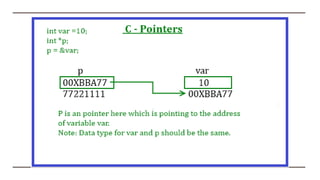
Pointer is a variable that stores the address of another variable. There are two operators used with pointers - the address operator (&) which returns the address of a variable, and the indirection operator (*) which accesses the value at the address stored in the pointer variable. Pointer arithmetic allows performing operations like incrementing and decrementing on pointers, with the offset calculated based on the data type of the pointer. Pointers can be compared to check if they point to the same memory location. Pointers to arrays store the base address of the entire array, while pointers to elements store the address of a single element.


![• Pointer assignment
int i=10;
int *p=&i;//value assigning to the pointer
• Here declaration tells the compiler that ‘p’ will be used to store
the address of integer value or in other word ‘p’ is a pointer to
an integer and *p reads the value at the address contain in p.
• We can assign value of 1 pointer variable to other when their
base type and data type is same or both the pointer points to
the same variable as in the array.
Int *p1,*p2;
P1=&a[1];
P2=&a[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-4-320.jpg)

![But in case of array it is possible, since there data are stored in a
consecutive
manner.
Ex:-
void main( )
{
static int a[ ]={20,30,105,82,97,72,66,102};
int *p,*p1;
P=&a[1];
P1=&a[6];
printf(“%d”,*p1-*p);
printf(“%d”,p1-p);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-6-320.jpg)





![Ex:-
void main()
{
static int arr[]={20,25,15,27,105,96}
int *x,*y;
x=&a[5];
y=&(a+5);
if(x==y)
printf(“same”);
else
printf(“not”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-12-320.jpg)

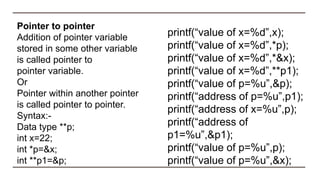
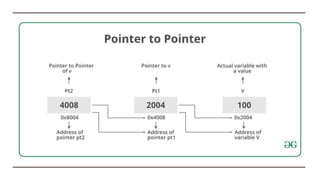
![Pointer vs array
Example :-
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int *ptr = arr;
printf("%pn", ptr);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![• In this program, we have a pointer ptr that points to the
0th element of the array. Similarly, we can also declare a
pointer that can point to whole array instead of only one
element of the array.
• Syntax:
• data_type (*var_name)[size_of_array];
Example:
int (*ptr)[10];
• Here ptr is pointer that can point to an array of 10 integers.
Since subscript have higher precedence than indirection, it is
necessary to enclose the indirection operator and pointer name
inside parentheses. Here the type of ptr is ‘pointer to an array
of 10 integers’.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![Note : The pointer that points to the
0th element of array and the pointer
that points to the whole array are
totally different. The following
program shows this:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Pointer to an integer
int *p;
// Pointer to an array of
5 integers
int (*ptr)[5];
int arr[5];
// Points to 0th element of the arr.
p = arr;
// Points to the whole array arr.
ptr = &arr;
printf("p = %p,ptr = %pn", p, ptr);
p++;
ptr++;
printf("p = %p,ptr = %pn", p, ptr);
return 0;
}
p = 0x7fff4f32fd50, ptr = 0x7fff4f32fd50 p =
0x7fff4f32fd54, ptr = 0x7fff4f32fd64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![p: is pointer to 0th element of the
array arr, while ptr is a pointer that
points to the whole array arr.
•The base type of p is int while base
type of ptr is ‘an array of 5 integers’.
•We know that the pointer arithmetic is
performed relative to the base size, so if
we write ptr++, then the pointer ptr will
be shifted forward by 20 bytes.
include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 5, 6, 7, 9 };
int *p = arr;
int (*ptr)[5] = &arr;
printf("p = %p, ptr = %pn", p,
ptr);
printf("*p = %d, *ptr = %pn", *p,
*ptr);
printf("sizeof(p) = %lu, sizeof(*p)
= %lun",sizeof(p),sizeof(*p));
printf("sizeof(ptr) = %lu,
sizeof(*ptr) = %lun",sizeof(ptr),
sizeof(*ptr));
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointers-240321160926-558bc165/85/pointers-of-the-programming-in-c-most-efficient-pptx-19-320.jpg)
