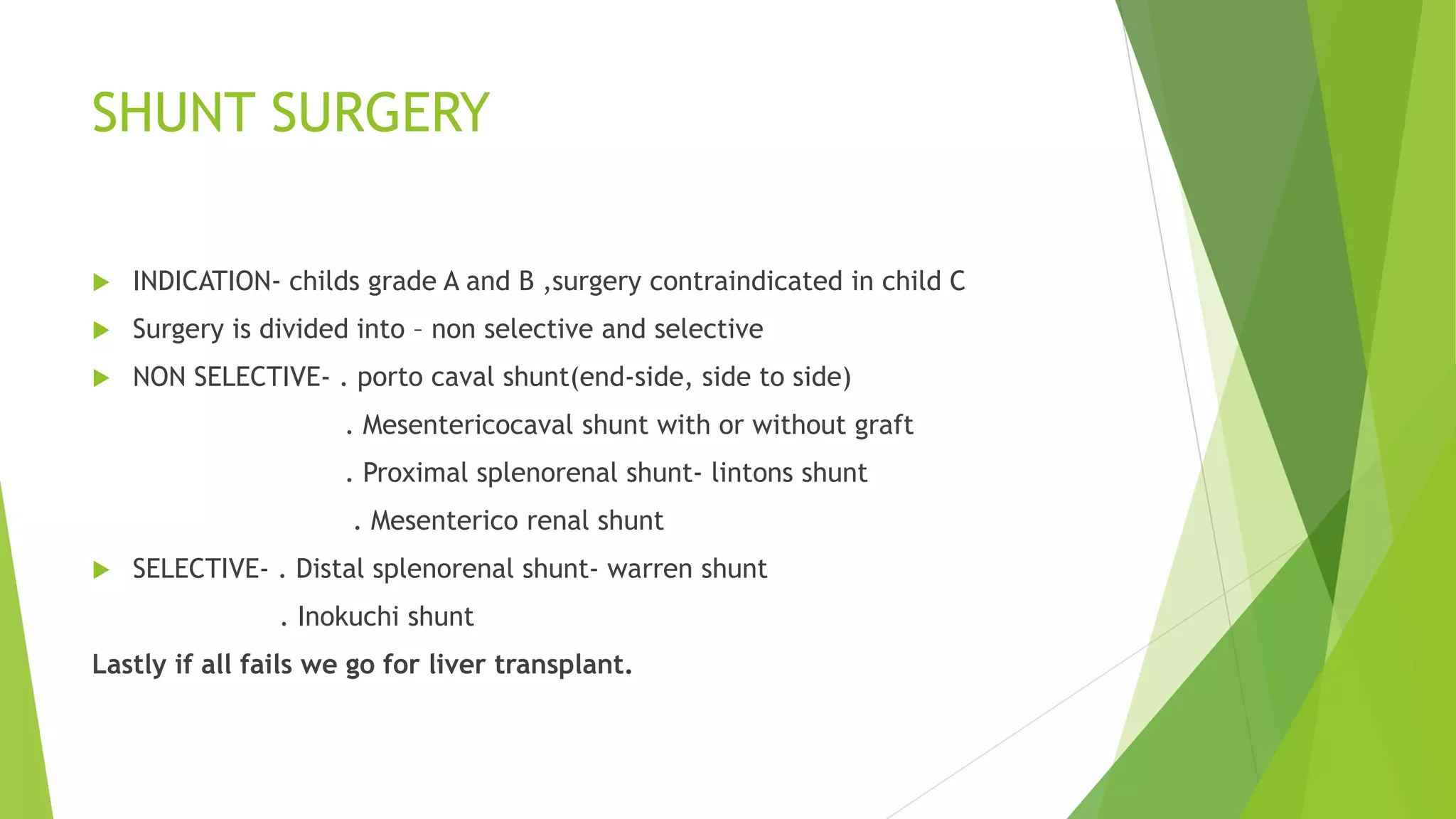
This document discusses portal hypertension, defined as a portal pressure higher than 5mm hg. Portal hypertension occurs due to increased portal venous resistance and can be prehepatic, intrahepatic, or posthepatic. The most common causes are portal vein thrombosis prehepatically and schistosomiasis or cirrhosis intrahepatically. Investigations include liver function tests, ultrasound, and the Child-Pugh score. Management includes treating varices with beta blockers, endotherapy, balloon tamponade, TIPSS, or shunt surgery. Transplant is the last option if other treatments fail.