1. The document describes SQL (Structured Query Language), which is used to modify and access data from a database. SQL allows users to specify conditions to retrieve specific data.
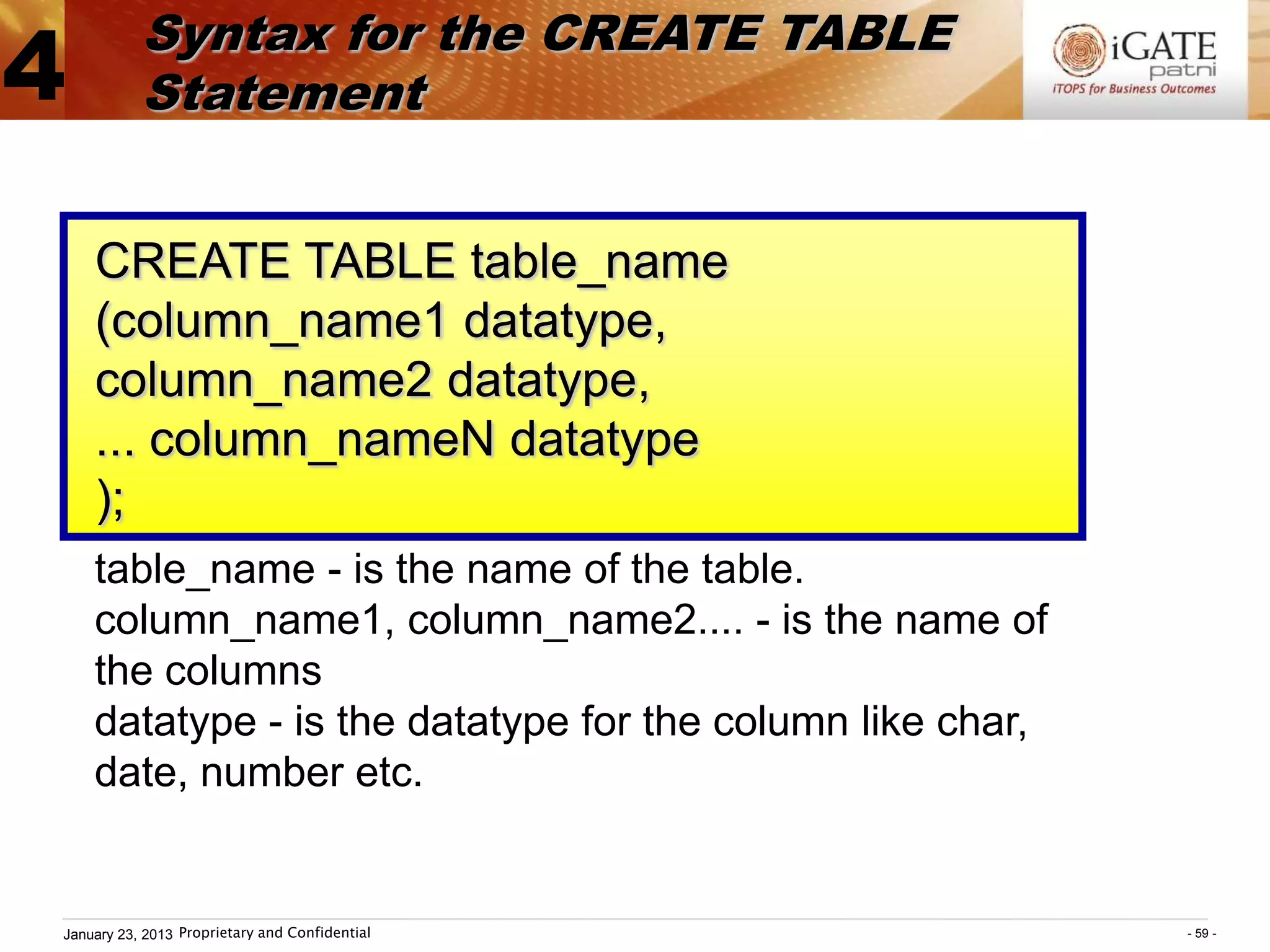
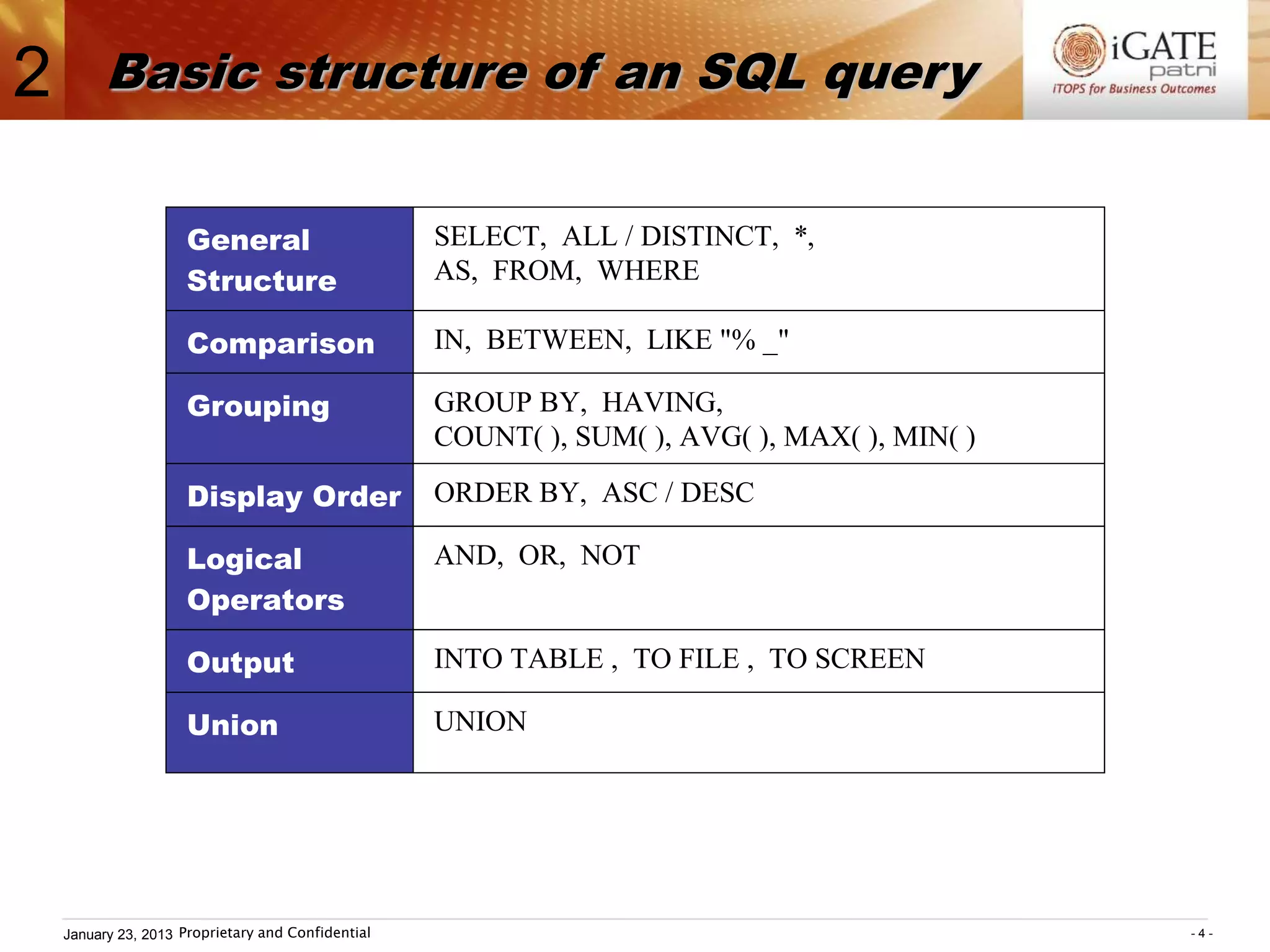
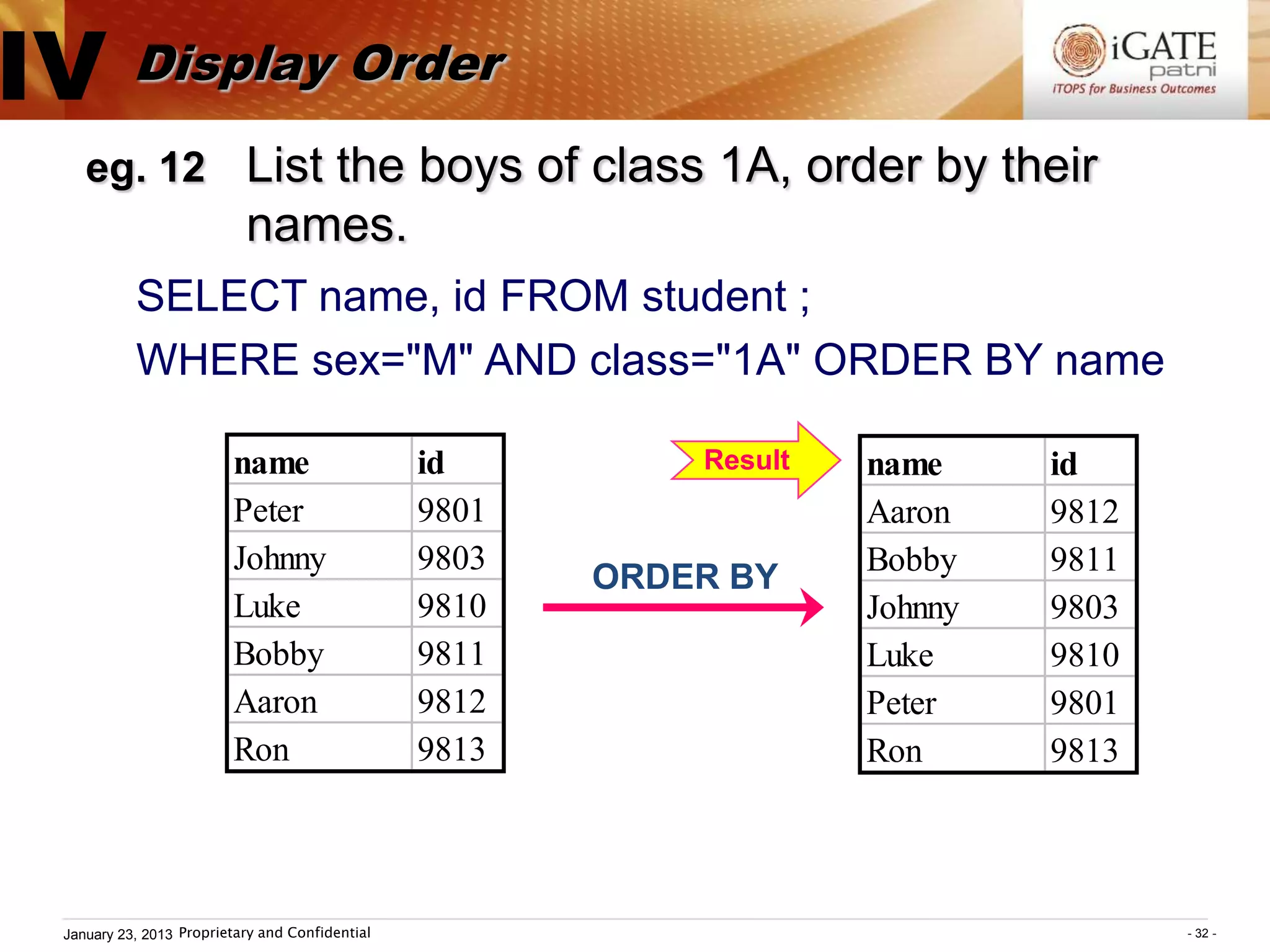
2. The general structure of an SQL query is SELECT...FROM...WHERE. The SELECT clause specifies the columns to return, the FROM clause specifies the table, and the WHERE clause specifies conditions to filter rows.
