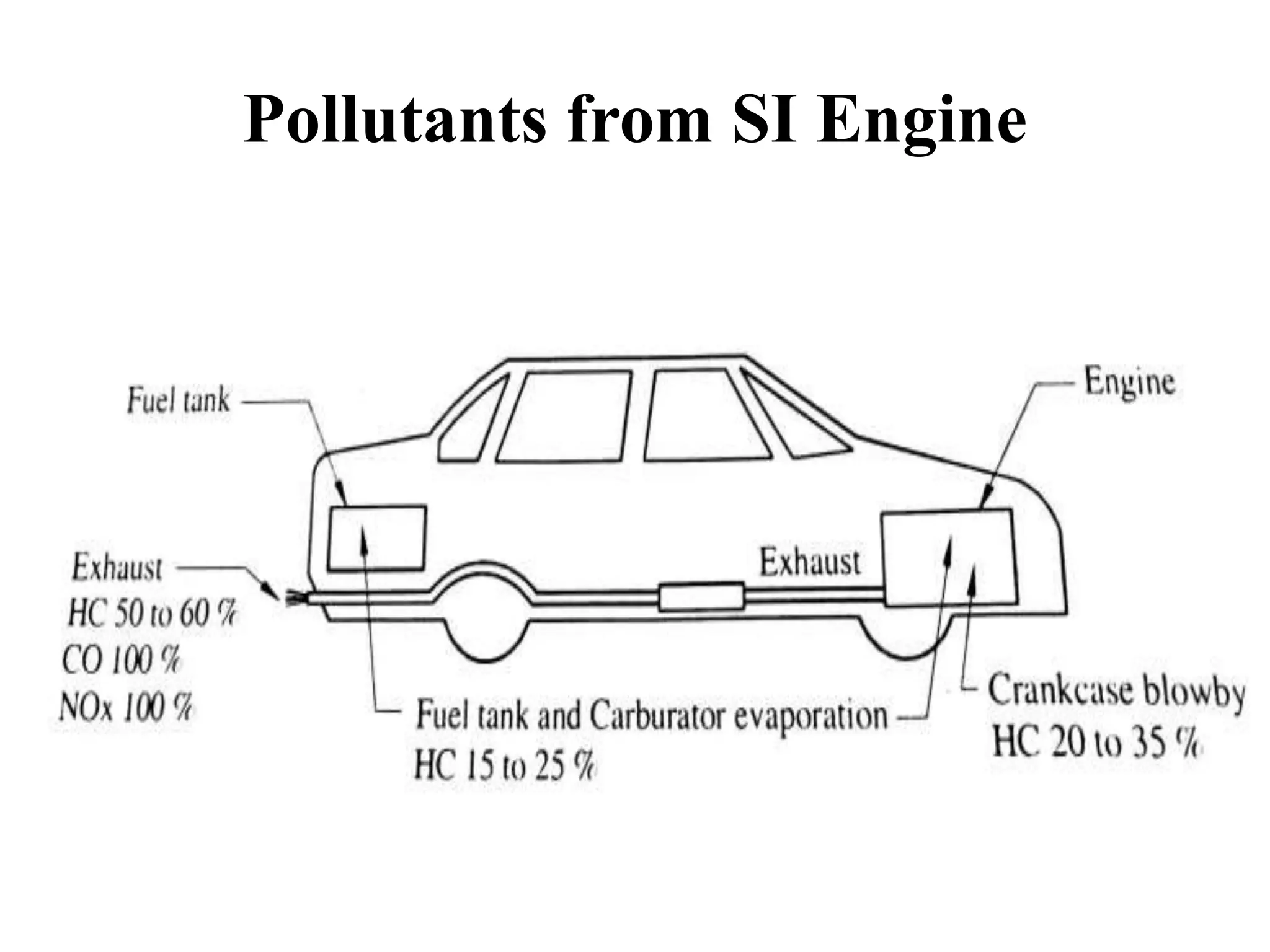
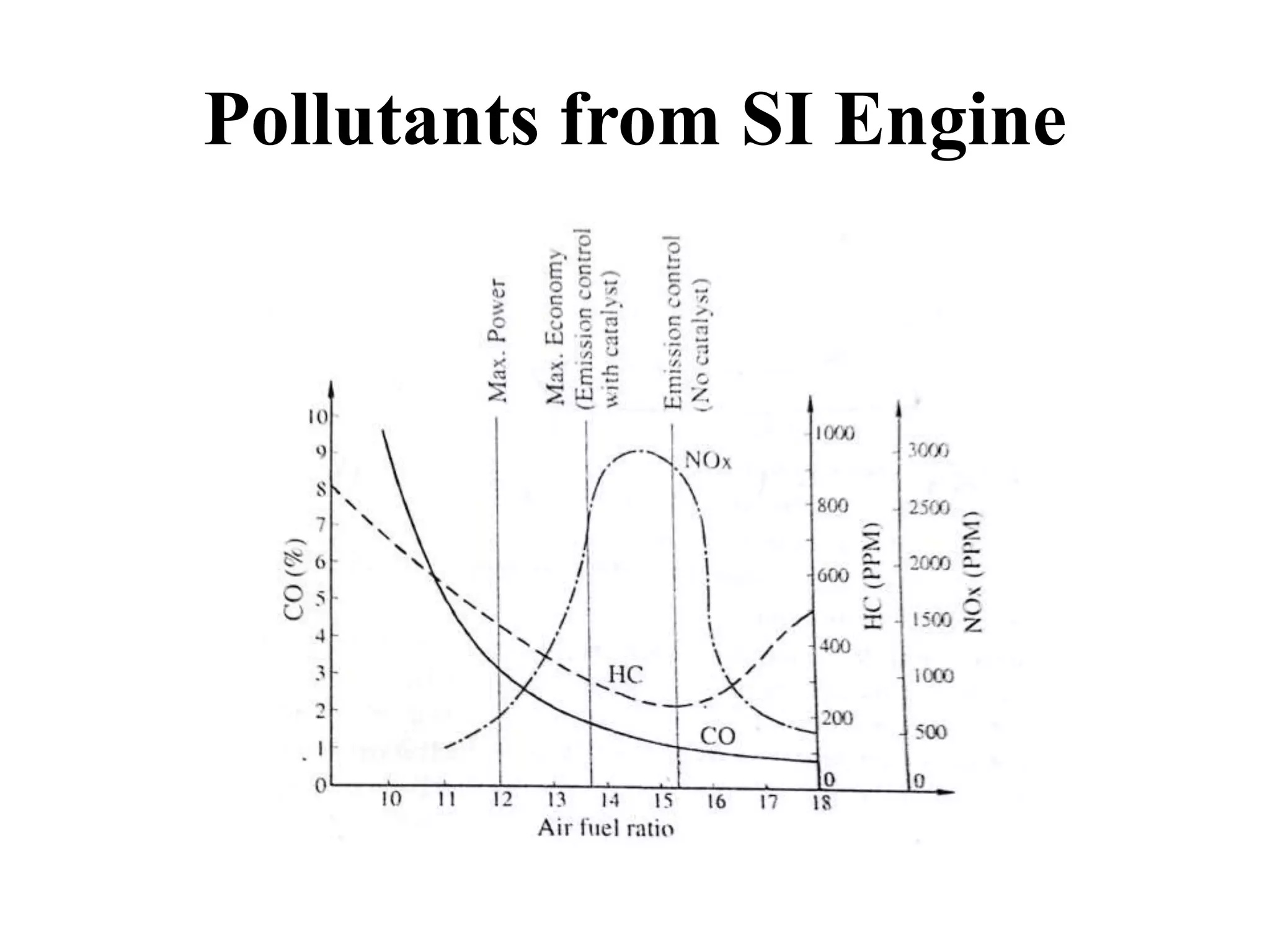
Internal combustion engines (ICE) emit significant pollutants, primarily due to the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, which releases carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere. Key factors contributing to these emissions include non-stoichiometric combustion and impurities in fuel and air, leading to environmental issues such as global warming and smog. Additional emissions result from crankcase blow-by and evaporative losses from fuel tanks and carburetors during operation.