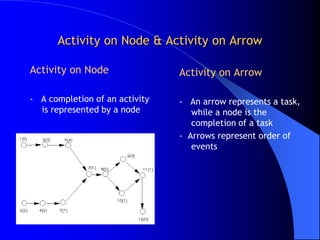
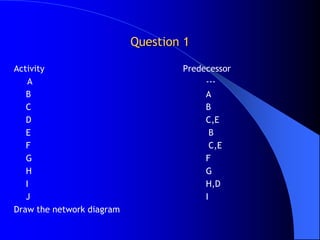
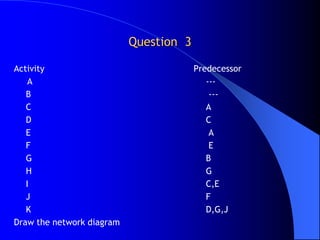
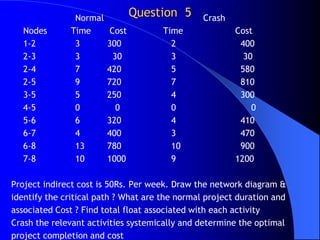
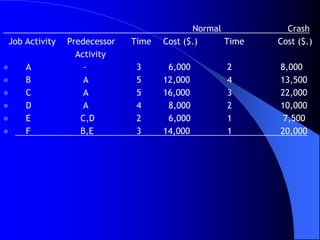
The document discusses network analysis techniques used for project planning and management. It covers key concepts like work breakdown structure, network diagrams, critical path method (CPM), program evaluation and review technique (PERT), activity times, event relationships, slack, floats, crashing, and normal vs crash schedules. The document contains examples of network diagrams and questions related to calculating activity times, identifying critical paths, and crashing project schedules.