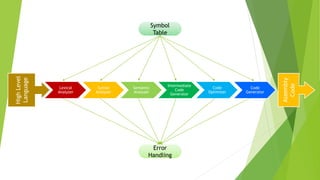
The document summarizes the six main phases of a compiler:
1. The lexical analyzer identifies tokens from the source code and removes whitespace and comments.
2. The syntax analyzer checks that the code follows grammar rules of the language and constructs a parse tree.
3. The semantic analyzer verifies type consistency and checks for semantic errors using the symbol table and parse tree.
4. The intermediate code generator produces machine-independent code in a form that can be optimized and executed.
5. The code optimizer improves performance by removing unused code and variables without altering meaning.
6. The code generator produces machine-specific object code by selecting instructions and registers for the target platform.