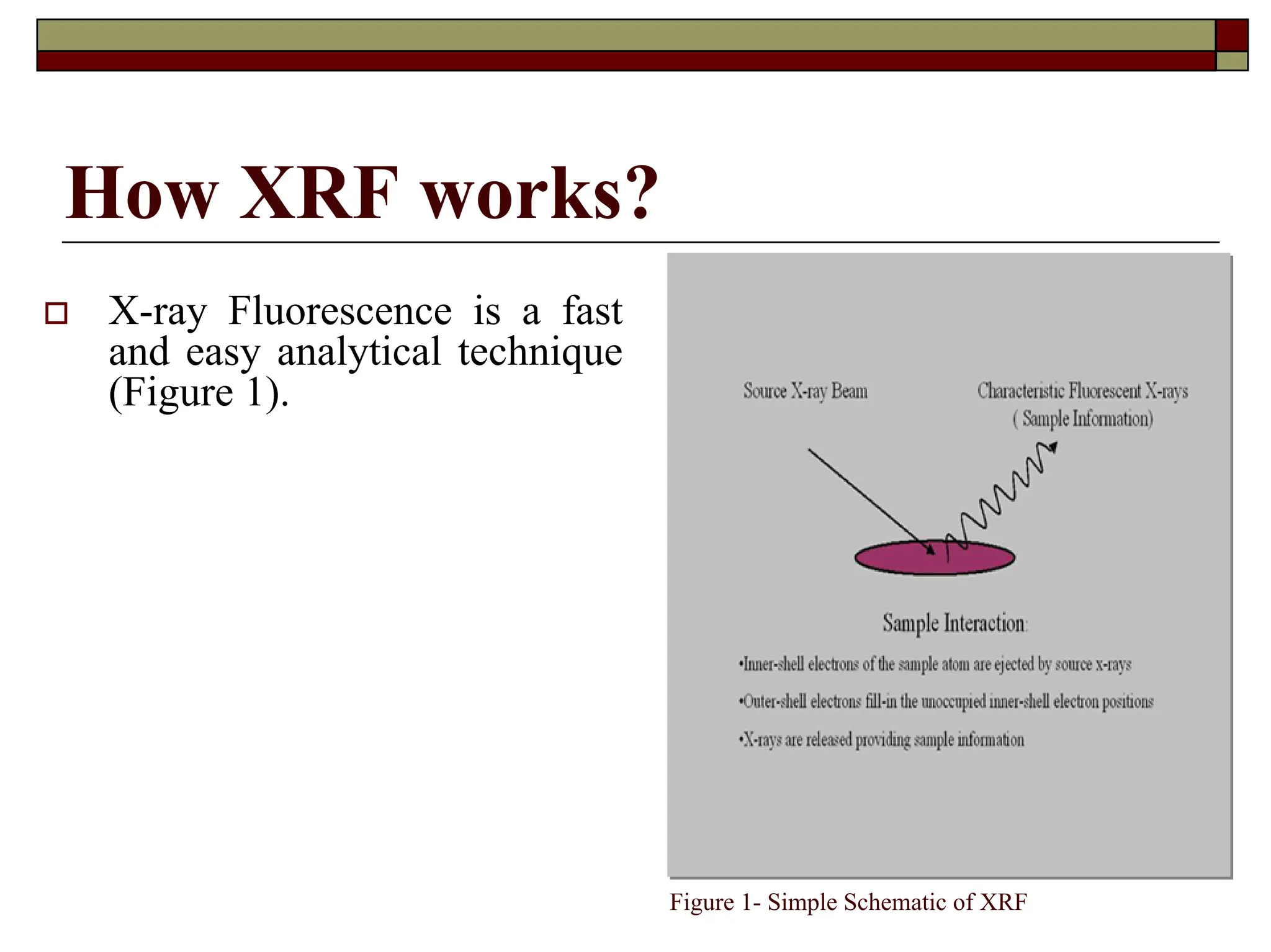
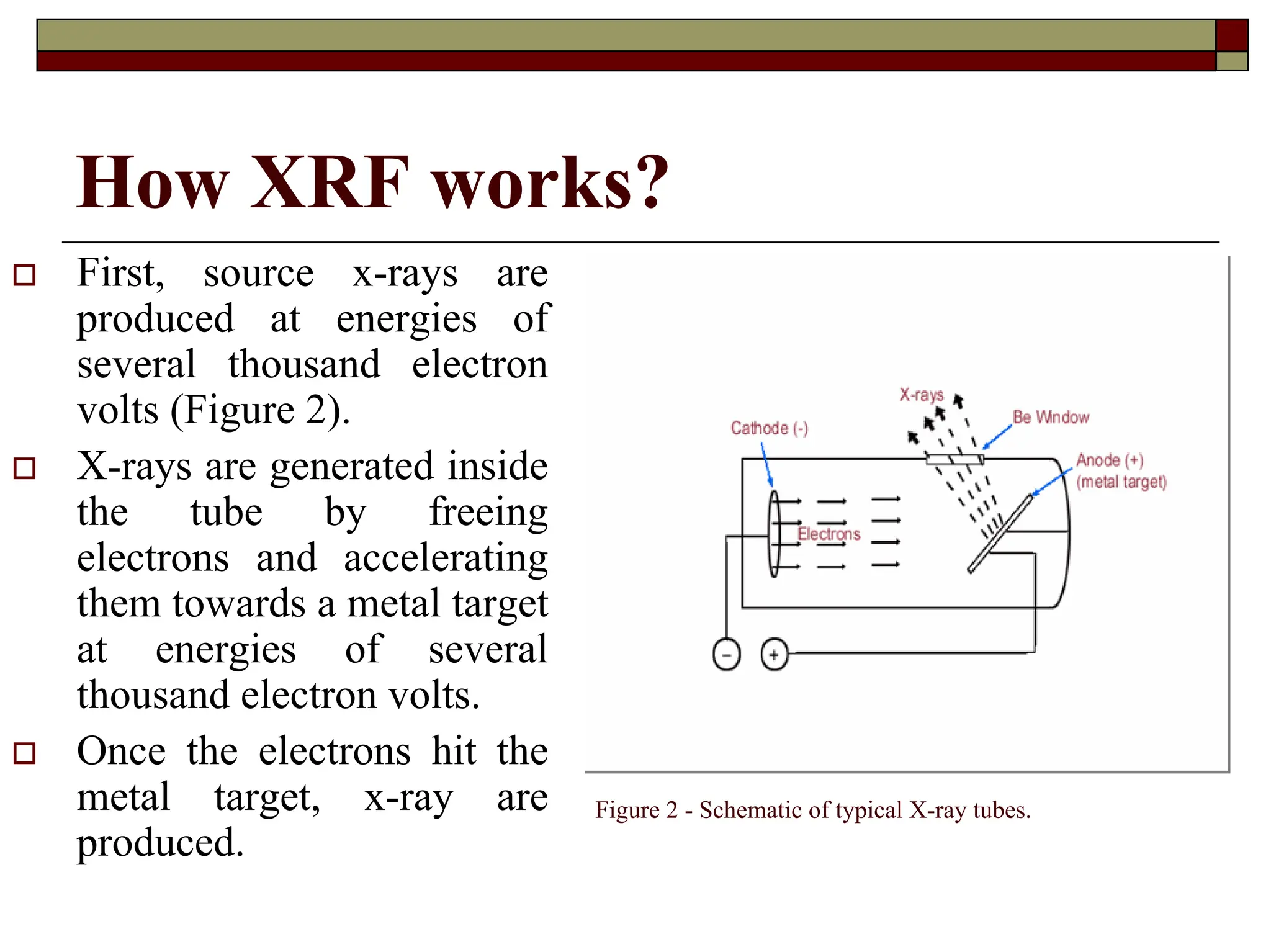
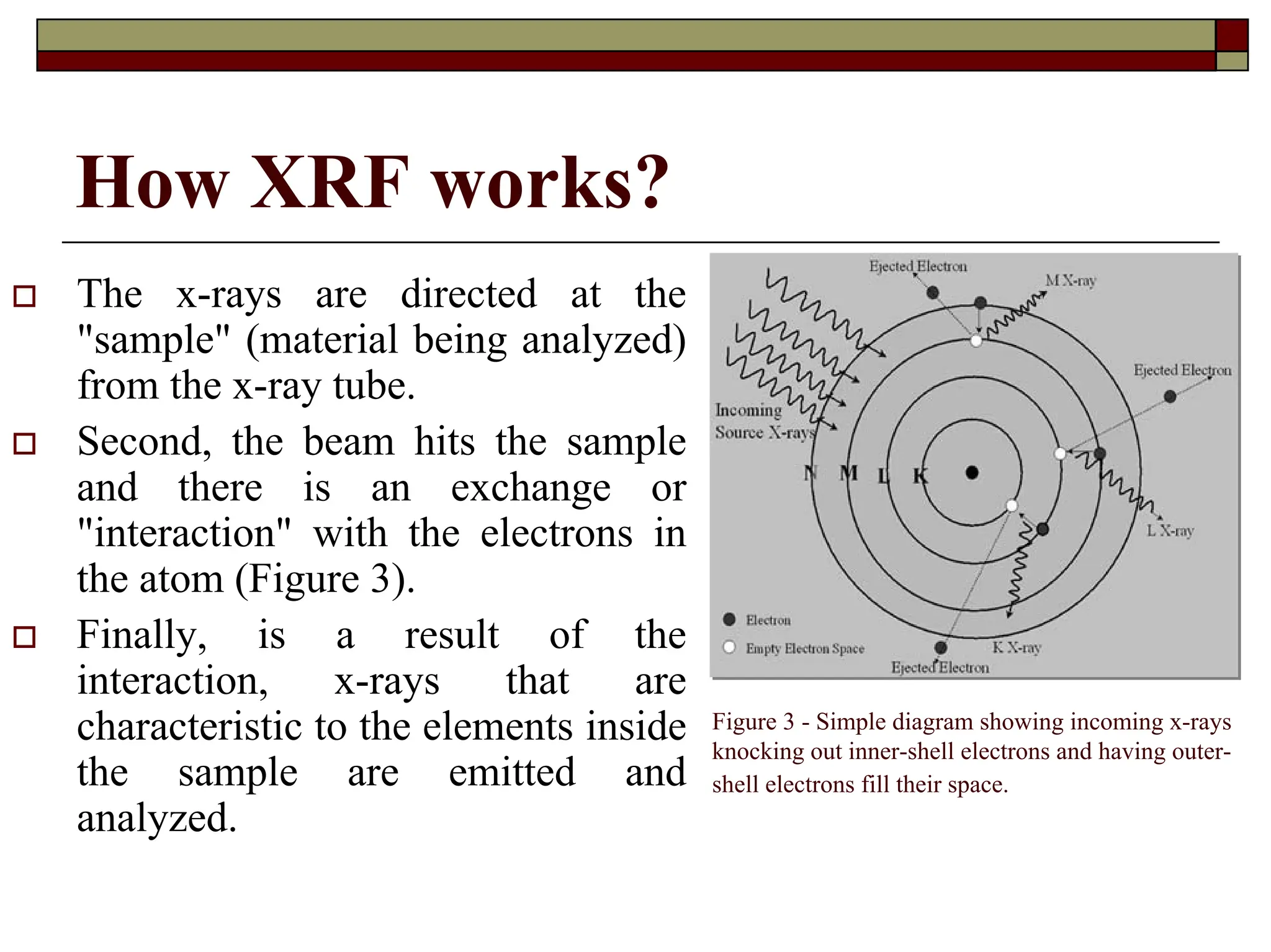
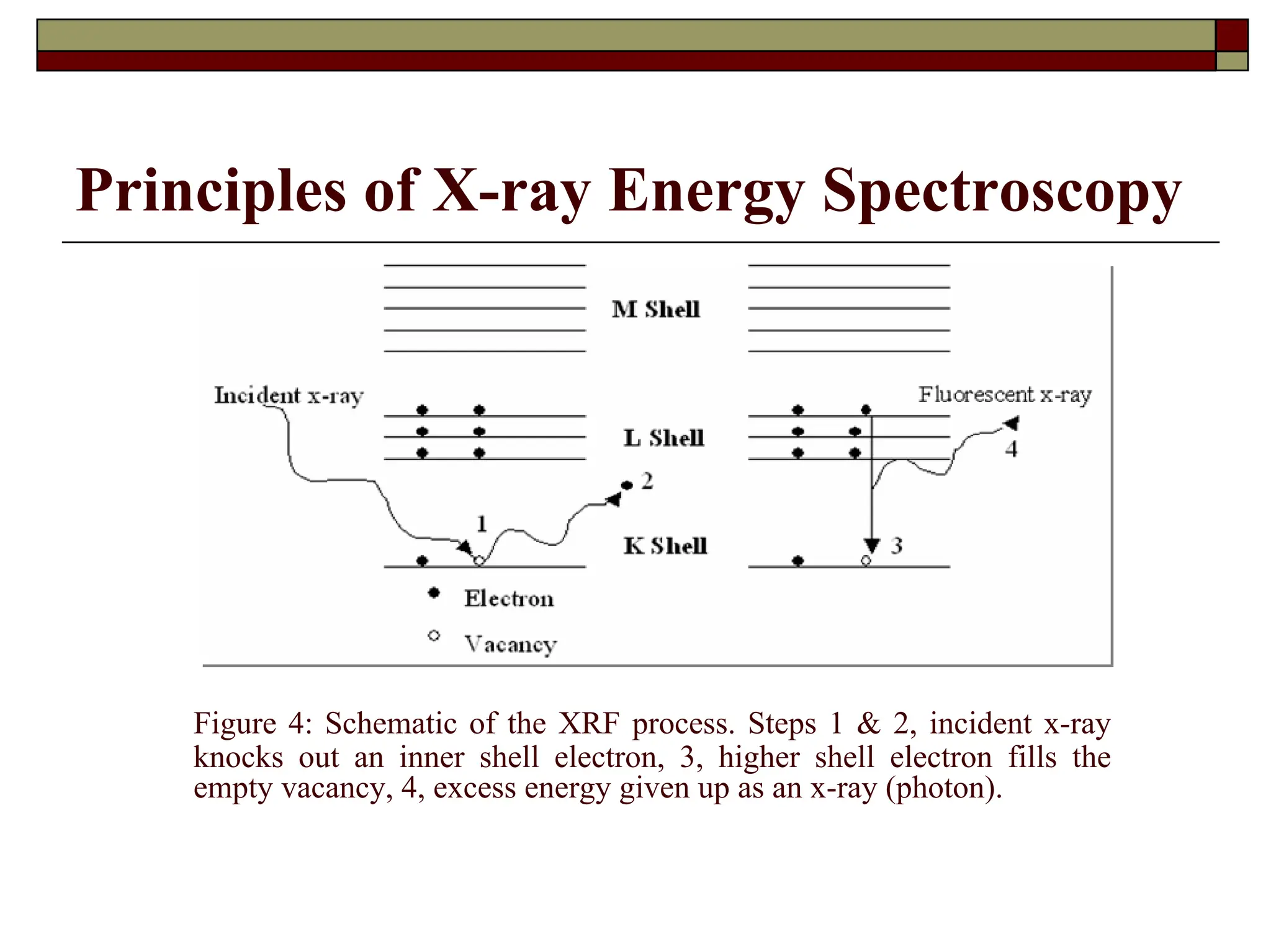