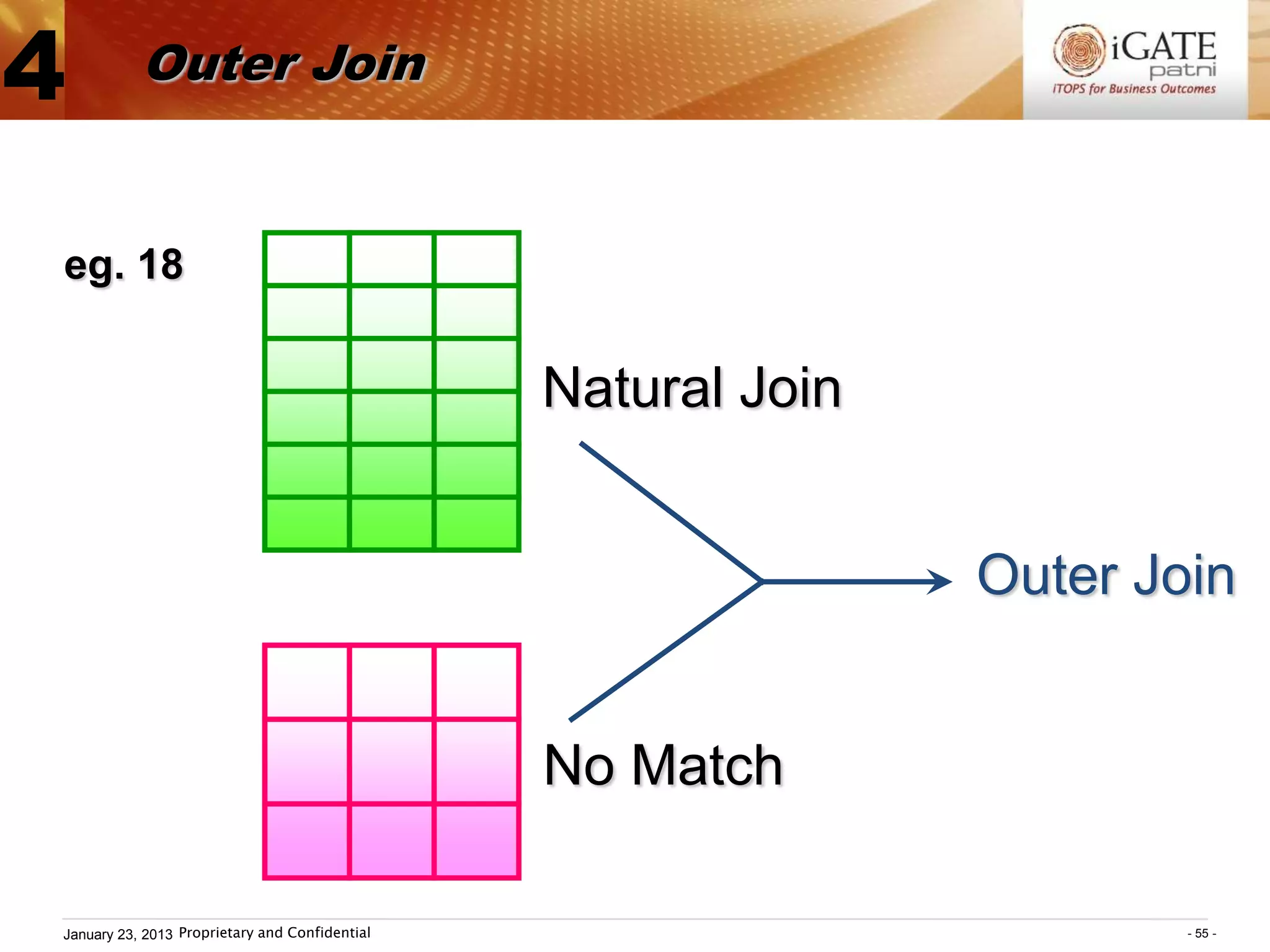
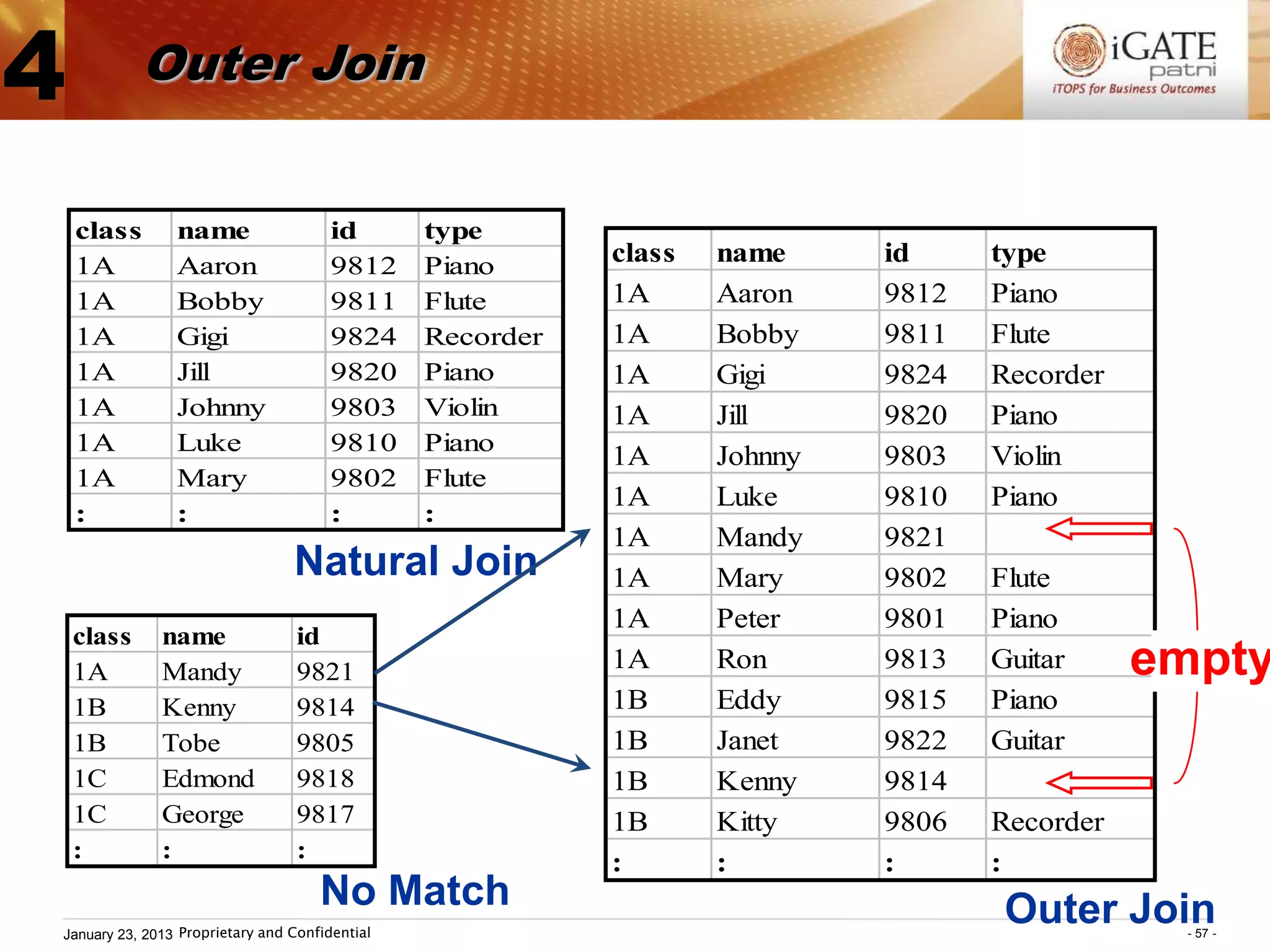
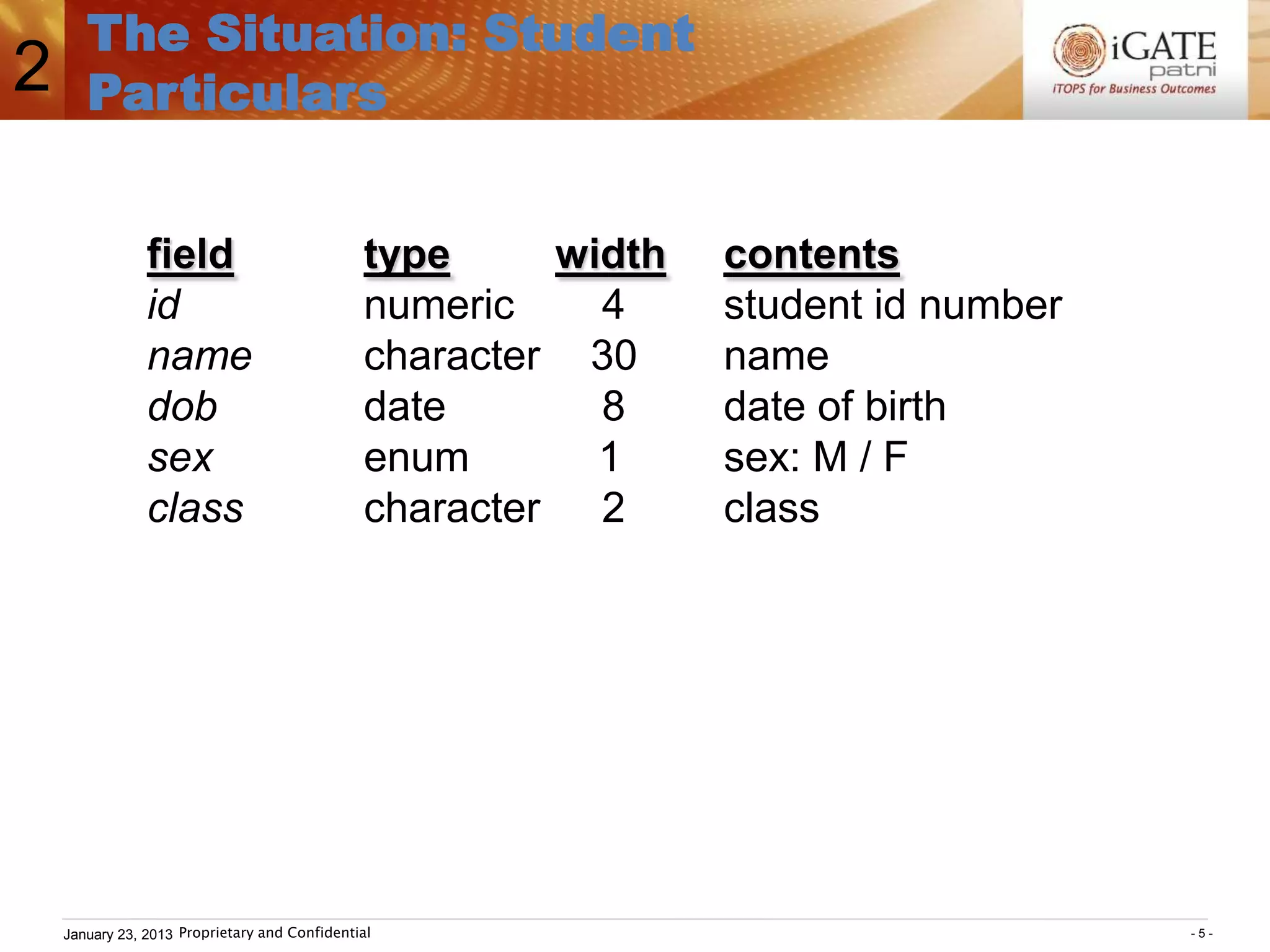
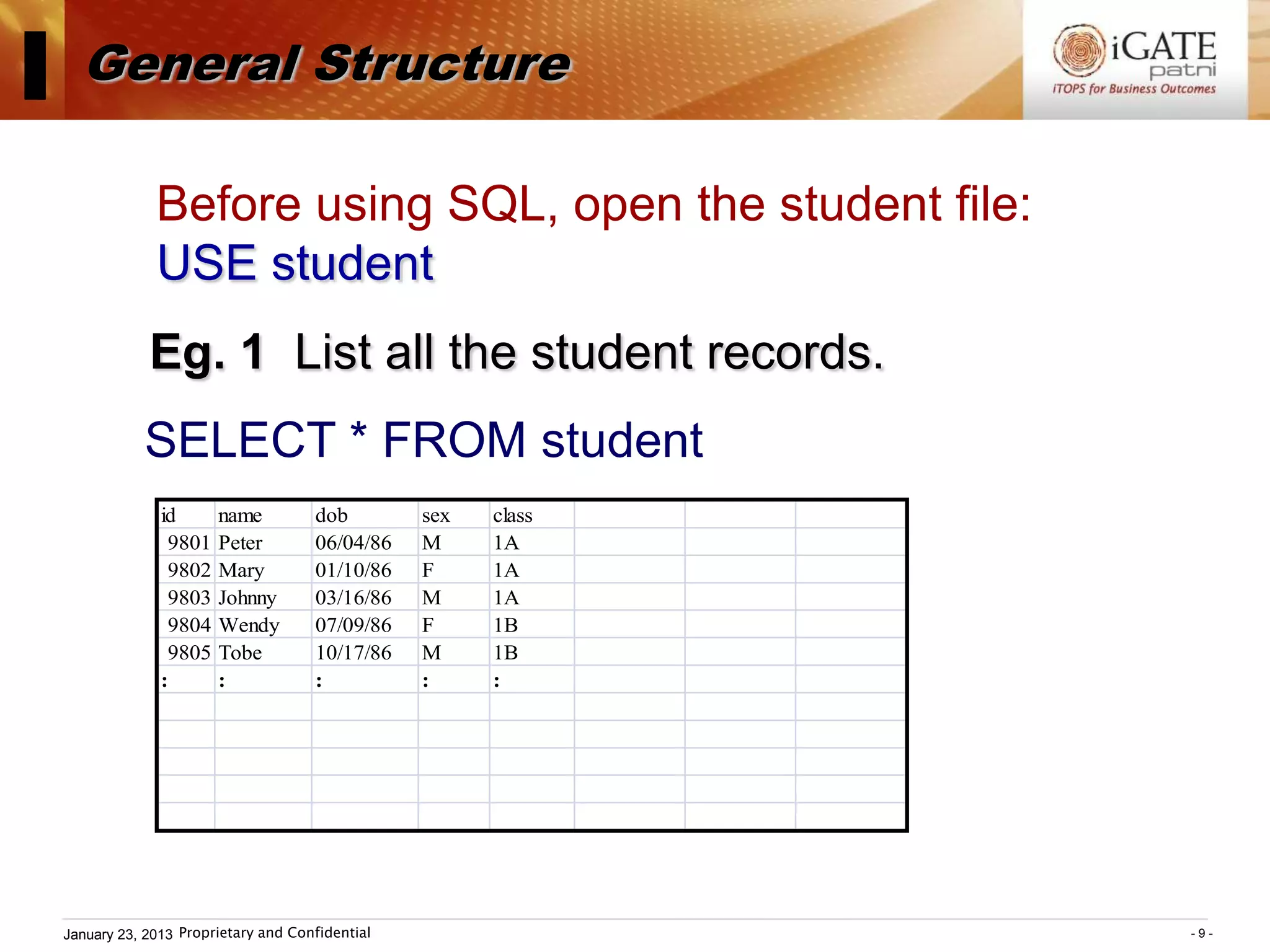
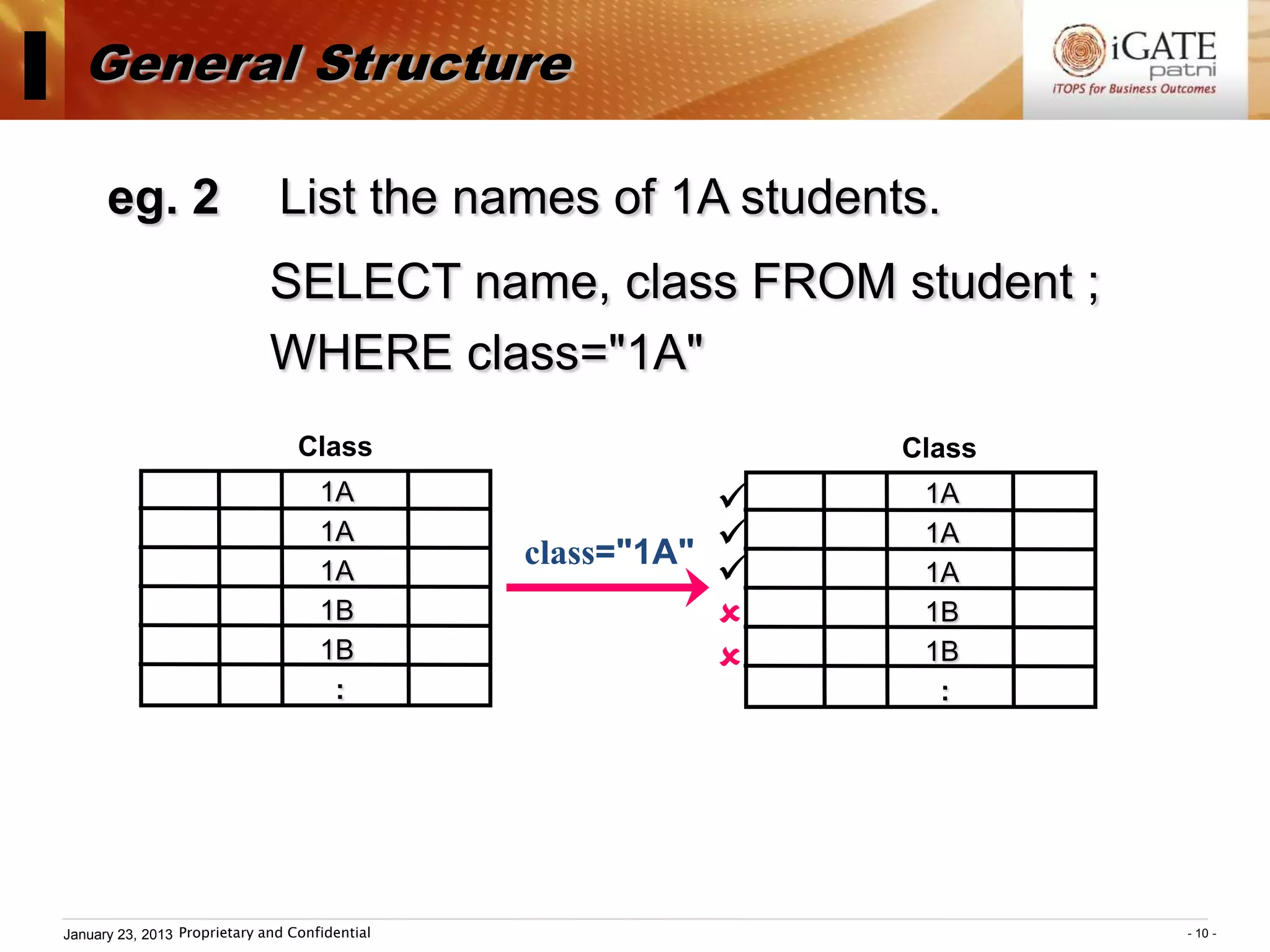
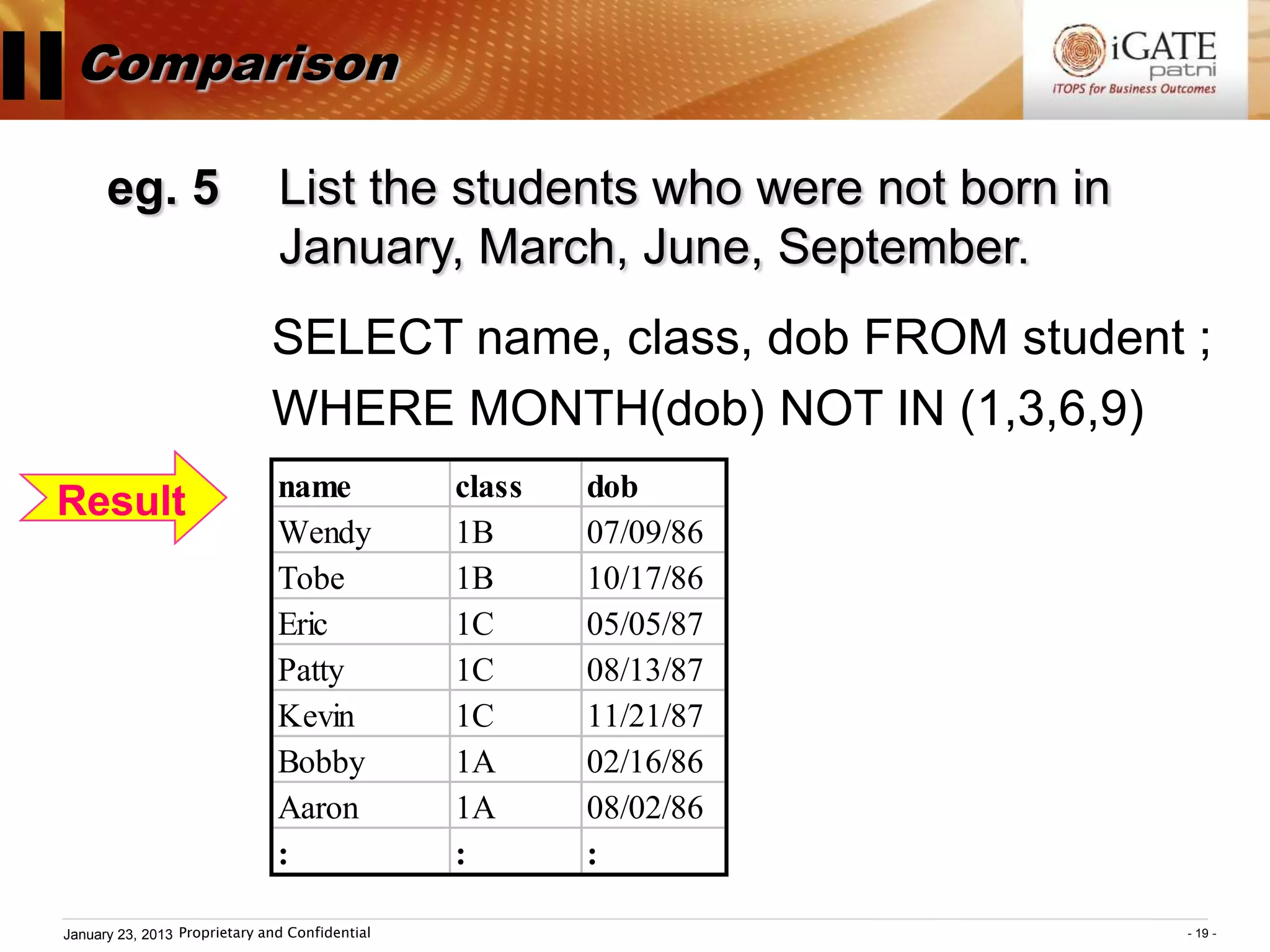
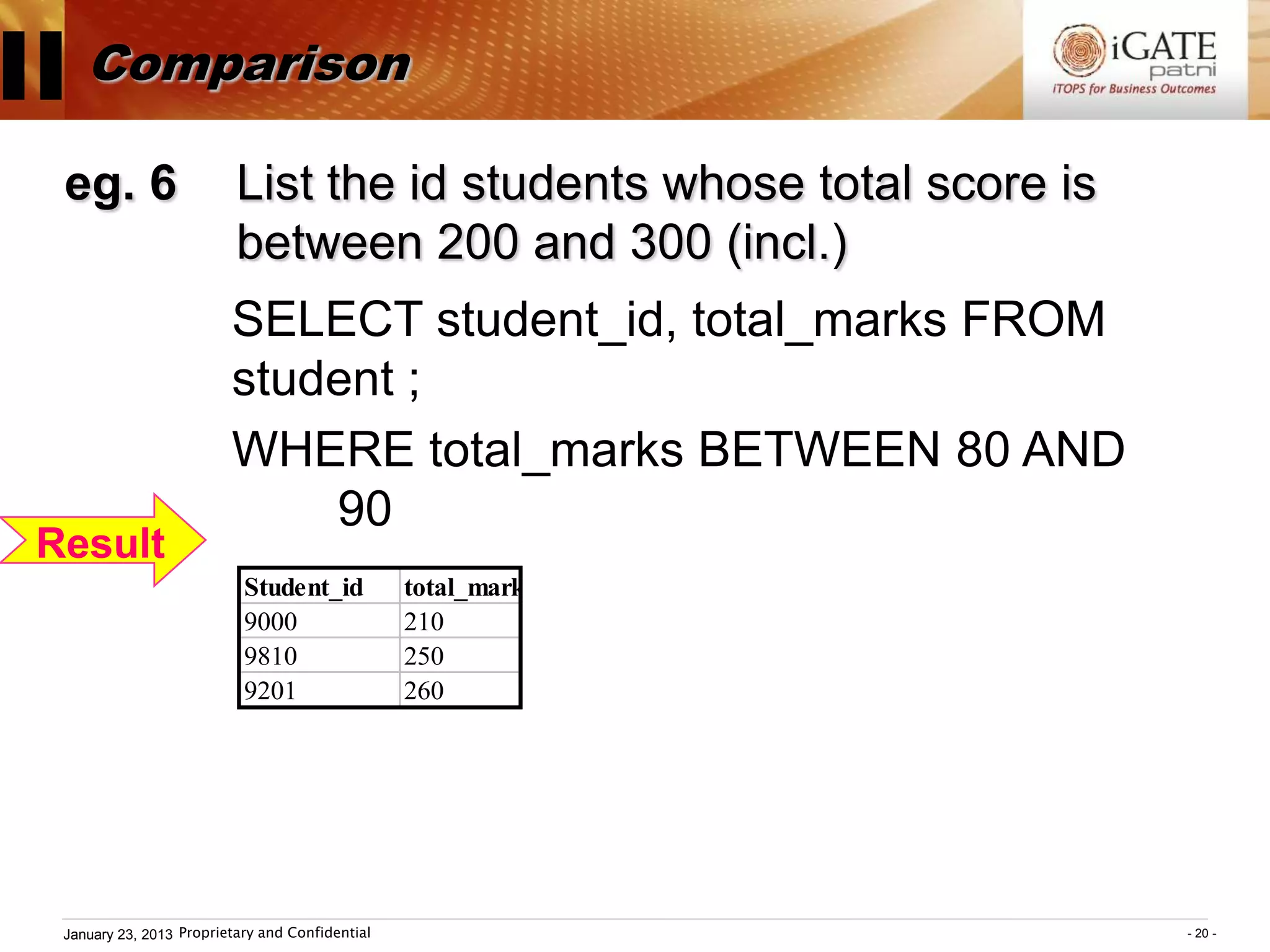
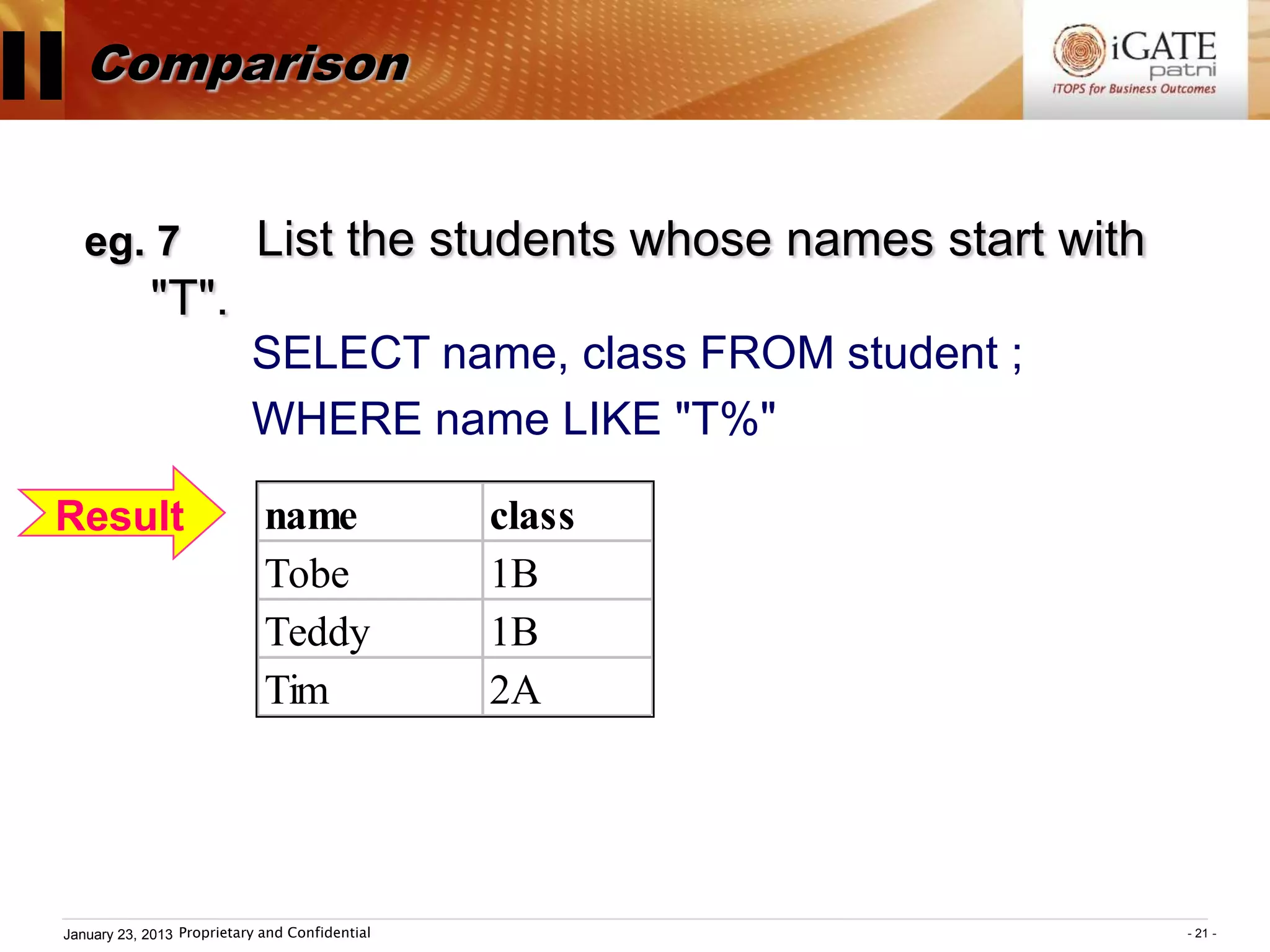
3. Examples show how to use comparison operators like IN, BETWEEN, and LIKE to filter rows based on column