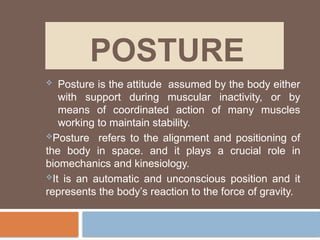
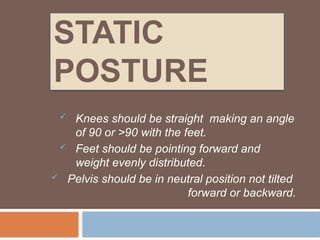
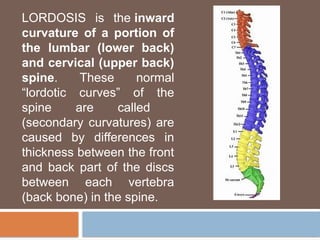
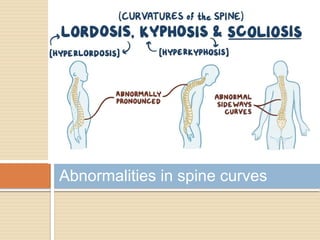
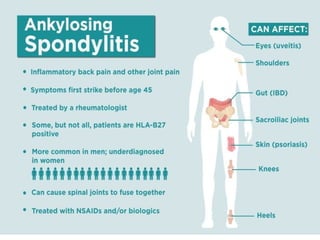
The document discusses posture, its types (static and dynamic), and the role of muscles and the spine in maintaining it. It details the significance of muscle tone, muscle strength, and outlines various postural pathologies including kyphosis, lordosis, scoliosis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Treatment options for these conditions are also provided, highlighting the importance of proper posture for biomechanics and overall health.