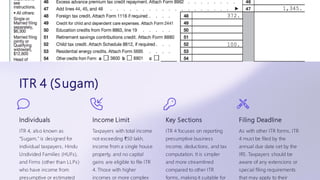
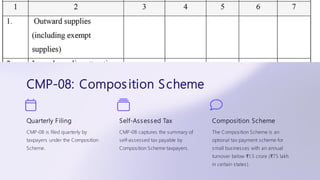
The document outlines the fundamental aspects of accounting, emphasizing its critical role in business through recording and reporting financial transactions. It discusses various accounting tools, processes such as cost and cash management, payroll, and tax compliance, and details the responsibilities and practices that accountants must adhere to. Moreover, it covers tax return filing processes, including different forms and requirements in India, providing a comprehensive overview for both aspiring accountants and business owners.