values. Grouping, aggregation functions, ordering, and set operations are also demonstrated.


![I General Structure
SELECT ...... FROM ...... WHERE ......
SELECT [ALL / DISTINCT] expr1 [AS
col1], expr2 [AS col2] ;
FROM tablename WHERE condition
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential -6-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-6-2048.jpg)
![I General Structure
SELECT [ALL / DISTINCT] expr1 [AS col1], expr2 [AS col2] ;
FROM table name WHERE condition
– The query will select rows from the source table
name and output the result in table form.
– Expressions expr1, expr2 can be :
• (1) a column, or
• (2) an expression of functions and fields.
– And col1, col2 are their corresponding column
names in the output table.
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential -7-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-7-2048.jpg)
![I General Structure
SELECT [ALL / DISTINCT] expr1 [AS col1], expr2 [AS
col2] ;
FROM table name WHERE condition
– DISTINCT will eliminate duplication in the output
while ALL will keep all duplicated rows.
– condition can be :
• (1) an inequality, or
• (2) a string comparison
• using logical operators AND, OR, NOT.
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential -8-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-8-2048.jpg)




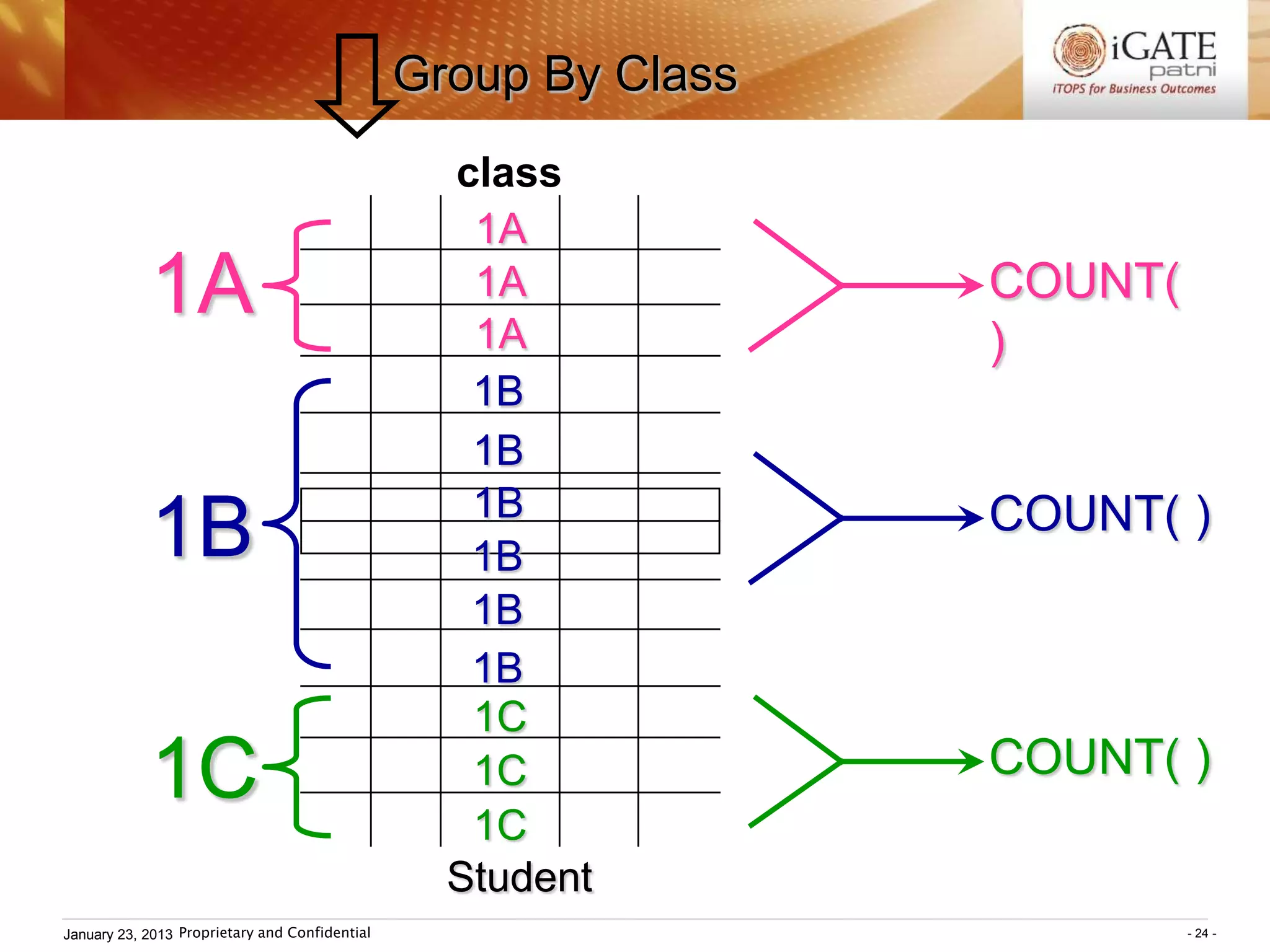
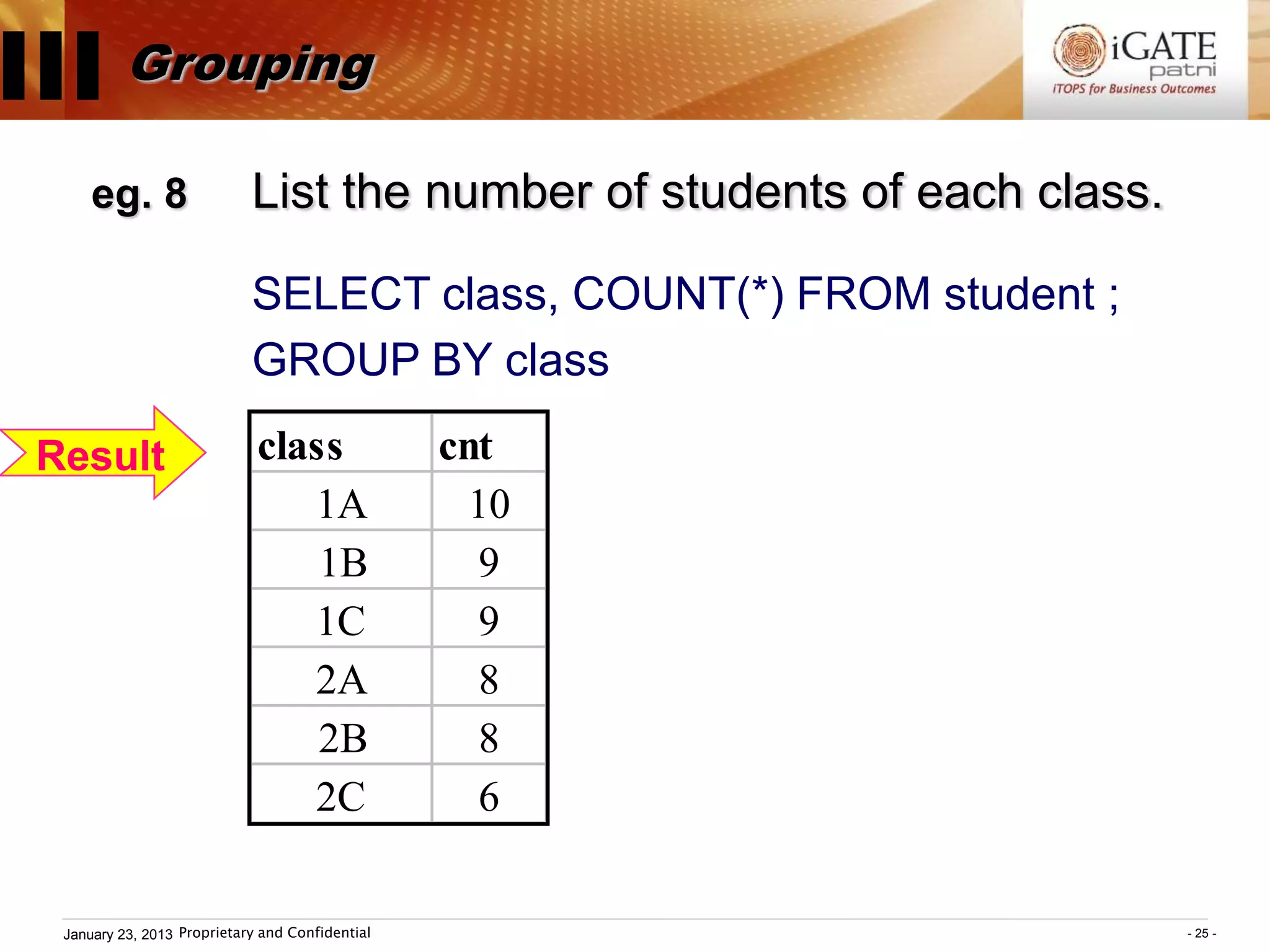
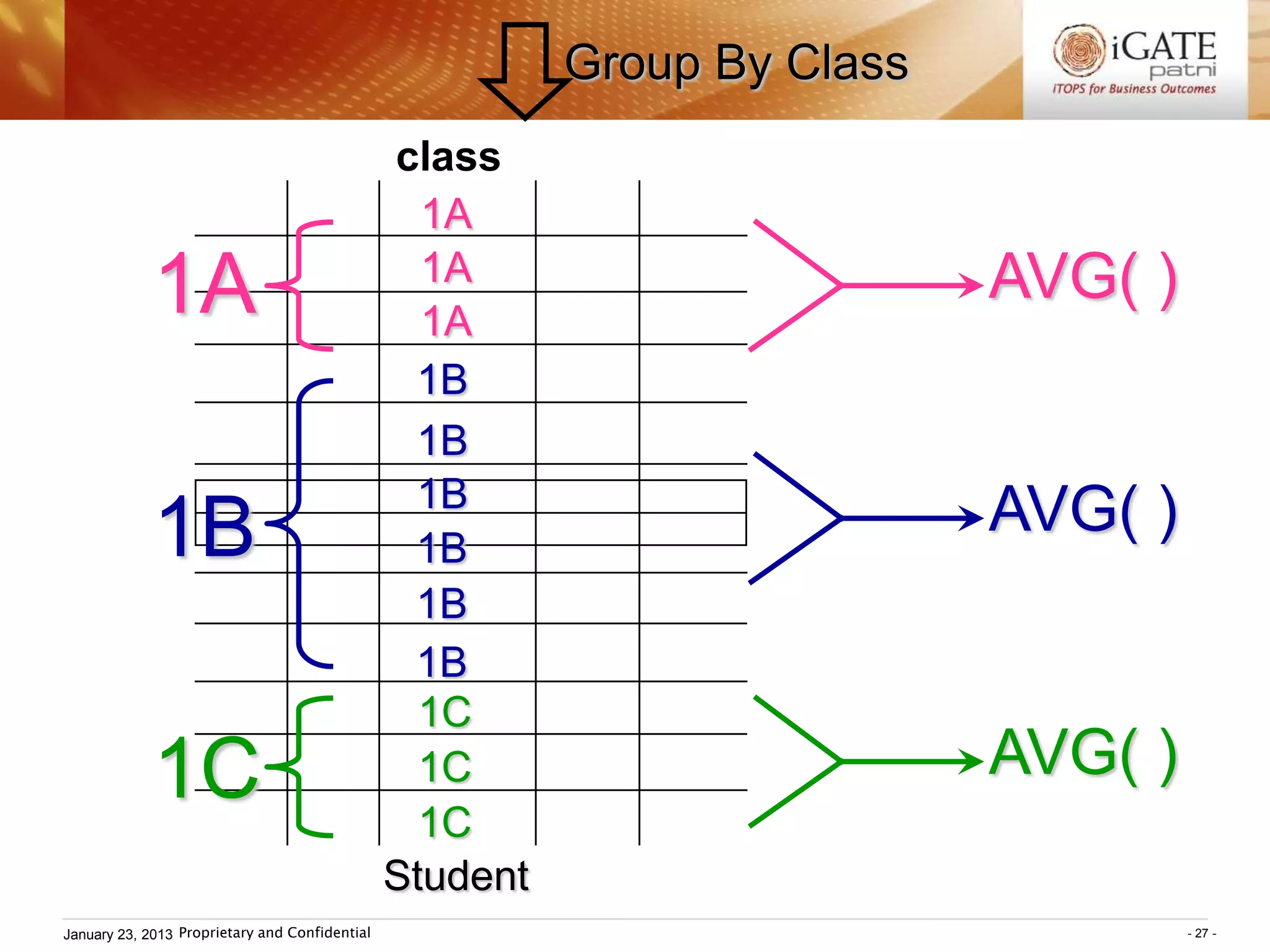
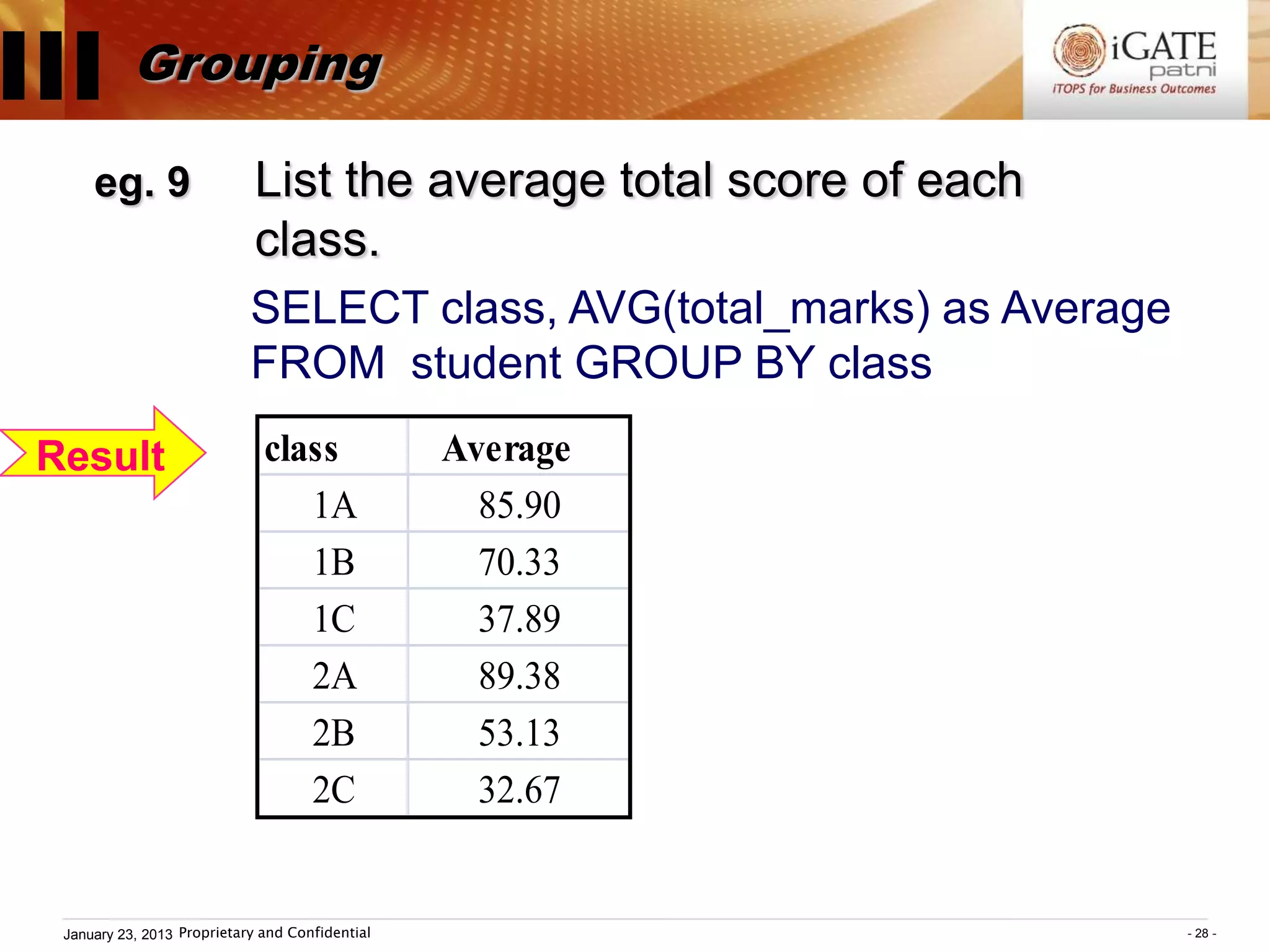
![III Grouping
SELECT ...... FROM ...... WHERE condition ;
GROUP BY groupexpr [HAVING requirement]
Group functions:
COUNT( ), SUM( ), AVG( ), MAX( ), MIN( )
– groupexpr specifies the related rows to be
grouped as one entry. Usually it is a column.
