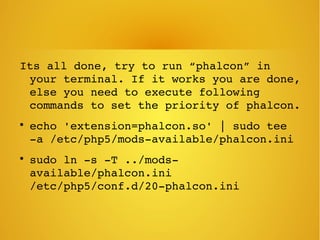
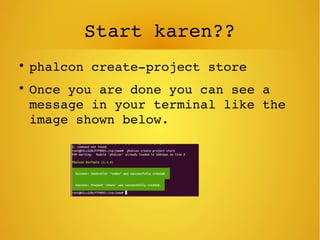
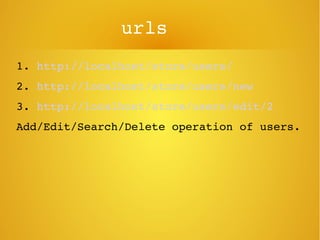
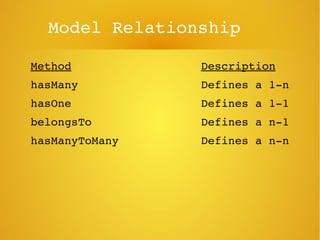
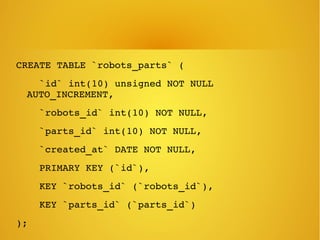
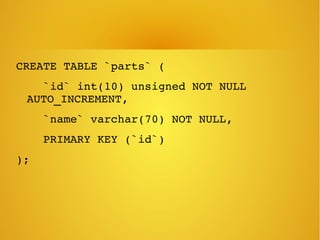
Phalcon is a PHP framework written as a C extension that provides high performance. It can be installed on Ubuntu via apt-get. Models define relationships between database tables and support validation. Views allow passing data from controllers and rendering layouts. The framework also includes features like access control lists, an events manager, and SQL injection protection.