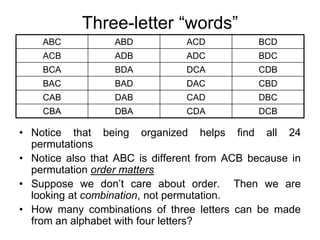
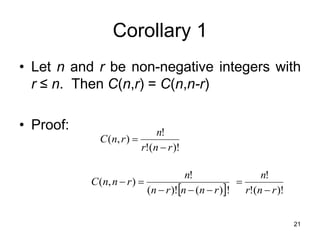
This document discusses permutations and combinations. Permutations refer to ordered arrangements where order matters, while combinations refer to unordered arrangements where order does not matter. The key differences are that permutations use factorials to count arrangements and combinations use binomial coefficients. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating permutations and combinations in situations like poker hands, lottery tickets, and seating arrangements.