– WHERE condition specifies the condition of
individual rows before the rows are group.
HAVING requirement specifies the condition
involving the whole group.
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential - 22 -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-22-2048.jpg)





![V Output
INTO TABLE tablename the output table is saved as a
database file in the disk.
TO FILE filename [ADDITIVE] output to a text file.
(additive = append)
TO SCREEN display on screen.
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential - 33 -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-33-2048.jpg)
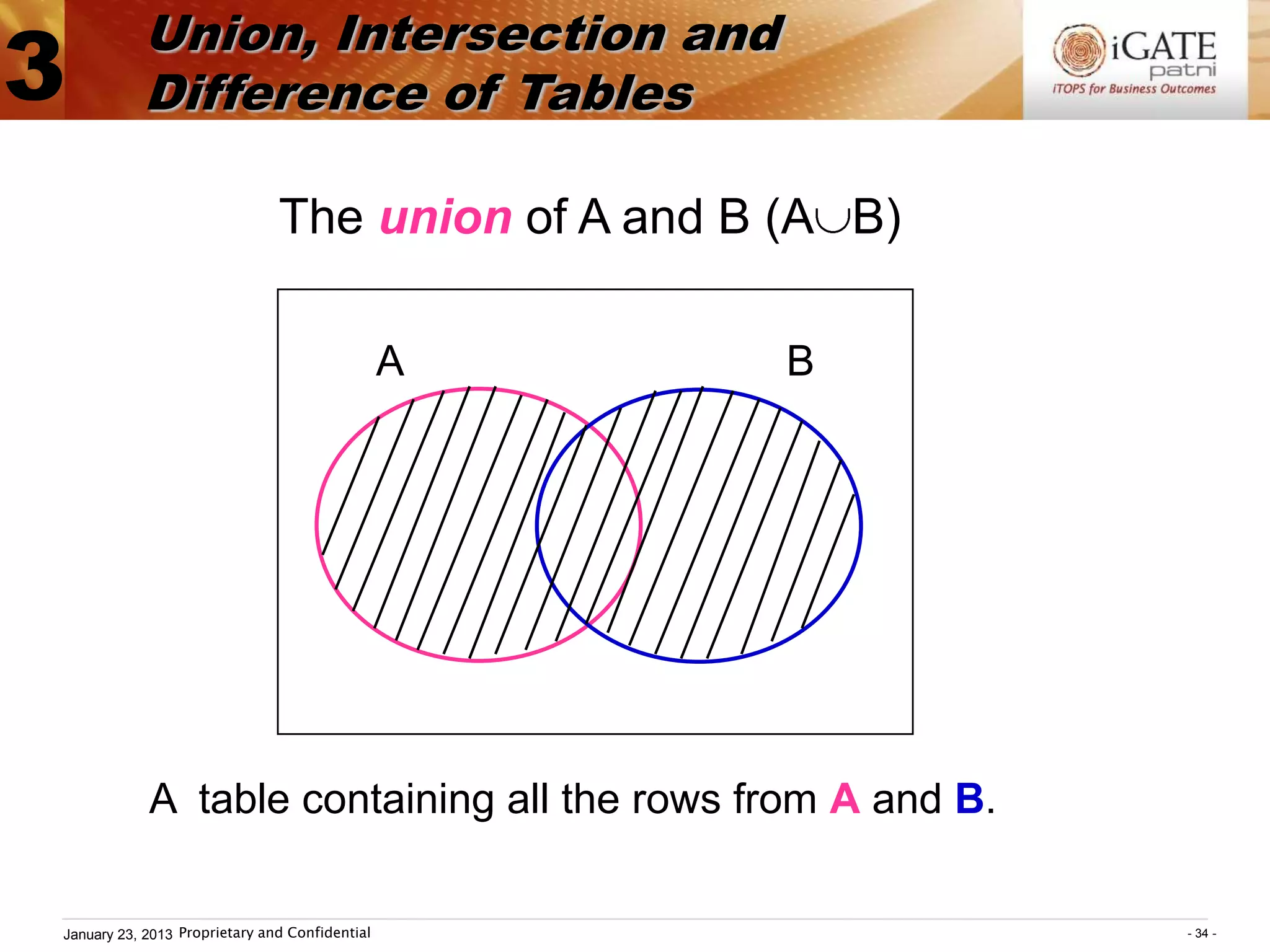