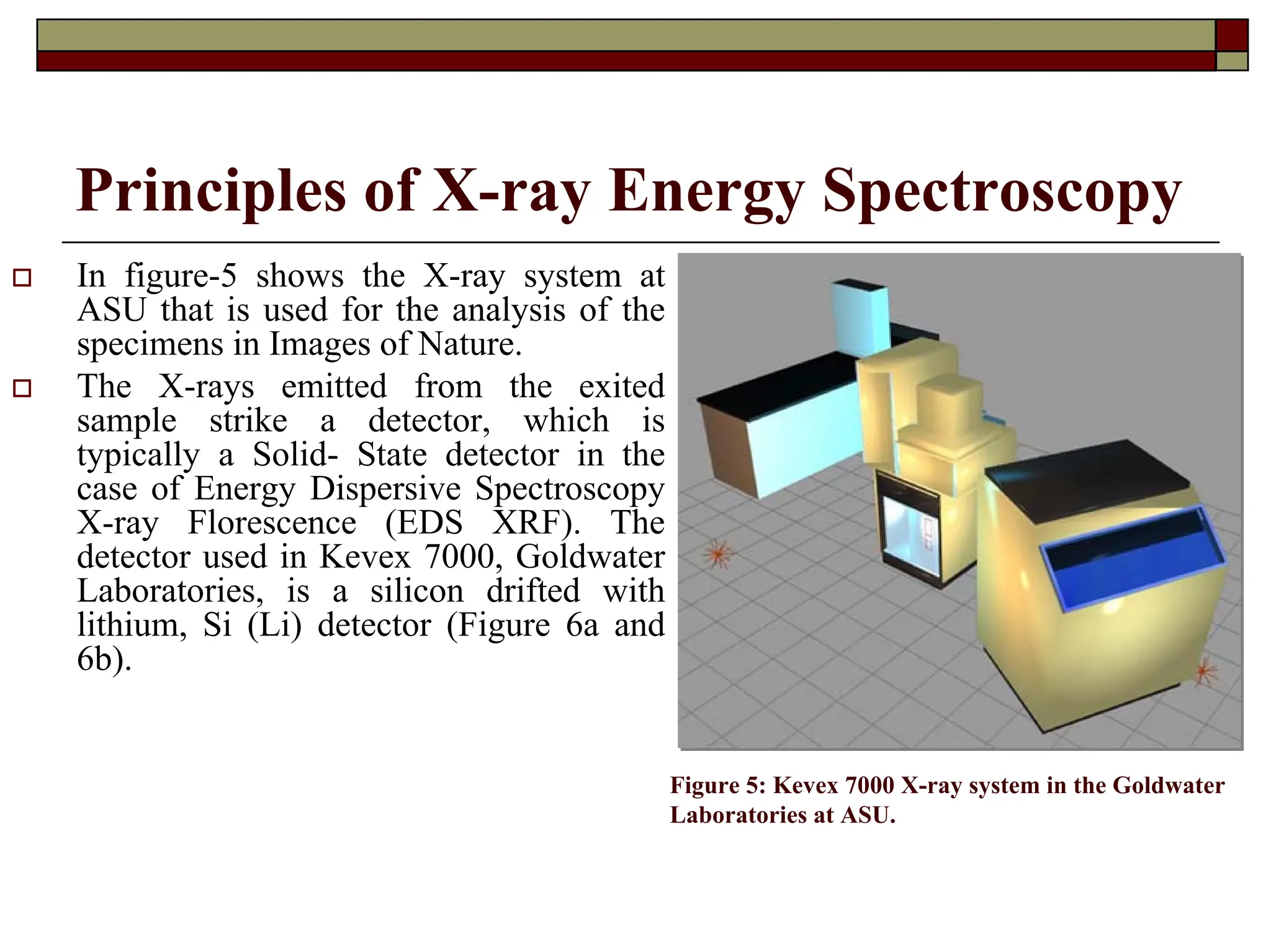
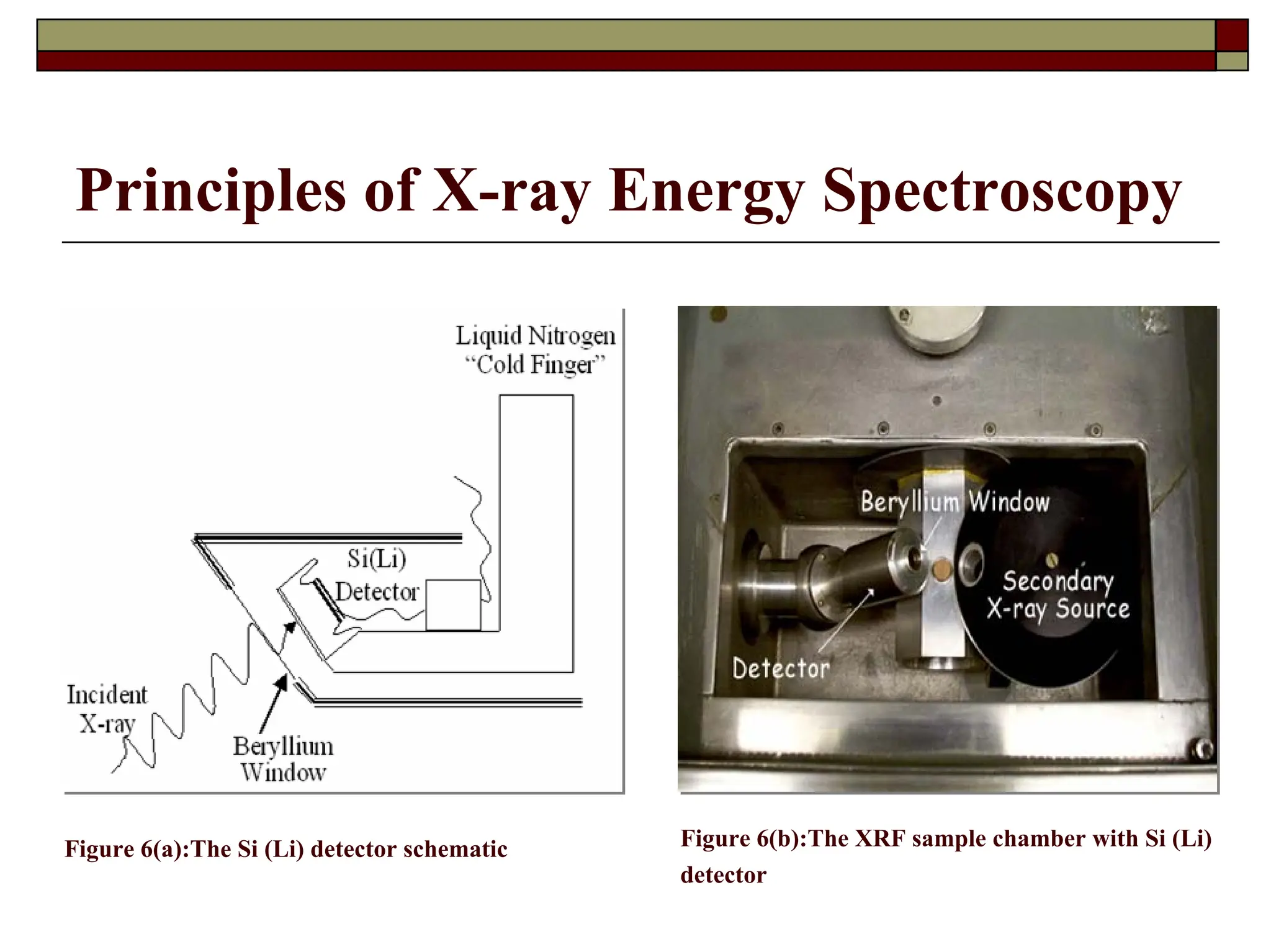
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is a nondestructive analytical technique used for elemental analysis of solids and liquids, employing intense x-ray beams to emit fluorescent x-rays which are then analyzed for qualitative and quantitative data on elements present in the sample. The emitted x-rays can be detected via energy dispersive or wavelength dispersive methods, enabling identification and concentration determination of elements ranging from sodium to uranium, with sample analysis depth varying based on energy and composition. XRF allows for rapid multi-element analysis and can be applied to a variety of samples, although some may require preparation for optimal results.