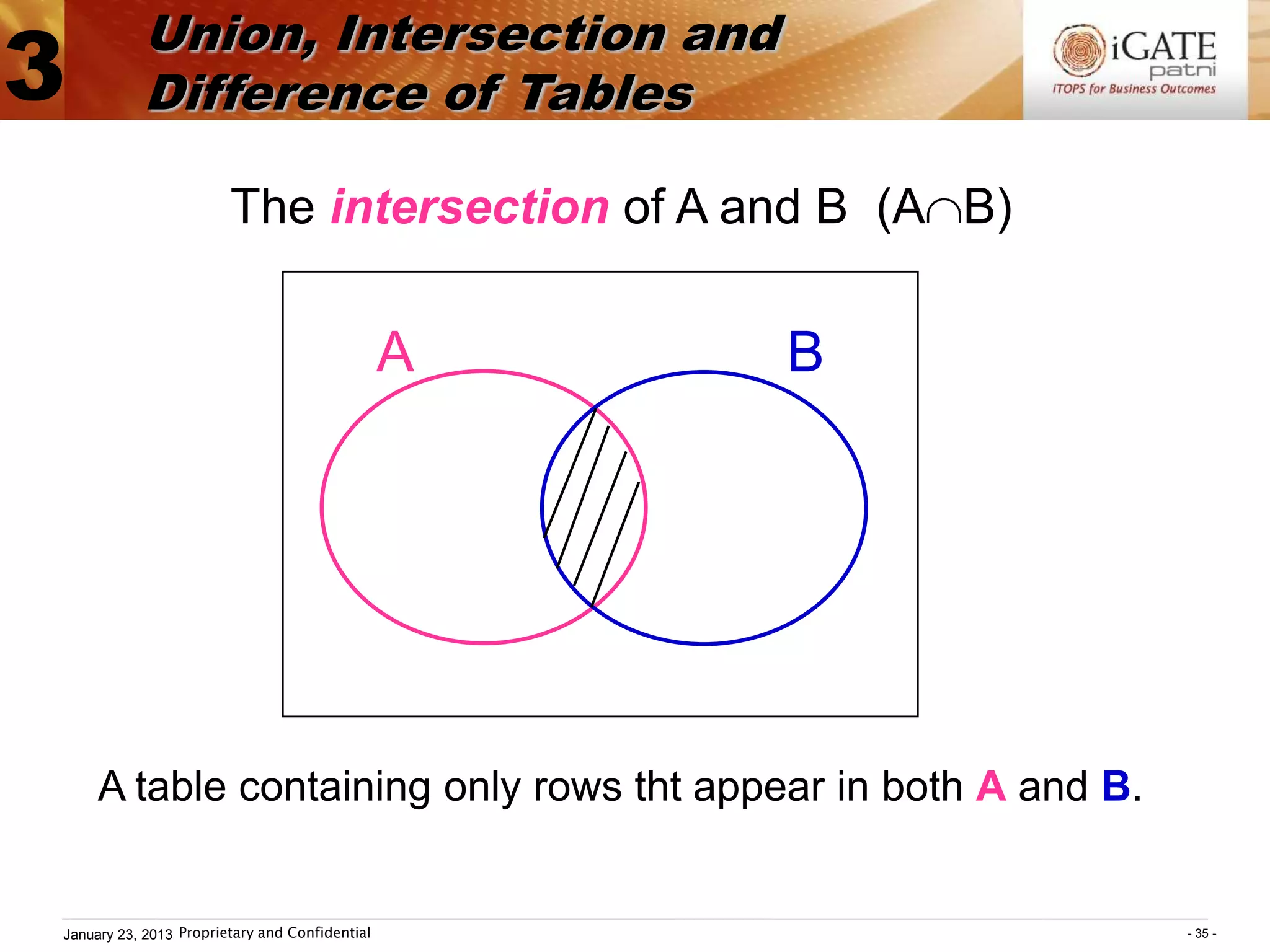
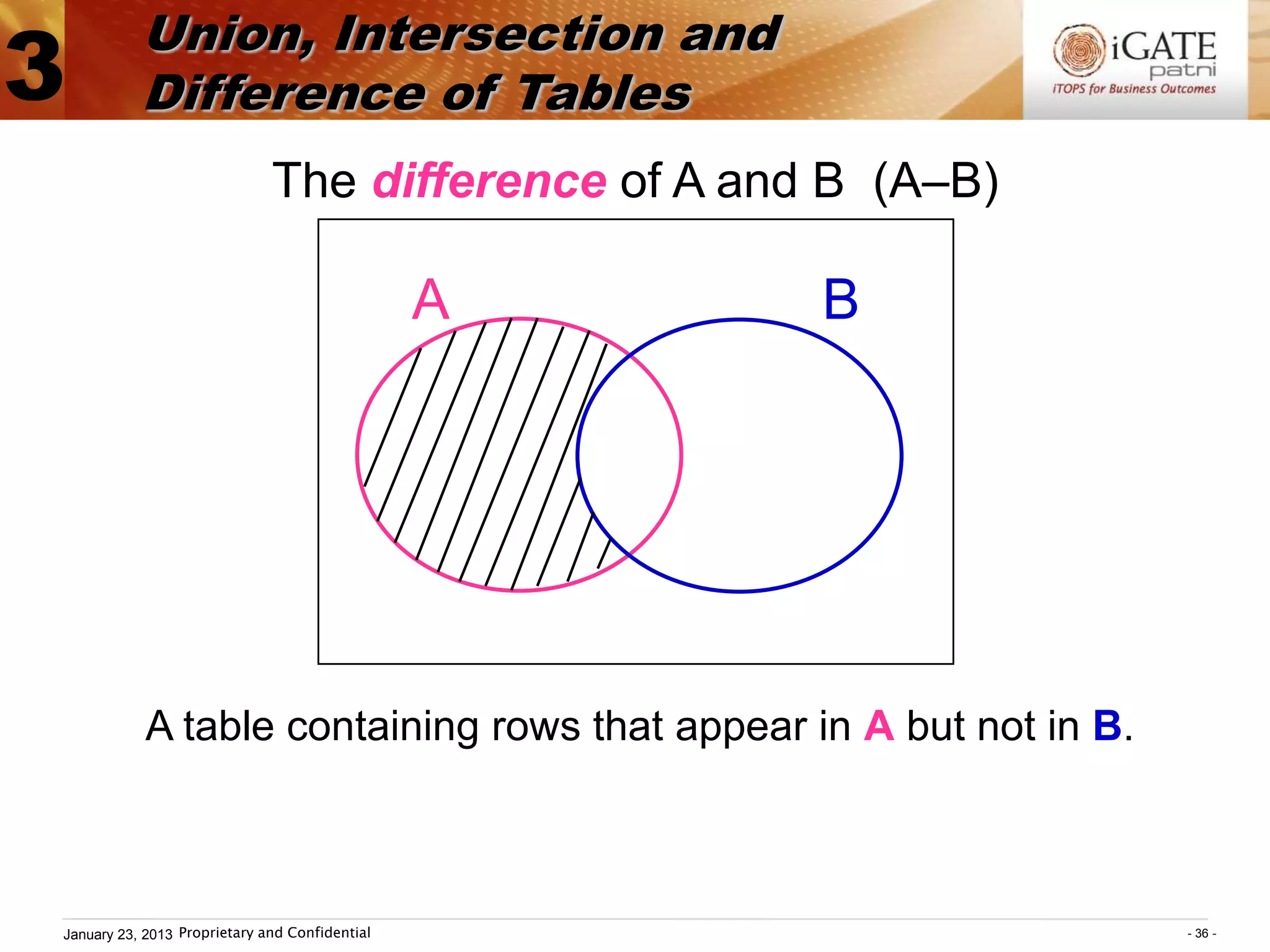
![Union, Intersection and
3 Difference of Tables
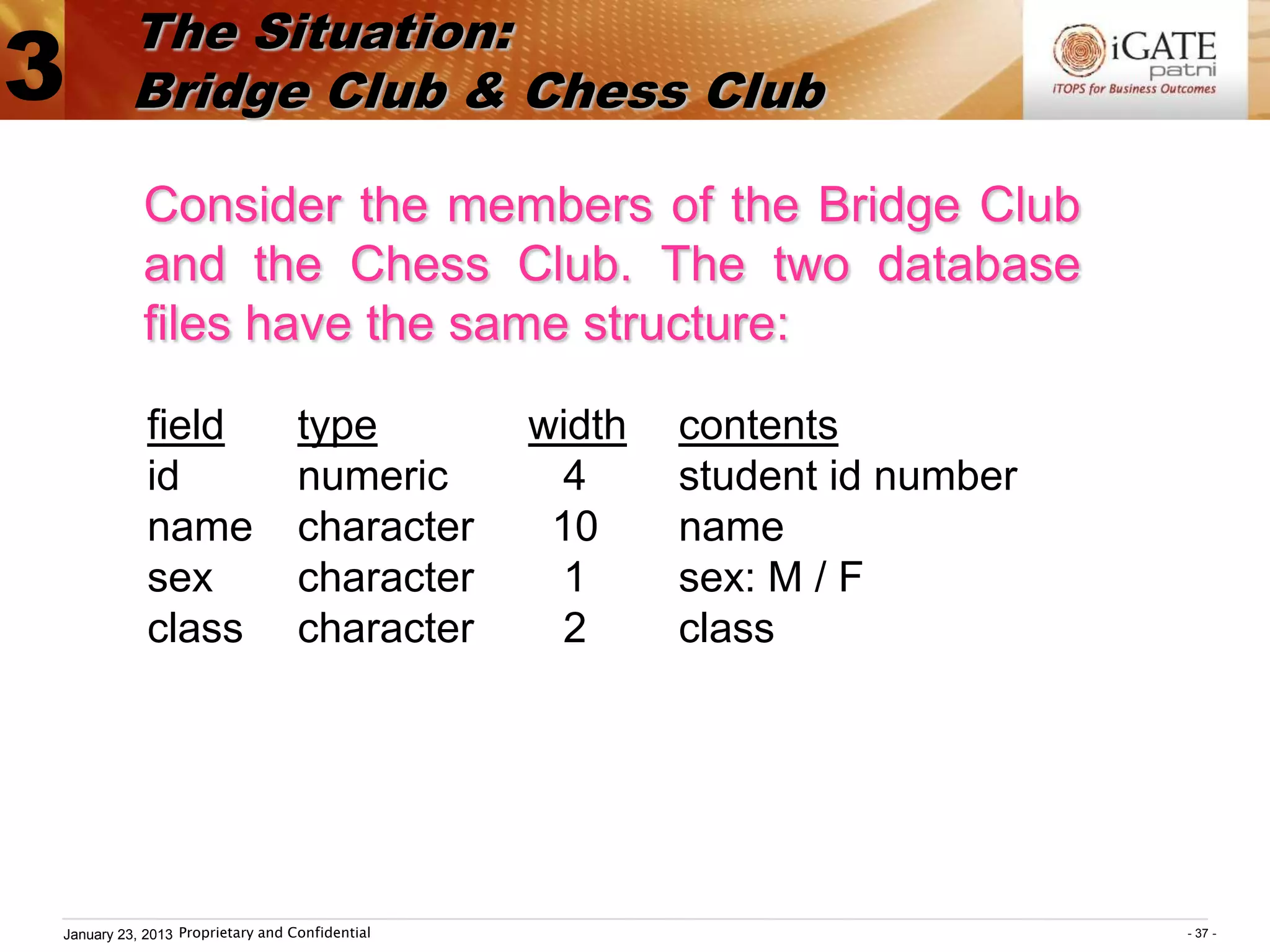
B rid ge [A ] C hess [B ]
id nam e sex class id nam e sex class
1 9812 A aron M 1A 1 9802 M ary F 1A
2 9801 P eter M 1A 2 9801 P eter M 1A
3 9814 K enn y M 1B 3 9815 E dd y M 1B
4 9806 K itty F 1B 4 9814 K enn y M 1B
5 9818 E dm ond M 1C 5 9817 G eorge M 1C
: : : : : : : :
Before using SQL, open the two tables:
SELECT A
USE bridge
SELECT B
USE chess
January 23, 2013 Proprietary and Confidential - 38 -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/positive-flow1971-130124013256-phpapp02/75/Positive-Flow-38-2048.jpg)